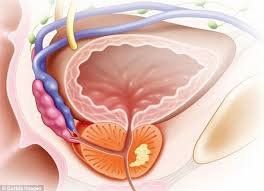
Mumps is a contagious viral infection caused by the Paramyxovirus family, affecting the salivary glands. The disease can spread via the respiratory route or through direct contact with the saliva of an infected individual.
1. What is Mumps?
Mumps is a contagious viral infection caused by the Paramyxovirus family, mainly affecting the salivary glands. It is transmitted by physical contact with the saliva of an infected person or through other respiratory routes. You can contract mumps by being in close contact with an infected person who was coughing or sneezing..
Currently, the MMR vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella, is part of the vaccination schedule for children. However, individuals living or working in environments with frequent exposure to others may still contract mumps even if they are vaccinated.
Children and adolescents are susceptible to mumps as they do not possess the antibodies for this virus.
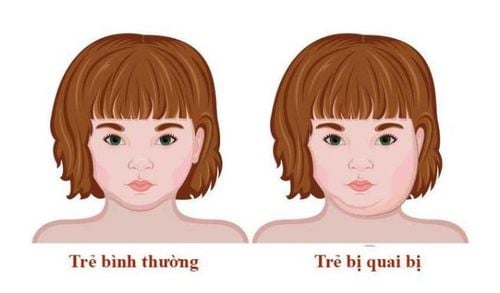
2. Symptoms of Mumps
Mumps typically has an incubation period of several weeks, followed by onsets of high fever of up to 38°C, fatigue, loss of appetite, and insomnia. After 1-3 days of fever, your salivary glands will become swollen. The swelling initially only affects one side of the face, however it may spread to the other side after a few days. The swelling is often asymmetrical, with one side being larger than the other. In severe cases, the swelling can disfigure the face, making chewing and swallowing difficult due to the severe enlargement of the salivary glands. The skin over the swollen glands appears inflated and shiny, and although it is not red, the area is painful and warm to the touch.
Common symptoms of mumps include:
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Insomnia
- Muscle aches and overall body pain
- Dry mouth
- Nausea and vomiting
- High fever
- Testicular swelling and pain in males
Basically, the symptoms of mumps are generally similar in both adults and children. Some individuals may not show any symptoms or may experience only mild signs despite being infected.
Less common symptoms include testicular swelling in males only occurs in about 10% of cases. Ovarian swelling could also occur in female patients, though it is very rare. Other serious complications of mumps can include pancreatitis, meningitis, or encephalitis.
Meningitis and encephalitis are serious complications of mumps. If you experience symptoms such as itching, severe headache, difficulty concentrating, seizures, or confusion, it could indicate that the infection has led to a dangerous complication.
3. Treatment for Mumps
Mumps is often mistaken for bacterial lymphadenitis or diphtheria. As mumps is a self-limiting condition, it can typically be managed at home, but close monitoring is crucial to promptly detect any serious complications
Key considerations when managing mumps at home include:
- Consume soft foods and use paracetamol to reduce fever and alleviate pain
- Avoid strenuous physical activity to prevent complications like meningitis, testicular or ovarian inflammation.
- Apply warm or cold compresses to the swollen salivary glands to reduce swelling.
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Avoid acidic foods, fruits, and alcoholic beverages.
- Patients with mumps should avoid exposure to cold wind or water, as this can exacerbate the swelling and pain in the affected glands. However, they should continue regular hygiene and personal care to prevent bacterial infections.
- Seek medical attention if symptoms such as persistent vomiting, severe headache, or stomach ache occur.
- Antibiotics should only be used if prescribed by a certified physician.
- Avoid using traditional remedies such as applying ink, ointments, or plant leaves to the swollen areas. These methods can cause skin burns and create conditions that facilitate bacterial infections, potentially leading to more severe inflammation or even sepsis.
- Patients with mumps should remain at home to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Mumps typically resolves within 5-7 days without complications. After 10 days, the swelling of the salivary glands usually subsides and full recovery is expected.
Currently, there is no specific antiviral medication for mumps, so the focus lies on symptomatic treatment until the infection resolves naturally.

4. Prevention of Mumps
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent mumps. If you have not received two doses of the MMR vaccines as a child, it is advisable to receive at least one dose immediately.
During a viral outbreak, it is recommended to limit exposure to crowded places.
You should also maintain a clean and well-ventilated, environment while using regularly disinfected household items
If you detect any symptoms of mumps, seek medical attention immediately to ensure appropriate intervention is administered, preventing the spread of the infection, and other serious complications.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.