This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The liver is a very important part of the body, at high risk of being damaged due to objective and subjective causes. Among the common diseases of the liver, fatty liver is a common disease, which can occur at any age.
1. What is fatty liver disease?
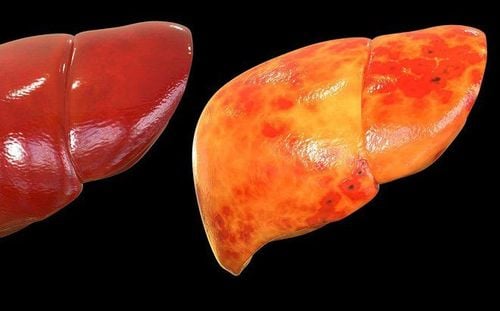
The liver is an important part of the body, plays a key role in metabolism, is the place to synthesize plasma proteins, store glycogen, create bile, play a very important role in the digestive system. However, if unfortunately, the amount of fat accumulated in the liver is too high to form fatty liver.When damaged, the liver can repair itself by regenerating new cells, replacing old damaged cells. However, if harmful agents continuously appear in the liver, fibrous tissue will form and cause cirrhosis which is more serious and difficult to treat.
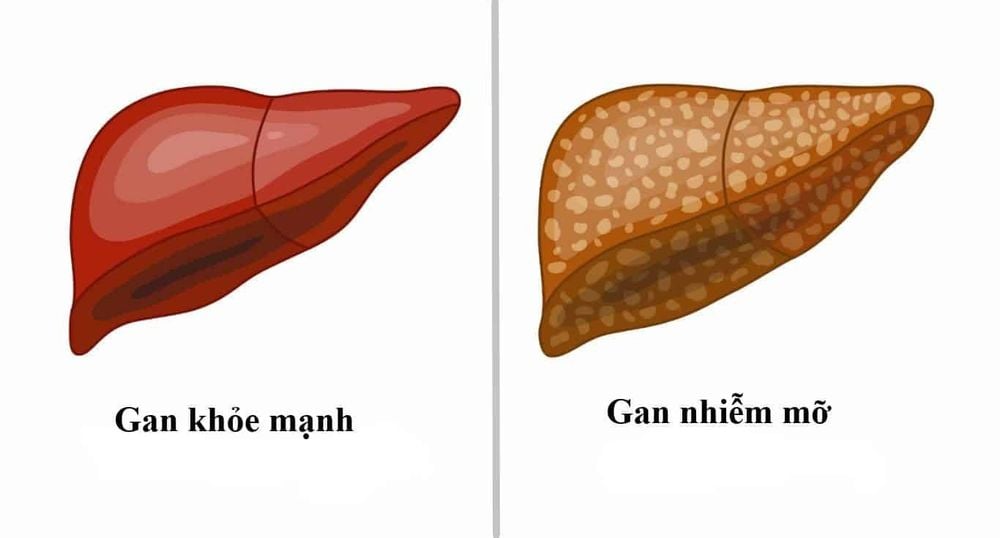
2. Diagnosis and assessment of fatty liver
To diagnose and evaluate the degree of fatty liver, doctors will conduct a clinical examination. Through the symptoms of the disease reported by the patient such as: loss of appetite, indigestion, bloating, fatigue, or asking a history of drug use, alcohol use and clinical examination, the doctor can assess whether risk of fatty liver.In addition, to be more sure of the results, the doctor may order the patient to conduct a number of tests including:
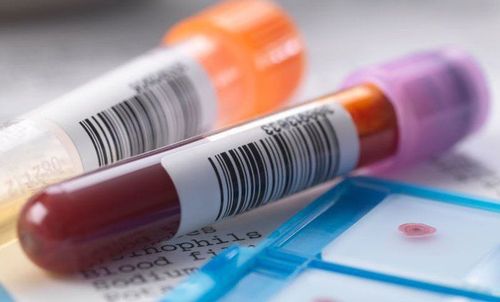
Blood tests: Blood test results show changes in liver enzymes in the blood ( elevated), blood fat, liver function tests such as blood coagulation, blood protein... and hepatitis virus tests help determine the extent and cause of liver damage. Ultrasound: Ultrasound helps to identify fatty liver through the image of a bright liver, increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma. Other imaging: In addition to the common methods above, fatty liver can also be diagnosed through computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Biopsy: A highly accurate diagnostic method, helping to determine the cause of fatty liver. The patient will be anesthetized to use a biopsy needle to remove a few pieces of liver tissue for cytology examination.
3. Results of assessing the degree of fatty liver
3.1 Assessment of the degree of fatty liver Fatty levels in the liver are measured simultaneously on the same liver volume, expressed by the CAP index (Controlled Attenuation Parameter). This index is calculated from the ultrasound signals during the measurement of liver stiffness. The CAP fat measurement value is expressed in units of dB/m (decibel/m).Meaning of fatty liver measurement results (reference):
S0: Fatty liver cells accounted for 0-10%; CAP: 100-233 dB/m => Normal S1: The percentage of fatty liver cells accounts for 11-33%; CAP: 234-258 dB/m => Mild fatty liver S2: The percentage of fatty liver cells accounted for 34-66%; CAP: 259-290 dB/m => Moderate fatty liver. S3: The percentage of fatty liver cells accounts for 67-100%; CAP: 290-400 dB/m => Severe fatty liver The normal value of CAP liver fat (S0: non-fatty liver) for both sexes is 201 ± 44 dB/m
3.2 Evaluation of the degree of liver fibrosis Liver fibrosis is an important prognostic factor in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver fibrosis is correlated with outcomes and mortality from liver disease.
Assessment of liver fibrosis by measuring the stiffness (elasticity) of the liver, is a non-invasive technique, used to identify low-risk cases of severe cirrhosis and cirrhosis. The elasticity of the liver is expressed in units of kPa (kiloPascals) ranging from 2.5kPa to 75kPa and is measured in a depth of 25mm - 65mm with a diameter of 0.1cm. The unit levels of kPa will correspond to 5 different degrees of liver fibrosis, which are:
F0: no fibrosis F1: mild fibrosis F2: Significant fibrosis: Fibrosis diffuses to the perivascular areas of the liver . F3: Severe fibrosis: The fibrosis is extensive and there is a connection of areas of the liver with cirrhosis. F4: Cirrhosis or advanced liver fibrosis. The normal value of liver stiffness (F0: no fibrosis) for men is 5.81 ± 1.54 kPa and for women is 5.23 ± 1.59 kPa. Approximately 90-95% of healthy individuals without liver disease have liver stiffness <7.0 kPa (mean 5.30 kPa).

Evaluate the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C. Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases at risk of affecting liver disease/ worsen liver disease. In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory and subclinical tests; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer. Specialist I Le Nguyen Hong Tram graduated as a Doctor of General Internal Medicine at the University of Medicine and Pharmacy in Ho Chi Minh City. Ho Chi Minh, doctor has many years of experience in the examination and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, especially gastrointestinal - hepatobiliary diseases, gastrointestinal endoscopy and general internal diseases. Currently, Dr. Tram is working at the Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.