This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Mai Kieu Anh - Deputy Head of Pediatric Inpatient Department and Head of Pediatric Resuscitation Unit, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Doctor Kieu Anh has nearly 10 years of experience working in the field of Emergency Resuscitation at the National Children's Hospital, especially in the field of pediatric resuscitation. His strength is examining and treating basic diseases in children, serious diseases requiring intensive resuscitation.Meningococcal meningitis in children is a dangerous infectious disease. If not detected and treated in time, the disease will progress quickly, have a high mortality rate and often leave serious sequelae later.
1. What is meningococcal meningitis?
Meningococcal disease is an inflammation of the membranes covering the central nervous system caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitides, with a mortality rate of 13% in the United States. This is the second most common bacteria that causes meningitis in children.Clinical manifestations vary from low-grade fever to bacteremia, or fatal malignancy within hours of onset.
The clinical picture is often severe and acute, with high mortality and sequelae if not treated promptly, especially if purulent meningitis is present.
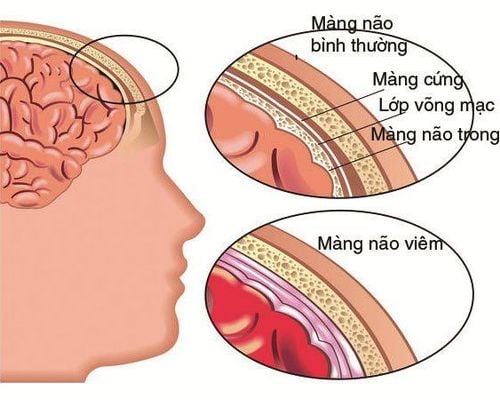
Although it is a rare disease with the rate of 0.26 cases / 100,000 people (according to US statistics), meningococcal disease has a fast spread rate, the ability to develop into an epidemic because of its easy transmission through sexual contact. respiratory droplets (droplets), especially in crowded places. The disease thrives in winter and is common in children and adolescents. In addition, the disease is more common and widespread in crowded communities, in urban areas than in rural areas.
2. What are the symptoms of meningococcal meningitis in children?
The disease often has a sudden onset with manifestations such as sudden high fever 39-40 degrees Celsius (sometimes up to 40-41 degrees Celsius), may be accompanied by chills, cough, sore throat, fatigue, muscle pain, vomiting, headache, convulsions. In severe cases, the child will lethargy, refuse to eat, stop playing or convulsions and eventually go into a coma.
The initial symptoms are very similar to those of seasonal flu, especially these two diseases are common in winter. Therefore, many families are subjective and think that their child has the flu, so they do not let them go to the doctor in time. So if the child has the above symptoms along with the meningococcal epidemic in the area where they live, the family should take the child to the hospital as soon as possible after the appearance of suspicious symptoms.
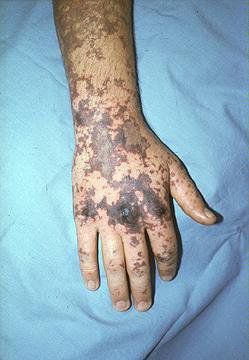
In addition, the child's skin will appear star-shaped rashes within 1-2 days after the fever. Erythema (a necrotic and rapidly spreading rash) dark red or blue-violet, 1-5 mm in diameter, may coalesce, sometimes with areas of necrotic skin, the surface is flat, not raised skin face. The rash appears early and spreads rapidly throughout the body, but is often concentrated in the trunk and lower extremities. At this time, the child's condition may have fallen into toxic sepsis, severe septic shock, multi-organ failure and possibly rapid death within 24 hours.
3. How to diagnose and treat meningococcal meningitis?
In addition to the typical clinical manifestations of purulent meningitis, to diagnose meningococcal meningitis, the doctor will do some more tests such as blood test, cerebrospinal fluid test, blood culture, culture. oropharyngeal fluid, oropharyngeal smear and cerebrospinal fluid...
When a patient has suspected meningococcal meningitis, the patient should be isolated as soon as possible to avoid spreading. Antibiotic therapy should be used immediately after blood culture to reduce the mortality rate of the disease.
Current specific antibiotics are still Penicillin G intravenously injected several times a day or third generation Cephalosporins such as Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone. In cases of penicillin G allergy, children can be substituted with Chloramphenicol. The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the individual patient's response.
Besides, when the child has fallen into shock, it is necessary to prescribe additional drugs to support the heart, adjust the electrolyte balance, support breathing and circulation... depending on the doctor's instructions. . Other supportive treatment measures such as: antipyretic, anticonvulsant, nutrition, hygiene care to prevent ulcers...
4. Prevention of meningococcal meningitis
This is an uncommon but dangerous disease with a high mortality rate. Therefore, we need to take precautions to reduce the incidence of disease in the community.
All patients with suspected meningococcal infection are isolated in the hospital for at least 24 hours after taking antibiotics.
Use prophylactic drugs for people who have been in contact with the source of the disease (who have had a confirmed diagnosis of meningococcal infection and are being treated) such as family members, roommates, colleagues.. .In this case, individuals who have contact with the patient should go to the Hospital for advice and prescribe preventive medicine as soon as possible.
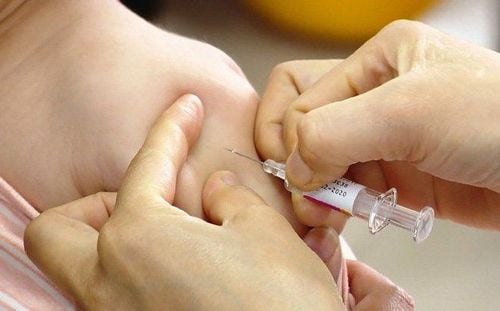
The best way to proactively prevent is to get the meningococcal vaccine as recommended. Currently, Vietnam has vaccines against 3 serotypes: A, B, and C, which are meningococcal AC vaccines and meningococcal BC vaccines. Children should be vaccinated with both vaccines to gain immunity to all 3 common meningococcal serotypes. BC vaccine can be given to children 6 months of age and older, AC vaccine can be given to children 2 years of age and older. However, to achieve sufficient and long-term immunity, children need to be vaccinated with a full dose and repeated according to the instructions of the doctor.
5. What to do when a child shows signs of meningococcal meningitis?
If the child has symptoms such as sudden high fever 39-40 degrees, chills, cough, sore throat, fatigue, muscle pain, vomiting, headache, convulsions, lethargy, refusal to breastfeed, especially at the place of birth. If you are living with meningococcal disease, parents should quickly bring their children to the hospital for timely examination and treatment. If the disease has been diagnosed, the child needs to be hospitalized for treatment and isolated to avoid spreading in the community, the family needs to comply and cooperate with the doctor to achieve the highest effectiveness in treatment.
For family members, siblings, friends who have contact with the Patient, it is necessary to quickly go to the Hospital for advice on antibiotic therapy to prevent disease.
Pediatrics Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is one of the leading places to treat respiratory infections and pediatric infectious diseases with strengths such as:
Dedicated team of doctors with extensive experience from leading pediatric hospitals in Vietnam: Professor Pham Nhat An, Doctor Mai Kieu Anh, Doctor CKII Nguyen Thi Tam, negative pressure room with one-way ventilation, helping to isolate patients well, limiting the spread of infection. infecting surrounding patients. Average hospital stay ≤ 4 days. No serious medical incident grade 4 or higher
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.