This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Thi Minh Thuyen - Pathologist, Pathology Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.If you've been diagnosed with multiple myeloma, your cancer care team will discuss treatment options with you. It is important that you think carefully about each of your options. Consider the benefits of each treatment option to limit possible side effects and risks.
1. Topical Treatments
Some treatments are called topical therapy, which means treating the tumor without affecting the rest of the body. These treatments are usually used for early-stage (less advanced) cancers, although they may also be used in some other situations.1.1 Surgery Surgery is sometimes used to remove solitary plasmacytomas, but it is rarely used to treat multiple myeloma. When spinal cord compression causes paralysis and severe muscle weakness, emergency surgery may be needed. Surgery to attach metal rods or plates can help support weak bones and may be needed to prevent or treat fractures.
1.2 Radiation Therapy Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used to treat areas of bone damaged by myeloma that have not responded to chemotherapy and/or other drugs and are causing pain or the bone may be near destruction. It is also the most common treatment for solitary plasmacytoma.
If myeloma severely weakens the bones of the vertebrae (back), these bones can collapse and put pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves. Symptoms include a sudden change in sensation (such as numbness or tingling), sudden weakness in the calf muscles, or sudden problems with urination.
This is a medical emergency, patients with these symptoms must go to the hospital immediately. Prompt treatment with radiation and/or surgery is essential to prevent paralysis.
The type of radiation therapy used most often to treat multiple myeloma or a solitary plasma cell tumor is called external beam radiation therapy, which means radiation is aimed at the cancer from a machine outside the body.
Side effects of radiation therapy may include:
Skin changes in the treated area, which can range from redness to blistering and peeling Fatigue Nausea Diarrhea (if treating the abdomen or pelvis) low blood count These symptoms improve when treatment ends
2. Body treatments

Multiple myeloma can also be treated using medication, either by mouth or directly into the bloodstream. These systemic therapies can reach cancer cells anywhere in the body.
2.1 Drug treatment There are different types of drugs that can be used to treat multiple myeloma.
2.1.1 Chemotherapy Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill or control cancer cells. These drugs can be taken orally or intravenously or intramuscularly. They enter the bloodstream and reach most areas of the body.
Chemotherapy drugs include:
Melphalan Vincristine (Oncovin) Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
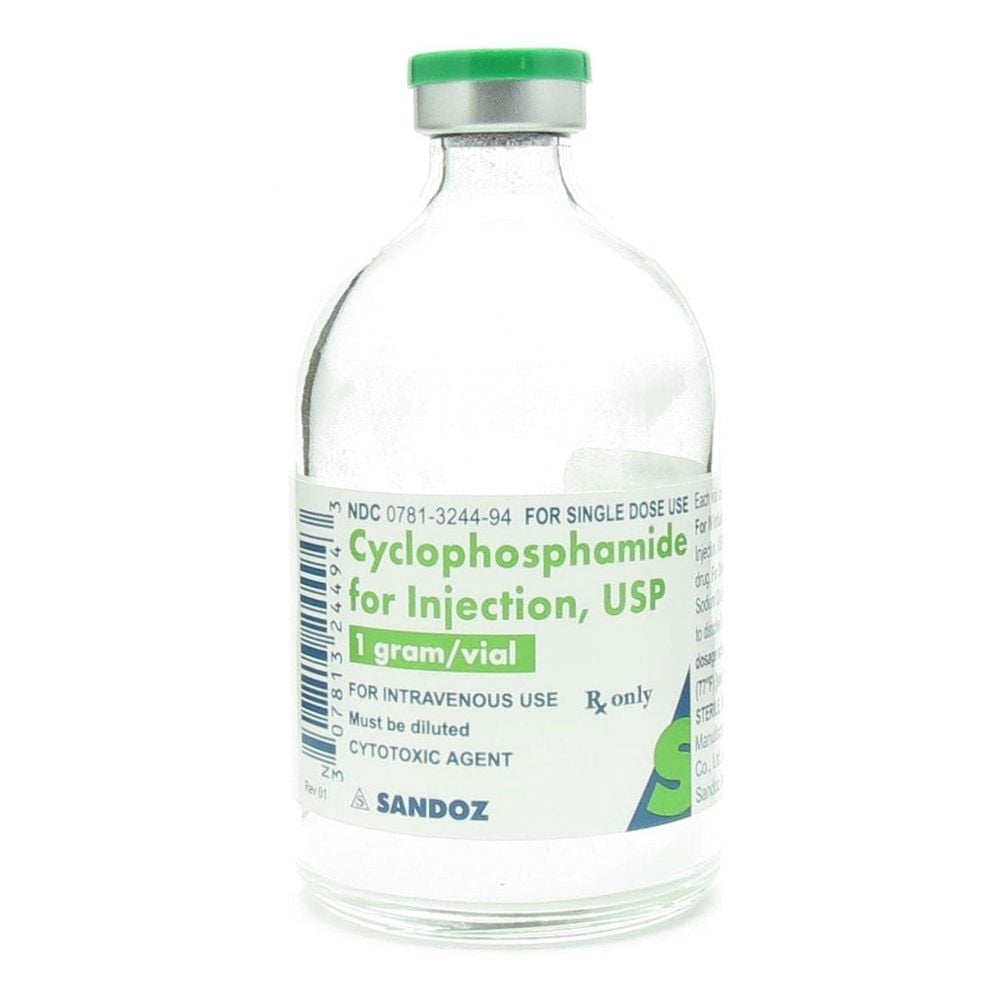
Etoposide (VP-16) Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Doxorubicin liposome (Doxil) Bendamustine (Treanda) Usually, one of the chemotherapy drugs is combined with other drugs such as corticosteroids and immunomodulators (the drug will changes in the patient's immune response). If a stem cell transplant is planned, most doctors avoid using certain medications, which can destroy bone marrow.
