This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor of Radiology, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Coronary artery disease occurs when the large blood vessels that supply the heart are damaged or diseased. Plaque contains cholesterol in the coronary arteries and inflammation is often the cause of coronary artery disease.
1. Symptoms of coronary heart disease
The coronary arteries supply blood, oxygen and nutrients for the functioning of the heart. Plaque buildup can narrow these arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart causing chest pain (angina). Once a complete blockage can cause a heart attack.
Some typical symptoms of coronary heart disease are: Chest pain (angina). Angina is often triggered by physical or emotional stress. Short of breath. If your heart can't pump enough blood to meet your body's needs, you may experience shortness of breath or extreme fatigue with activity.
2. When to see a doctor
If you have risk factors for coronary artery disease such as: high blood pressure, high cholesterol, tobacco use, diabetes, obesity, a large family history of heart disease, you need to seek medical advice. Consult your doctor about preventive measures for coronary heart disease.
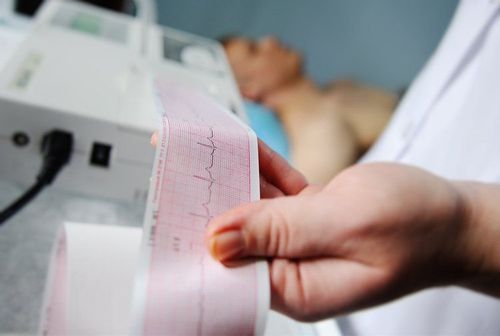
3. Coronary disease on ECG
ECG is an invaluable tool in acute and chronic myocardial ischemia. Optimal use of the ECG will provide information on diagnosis, prognosis, and appropriate treatment. In coronary artery disease, the ECG will also provide information on the expansion, localization of the heart, and the time course of the ischemia.
In the case of acute coronary syndromes, ECG is used to classify the syndrome: Acute coronary syndrome with ST elevation (STE-ACS) and acute coronary syndrome in patients without ST elevation (NSTE- ACS). The basic classification will help the doctor to identify and treat immediately:
Acute ST-elevation coronary syndrome (STE-ACS): Acute coronary syndrome with ST-segment elevation on ECG is classified as STE-ACS. Almost all patients with myocardial infarction are classified into this group. Acute coronary syndromes in non-ST-segment elevation patients (NSTE-ACS): Acute coronary syndromes without ST-segment elevation on ECG are classified as NSTE-ACS. If the patient has had a myocardial infarction, then the condition is classified as an NHFI (Non ST-elevation myocardial infarction). If the patient is not having an infarction, the condition is classified as unstable angina.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
LEARN MORE
Electrocardiogram in coronary heart disease Electrocardiographic image of myocardial ischemia Diagnosing myocardial infarction by electrocardiogram