This is an automatically translated article.
Overactive bladder (OAB) causes a sudden urge to urinate, it can also cause urinary incontinence. It can be difficult to manage symptoms because an overactive bladder can be unpredictable. If you have overactive bladder, don't despair because there are FDA-approved treatments that can help control your symptoms.
1. What is an overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder (OAB) causes a sudden urge to urinate, it can also cause urinary incontinence, also known as incontinence. Overactive bladder affects about 33 million Americans, with women affected more often than men.
It can be difficult to control symptoms because an overactive bladder can be unpredictable. This can cause some people with the disease to limit their social activities, which can affect their quality of life. It can also cause isolation and emotional distress.
But there are some treatments that can help you manage your symptoms. Treating an overactive bladder can also improve your condition and reduce the incidence of urinary incontinence.
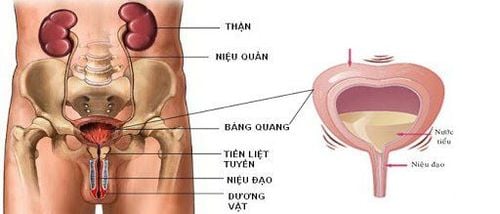
Bàng quang hoạt động quá mức (OAB) gây ra cảm giác muốn đi tiểu đột ngột, tiểu không tự chủ
2. Overactive bladder symptoms
People with overactive bladder have bladder muscles that contract too often or contract without warning. This can lead to worrisome urinary symptoms such as:
Excessive need to urinate (frequent urination), defined as eight or more urinations in a day or two or more times at night (nocturia). An immediate need to urinate (urinary urgency). Urinary incontinence due to an immediate need to urinate (incontinence). These symptoms affect more than 33 million Americans. Many people do not seek treatment, possibly because they are embarrassed or unaware of treatment options. In the United States, 30% of men and 40% of women live with overactive bladder symptoms.
The good news is that there are therapies for these symptoms. These include topical medications, patches or gels, the first over-the-counter (OTC) treatment for women with overactive bladder, and bladder injections for patients with severe symptoms. more important.
3. Cause
Some known causes of overactive bladder include neurological disorders such as spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and stroke. However, the cause of the disease is unclear. The risk of an overactive bladder increases with age.
Some conditions such as urinary tract infections, early pregnancy, uncontrolled diabetes, prostate disease and bladder tumors also have similar symptoms to an overactive bladder and need to be eliminated. unless an accurate diagnosis can be made.
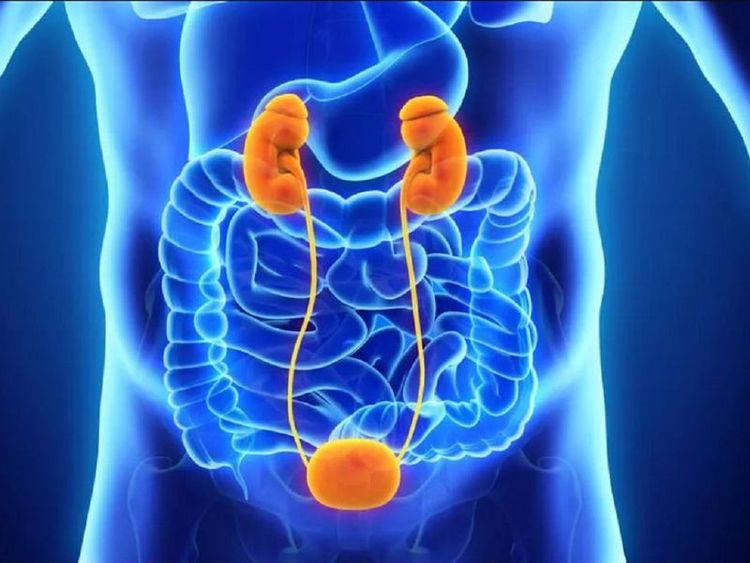
Thuốc lợi tiểu có thể gây ra các triệu chứng giống bàng quang hoạt động quá mức
4. Choice for people with overactive bladder
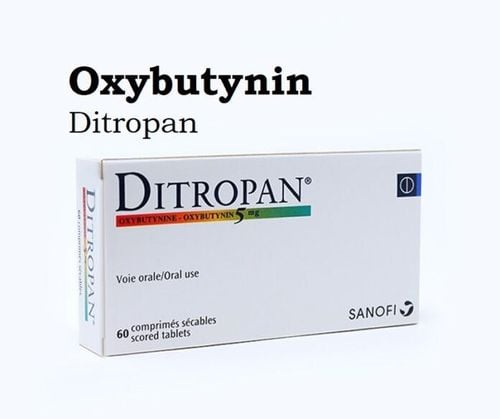
There are several treatment options for overactive bladder that help the bladder muscle relax and prevent it from contracting at the wrong time. Anticholinergics are a widely used medication for overactive bladder. These medications contain oxybutynin, tolterodine, fesoterodine, or solifenacin, and are thought to inhibit involuntary bladder contractions.
The FDA has also approved Myrbetriq (mirabegron), a drug that improves the bladder's ability to store urine by relaxing the bladder muscles during filling. Side effects of Myrbetriq include increased blood pressure and urinary tract infections. In certain cases, Myrbetriq may increase the chance that you will not be able to empty your bladder on your own, for example: If you are also taking other medicines to treat your overactive bladder.
For women 18 years of age and older, there is also a patch, called Oxytrol for Women, that is applied to the skin every four days. This over-the-counter patch is available without a prescription and provides oxybutynin. For men, the oxybutynin patch is available by prescription only and is called Oxytrol. Side effects of the Oxytrol patch include skin irritation, drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, hallucinations, and blurred vision.
For adults who cannot use or do not respond adequately to anticholinergics, Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) can be injected. Botox is injected directly into the bladder muscle under local or general anesthesia in the doctor's office using a small camera that allows the urologist to see the inner wall of the bladder.
Botox causes the bladder to dilate, increases urine storage capacity and reduces urinary incontinence. When the effects of Botox wear off, more injections can be given, but no earlier than three months from the last injection.
Botox can cause serious side effects that can be life-threatening, including difficulty breathing or swallowing, and spreading toxin effects. These problems can occur hours, days, or weeks after the injection. Call your doctor or get medical help right away if you have any of these problems after having Botox treatment. Less serious side effects of Botox include urinary tract infections and urinary incontinence.
There are many treatment options for patients with overactive bladder. Not every drug is suitable for every patient. Patients should seek help from a healthcare professional to determine if their symptoms are caused by an overactive bladder or another condition, and decide what treatment is appropriate. the best.
Vinmec International General Hospital now has a Urology Screening Package - Stones, which helps patients detect urinary diseases and stones early even when there are no symptoms. The package of Urology Screening - Stones at Vinmec Hospital includes many utilities such as:
Customers are examined and consulted by urologists. Perform diagnostic X-ray and ultrasound services. Early detection of urinary diseases, stones and timely treatment advice.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: fda.gov, healthline.com