Side effects of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells but can also destroy normal cells. They are used very carefully to avoid or reduce the side effects of chemotherapy. These side effects depend on the type and dose of the drug and the length of time it is taken.
Common side effects of chemotherapy include:
Hair loss Mouth ulcers Loss of appetite Nausea and vomiting Low blood count Chemotherapy often leads to a decrease in blood cell counts, which can cause:
Infection : increased risk of serious infections (due to low white blood cells) Easy bruising or bleeding (due to low platelets) Anemia: Feeling excessively tired or short of breath (due to low red blood cells)

Most side effects are temporary and go away after treatment ends.
If you have side effects, your cancer care team can provide step-by-step support to ease them. For example, use medicine along with chemotherapy to prevent or reduce nausea and vomiting.
In addition to these temporary side effects, some chemicals can permanently damage certain organs such as the heart or kidneys. The possible risks of these drugs are carefully weighed against their benefits, and organ function is closely monitored during treatment. If organ damage is severe, the drug will be stopped and may be replaced with another.
2.1.2 Corticosteroids (steroids)
Corticosteroids, such as dexamethasone and prednisone, play an important role in the treatment of multiple myeloma. They may be used alone or in combination with other medications. Corticosteroids are also used to help reduce the nausea and vomiting that chemotherapy can cause.
Common side effects of these steroids include:
High blood sugar. Eat a lot and gain weight. Sleep influence. Mood swings (some people become irritable). When used for a long time, corticosteroids also suppress the immune system. This increases the risk of serious infection. Steroids can also weaken bones. Most of these side effects go away after stopping the medication.

2.1.3 Immunomodulators The way immunomodulators affect the immune system is completely clear. Three immunomodulators are used to treat multiple myeloma:
Thalidomide (Thalomid) Lenalidomide (Revlimid) Pomalidomide (Pomalyst) Proteasome Inhibitors
Proteasome inhibitors work by blocking enzyme complexes ( proteasomes) in cells break down proteins important for controlling cell division. They seem to affect cancer cells more than normal cells, but they also have side effects.
Bortezomib (Velcade) Carfilzomib (Kyprolis) Ixazomib (Ninlaro) Monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies are proteins made by the body's immune system that help fight infection. Monoclonal antibodies attack a specific target, such as a protein on the surface of myeloma cells.
Anti-CD38 antibody + Daratumumab (Darzalex)
+ Isatuximab (Sarclisa)
Anti-SLAMF7 antibody + Elotuzumab (Empliciti)
2.1.4 Combination of drugs Although a single drug can be used to treat multiple tumors marrow, but it is better to use at least 2 or 3 different drugs in combination because of better response.
The choice and dosage of the drug depends on many factors, including the stage of the disease, physical condition, age and kidney function of the patient. If a stem cell transplant is planned, most doctors will avoid using certain drugs that can destroy bone marrow.
