This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Mai - Radiologist - Diagnostic Imaging Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is increasingly common, progresses silently, causing many serious complications. This condition is usually caused by excess fat in the liver that affects the function of the liver.
From 1980 to 2013 obesity increased by 27.5% in adults and 47.1% in children. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is currently 24% globally. In Vietnam currently, the obesity rate is about 25% of the population.
1. What is fatty liver disease?
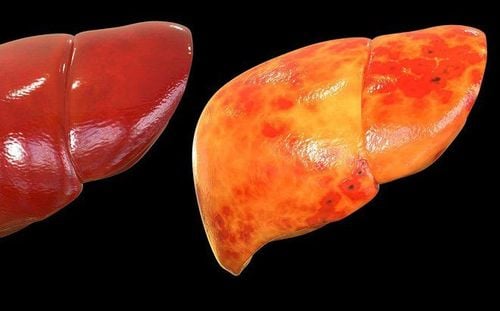
The liver is the second largest organ in the body after the brain. The main job of the liver is to metabolize all the substances absorbed from the digestive system, and at the same time eliminate excess substances in the body. In the average person, the amount of fat in the liver makes up only 2 to 4 percent of the weight of the liver. But when this amount of fat increases above 5%, fatty liver disease will appear. When excess fat in the liver is too much, it will affect liver function. If detected in time and with good treatment, liver cells can repair themselves by creating new cells to replace damaged cells. On the contrary, if these conditions persist for a long time, it will gradually cause fibrosis and eventually cause cirrhosis of the liver.In the early stages, most of the fatty liver does not cause significant symptoms that cause patients to go to the doctor, most of them are discovered incidentally during routine physical examination. When it comes to the late stage, there are often symptoms of real liver damage such as loss of appetite, weight loss, abdominal pain, fatigue and jaundice.

2. Fatty liver disease includes which types?
Fatty liver can be divided into 4 main groups as follows:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver This is a medical condition not related to alcohol but due to a disorder of fat metabolism in the liver leading to an excess of fat in the cells. liver cells. When the percentage of fat in the liver accounts for more than 10% of the liver, it will be classified into this group.
Alcoholic fatty liver The main cause is excessive alcohol use. Alcoholic fatty liver has early symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis. When drinking, alcohol will directly enter the blood and metabolize in the liver, drinking too much alcohol damages liver cells and leads to impaired fat metabolism, causing fatty liver.
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis The real cause is not alcohol. When the amount of fat in the liver accumulates more and more, reaching a certain level, the volume of the liver increases but liver function declines. The main symptoms are of hepatocellular failure syndrome such as loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, jaundice.
Acute fatty liver disease in pregnancy This is a rare complication in pregnancy and can be life-threatening. The etiology is unknown, but it is more common in patients with risk factors such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and obesity.

3. Non-invasive methods used to assess the degree of fatty liver disease
To diagnose fatty liver, the gold standard is a liver cell biopsy for testing. Diagnosis is confirmed when the amount of fat is >5% of hepatocytes. However, this method is invasive and besides there are many non-invasive diagnostic tools of high value in the evaluation of fatty liver. Some commonly used methods are ultrasound, B mode elastography, computed tomography CT-scan, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
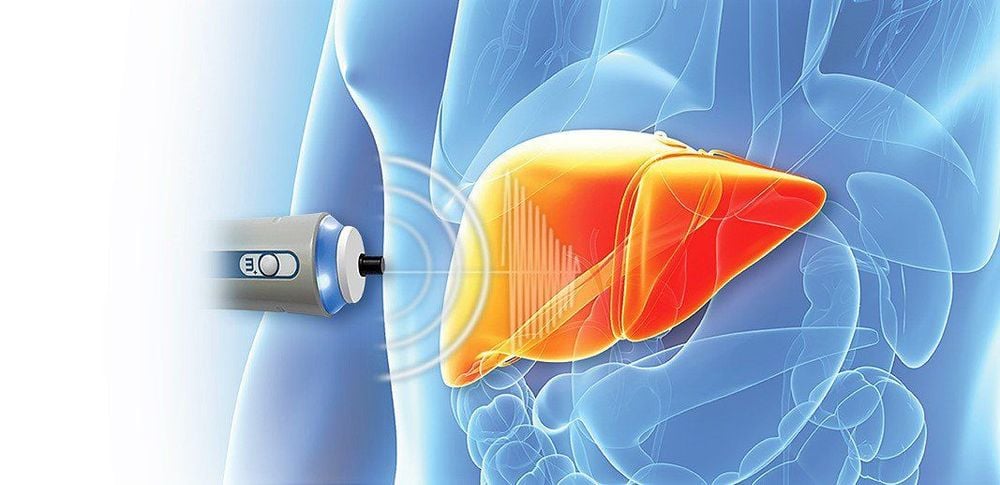
3.1. Elastography of the liver B Mode
The image of fatty liver on ultrasound is measured based on the increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, creating a characteristic image called bright liver. Each degree of fatty liver in each subject with the increase in echogenicity will be different. B-mode ultrasound has many advantages in diagnosing the degree of fatty liver because of its availability, low cost but still high sensitivity and specificity. Based on the deep sound characteristics, opacities of the diaphragm and blood vessels to divide the degree of fatty liver.
Degree of fatty liver on ultrasound:
Grade 1: there is a slight increase in diffuse echogenicity in the parenchyma, there is no significant change in the degree of aspiration, and the presence of the diaphragm and the static border The circuit is still clear. Grade 2: The diffuse echogenicity and aspiration of the liver parenchyma have increased, while the diaphragm is defined as the degree of diaphragmatic visibility and the intrahepatic venous border is reduced. Grade 3: Significant increase in diffuse echogenicity and aspiration of parenchyma, diaphragm region and intrahepatic venous border are no longer visible. However, this method still has disadvantages such as not detecting fatty liver level < 10%, not distinguishing between simple fatty liver and steatohepatitis, not accurately determining the degree of liver fibrosis.
3.2. Computed tomography (CT) scan
This is a highly valuable imaging tool in the case of small granulomatous fatty liver. On CT-scan without contrast, the liver has a larger density than the spleen and blood. Fatty liver can be diagnosed if the density of the liver is 10HU less than that of the spleen or the density of the liver is less than 40HU. In addition, in severe cases the blood vessels of the liver may be hyperattenuated compared with fatty liver tissue.
3.3. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging is also a valuable method in diagnosing the degree of fatty liver. Based on magnetic macular chemical shift (GRE) imaging with inphase and outphase imaging, fatty liver can be assessed for signal loss on outphase versus inphase imaging and liver fat can be measured. quantified by assessing the loss of signal strength.
3.4. Some other methods
Besides imaging tests, the assessment of fatty liver can also be based on the assessment of the patient's risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome ; blood tests such as elevated liver enzymes AST, ALT, GGT and some scores such as Fatty Liver Index, SteatoTest or NAFLD Fat score.
To prevent fatty liver disease, you should check your general health regularly to make appropriate dietary adjustments as well as timely treatment interventions.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.