A minor stroke, also known as a transient ischemic attack (TIA), occurs when blood flow to the brain is temporarily interrupted. According to statistics, 50% of patients who experience a TIA will suffer a full stroke within 5 years. Therefore, recognizing the symptoms of a minor stroke can help prevent serious complications.
1. What Is a Minor Stroke?
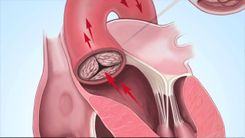
A minor stroke, or TIA, does not cause the death of brain cells like a full stroke. However, it presents similar symptoms and serves as a warning sign for future strokes. Typically, a TIA lasts less than 24 hours and often only a few minutes to 1–2 hours. Research indicates that 90% of TIAs resolve within 4 hours without causing permanent damage.
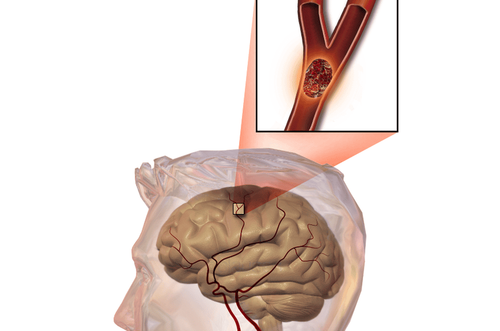
The primary cause is a temporary decrease in blood supply to the brain. Approximately 15% of the body’s total blood supply is required to nourish the brain and nervous system, transported by the heart and arterial system. When this supply is disrupted, brain function and other bodily systems are affected. According to the American Heart Association, experiencing a TIA reduces life expectancy by 20%. About 10–15% of patients will have a full stroke within 3 months of a TIA, with half of these occurring within 48 hours.

2. Symptoms of a Minor Stroke
A TIA can be difficult to diagnose due to its transient nature. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden increase in blood pressure
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness in the hands or feet
- Dizziness
- Sudden vertigo
- Loss of consciousness
- Altered awareness
- Temporary memory loss
- Tingling sensations in the body
- Personality changes
- Difficulty speaking
- Loss of balance
- Vision changes, such as blurred vision or double vision
Some minor stroke symptoms may resemble those of other conditions, such as:
- Migraines: Often accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light, and strong sounds, with gradual onset over 30 minutes.
- Fainting: A sudden loss of consciousness without other symptoms.
- Transient seizures: Symptoms may start in one part of the body and spread gradually.
- Transient global amnesia: Sudden memory loss without focal neurological deficits after regaining alertness.
3. Causes of a Minor Stroke
Several risk factors can lead to a TIA, including:
- Family history: Having family members who have experienced TIAs increases your risk.
- Age: Older adults, especially those over 55, are more susceptible.
- Gender: Men experience more TIAs, but women have a higher fatality rate from strokes.
- Previous strokes: Individuals with a history of strokes are 10 times more likely to have another.
- Sickle cell disease: This condition reduces oxygen in red blood cells and increases the risk of arterial blockages, leading to restricted blood flow to the brain.
- High blood pressure: This is the most common cause of TIAs and full strokes. Uncontrolled hypertension signals a greater risk of severe strokes in the future.

4. Diagnosis and Treatment of a Minor Stroke
4.1 Diagnosis
Because TIA symptoms are often subtle, diagnosis usually requires medical evaluation, including:
- Blood tests: Detect lipid disorders and the risk of atherosclerosis or stroke.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Identifies atrial fibrillation or other heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Echocardiography: Detects heart valve damage or signs of heart failure.
- Carotid and vertebrobasilar artery ultrasound: Reveals arterial wall damage and atherosclerosis.
- Transcranial Doppler ultrasound: Assesses cerebral blood flow and circulation.
- CT or MRI brain scans: Excludes conditions such as brain tumors or traumatic injuries.
4.2 Treatment
A TIA requires treatment similar to that for a full stroke. Treatment plans depend on the underlying cause and severity and may include:
- Medications: Stabilize underlying conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, or blood clots to improve brain blood supply.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopt a healthy diet, quit smoking, lose weight, and reduce fatty food intake.
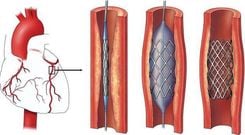
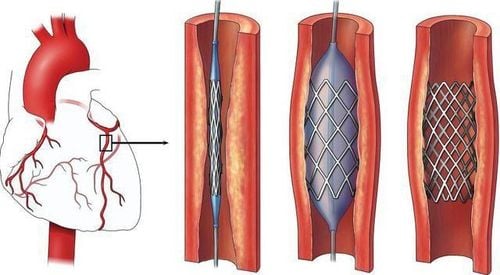
- Surgical intervention: In cases where carotid artery narrowing exceeds 70%, specific procedures may be required.
A minor stroke, or TIA, is a temporary interruption of blood flow to the brain. Recognizing its symptoms—such as sudden high blood pressure, memory loss, dizziness, and altered awareness—can help prevent severe complications. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately for timely diagnosis and treatment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.