2.1.5 Bisphosphonates for Bone Disease Myeloma cells can weaken and even fracture bones. Medicines called bisphosphonates can help strengthen bones by slowing this process. They can also help relieve pain in weak bones.
Sometimes pain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are combined with bisphosphonates to help control or relieve pain. Bone pain can be a difficult symptom to manage during and after myeloma treatment.
Bisphosphonates include:
Pamidronate (Aredia) Zoledronic acid (Zometa) Denosumab (Xgeva, Prolia)

These drugs are given intravenously. Most patients receive treatment once a month, but less often if the response is good. Bisphosphonate treatment helps prevent further bone damage in many patients with multiple myeloma.
2.2 Stem cell transplant (SCT) In the case of a stem cell transplant, the patient receives high doses of chemotherapy to destroy the cells in the bone marrow. The patient then receives new and healthy hematopoietic stem cells. In the past, new stem cells were obtained from bone marrow, hence the term bone marrow transplant. Currently, stem cells are usually obtained from blood (peripheral blood stem cell transplantation).
Stem cell transplantation (SCT) can be autologous or allogeneic.
2.2.1 Autologous stem cell transplantation
For autologous stem cell transplantation, the patient's stem cells are removed from the bone marrow or peripheral blood prior to transplantation. They are stored until needed for transplantation. Then, the patient is given high-dose chemotherapy, sometimes with radiation, to kill the cancer cells. The stored stem cells are then returned to the patient's bloodstream by intravenous route.
This is a standard treatment for patients with multiple myeloma. Although an autologous stem cell transplant can stave off myeloma for some time (even years), it does not cure the disease and will often recur.
2.2.2 Allogeneic stem cell transplant
For allogeneic stem cell transplantation, the patient receives hematopoietic stem cells from another person - the donor. Treatment outcomes are best assessed when the donor's cells adapt to the patient's cells, and the donor is closely related to the patient, such as a sibling. Allogeneic transplants are more risky than autologous transplants, but are better at fighting cancer, because transplanted (donor) cells can actually help destroy cancer cells .
● Side effects
The early side effects of stem cell transplant (SCT) are similar to those of chemotherapy and radiation, but more severe. One of the most serious side effects is a decrease in blood volume, which can pose a risk of infection and serious bleeding.
The most serious side effect from allogeneic transplantation is rejection. It occurs when new immune cells (from the donor) see the patient's tissues as foreign and attack them. Transplant rejection can affect any part of the body and can be life-threatening.
3. Supportive treatments
3.1 Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) Patients with multiple myeloma often have low normal antibody levels. This can lead to problems with lung and/or sinus infections. The amount of antibodies in the blood can be checked and if low, antibodies from the donor can be given intravenously (IV) to increase the amount of antibodies and help prevent infection, these are called immunoglobulins.
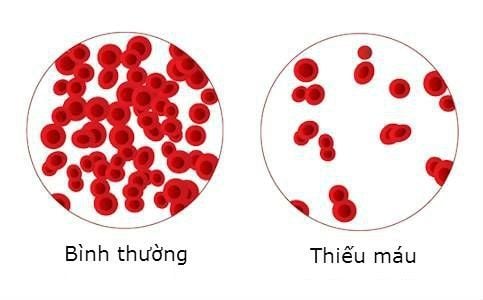
3.2 Treatment of anemia Some patients develop anemia as a result of multiple myeloma itself or its treatment. Can be improved by:
Blood transfusion. Epoetin (Procrit) and darbepoetin (Aranesp): are medicines that can help improve red blood cell counts to reduce blood transfusion in some patients receiving chemotherapy. But these drugs are used less often because they are associated with lower survival rates in some patients. circulation (increasing blood viscosity), this method can be used to remove myeloma protein from the blood. Usually, this is done through a large catheter (catheter) placed in a vein in the neck, below the collarbone, or in the groin area. This catheter is connected to a machine, and blood flows into the machine.
The machine separates the blood cells from the plasma (the liquid part of blood), and then returns the blood cells to the patient, along with saline solution or donor plasma. Discarded plasma, which contains abnormal antibody proteins made by cancer cells.
Although this method reduces abnormal protein levels and may relieve symptoms for a while, it does not kill the cancer cells. That means that without further treatment, the protein will build up again. For this reason, this technique is often treated with chemotherapy or some other type of drug treatment to kill the cancer cells that make the protein.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: American Cancer Society