This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Vu Duy Chinh - High-Tech Unit for Treatment of Cerebral Palsy and Autism - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Cerebral palsy is a serious neurological condition caused by brain damage, the disease leaves lifelong sequelae, seriously affecting the quality of life of patients. So what is the cause of cerebral palsy? What are the symptoms and signs of the disease?
1. What is cerebral palsy?
Cerebral palsy is a term for a group of medical conditions caused by brain damage that does not progress over time, caused by causes before birth, during and after birth until less than 5 years of age. Cerebral palsy causes multiple disabilities in motor, mental, sensory and behavioral... leaving heavy consequences for the children themselves, their families, but also affects economic and social development. AssemblyDue to damage to one or more parts of the brain, the patient cannot move the muscles normally. In addition to affecting movement, many cases of children with cerebral palsy are accompanied by other disabling conditions that need to be treated such as: mental retardation, learning disorders, epilepsy, behavioral changes. , vision, hearing, and language problems. The rate of cerebral palsy is about 2/1000 newborns, the disease has a higher incidence in boys than girls (1.35/1).
2. Causes of cerebral palsy
There are many causes of cerebral palsy in children, divided into 3 main groups as follows:
2.1 Prenatal causes
2.1.1 Infections during pregnancy
Infections in pregnant women such as rubella, viruses during the first 3 months of pregnancy can damage the brain of the fetus and cause cerebral palsy later in life. Other infections such as infection of the amniotic fluid and infection of the mother's genitourinary system can also cause premature birth, another risk factor for cerebral palsy.2.1.2 Lack of oxygen in the fetal brain
When placental function is impaired (placental insufficiency) or is detached from the uterine wall before delivery (placenta abruption) or placenta previa (placenta attaches to the lower uterine segment causes internal bleeding) 3rd trimester) can reduce the oxygen supply to the fetus, leading to fetal brain damage, which is a cause of cerebral palsy.
2.1.3 Other causes and abnormalities
Children with structural abnormalities of the nervous system also have an increased risk of developing cerebral palsy.
Mother's disease: Thyroid disease, gestational diabetes, pregnancy toxicity, pre-eclampsia ....
Heredity: Family factors.
Using drugs without consulting a doctor during pregnancy, exposed to harmful chemicals during pregnancy.
2.2 Causes during childbirth
2.2.1 Premature birth, low birth weight
Preterm birth is a baby born before 37 weeks of gestation from the first day of the last menstrual period before pregnancy. Babies born prematurely, especially before 32 weeks and especially before 28 weeks of gestation, have a very high risk of cerebral palsy. The reason is that premature babies are at very high risk of cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral edema causing damage to the developing delicate tissues of the brain or causing brain damage in the form of periventricular leukoplakia. Low birth weight: One study found that premature babies with a birth weight less than 1,500 grams were 30 times more likely to have cerebral palsy than full-term babies.
2.2.2 Asphyxiation during labor and birth
Babies born with asphyxiation often do not cry right away, their whole body is pale or white, requiring emergency care. The rate of asphyxia in children accounts for only 10% of all cerebral palsy patients.2.2.3 Obstetric Trauma
The most obstetric traumas are difficult births requiring the use of birth support measures such as: Using suction cups, forceps intervention ...2.3 Causes after giving birth
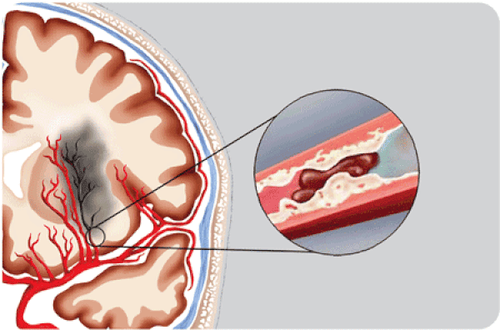
2.3.1 Brain hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage in newborns and brain hemorrhages in young children due to vitamin K deficiency are common diseases in developing countries like Vietnam, if not treated well, can cause sequelae of cerebral palsy. Other blood diseases leading to clotting disorders are also contributing factors to the increased risk of cerebral hemorrhage in children, leading to cerebral palsy.
2.3.2 Yellow skin
Physiological jaundice usually appears on the 2nd - 4th day after birth, pale yellow and usually without any other symptoms. Physiological jaundice usually lasts for about 1 week in full-term infants and 2 weeks in premature infants.When blood bilirubin levels are high, the liver is not able to metabolize and excrete due to immature liver function in newborns, which will cause pathological jaundice. In this case, the elevated bilirubin in the blood can cross the vascular-brain barrier and settle mainly in the basal nuclei of the brain (hence the name nuclear jaundice) and damage the structures of the brain. This causes cerebral palsy.
Children with pathological jaundice are common in children with mother-child blood group incompatibility (blood group ABO, Rh, and subgroup...). Manifestations in children are dark yellow skin and whole body, yellow sclera of the eyes. If not monitored and treated promptly, the baby may appear to stop sucking, cyanosis and extensor limb stiffness (signs of brain damage).
2.3.3 Postpartum hypoglycemia
Recently, the cause of brain damage due to hypoglycemia after birth has been reported to be relatively common. When blood sugar is low, children become comatose, respiratory failure is one of the causes of brain damage in children leading to cerebral palsy.2.3.4 Acquired cerebral palsy
Children suffer from diseases that cause neurological damage in the first years of life, lasting until before the age of 5, such as: meningitis, encephalitis, traumatic brain injury, drowning...3. Classification of cerebral palsy according to clinical type
3.1 Spastic cerebral palsy
Spastic cerebral palsy accounts for 70-80%. Children with this form show muscle spasticity, always in a state of increased muscle tone. All movement activities of children are very difficult. Difficulty holding, crawling or walking. This clinical form is further divided into three subgroups:Spasticity of the lower extremities The child has obvious spasticity in the lower extremities. In this form, due to the contraction of the adductor thigh muscles, the child's legs are always pulled inward, causing the child to have a very characteristic cross-legged gait.
Spastic hemiparesis Often manifests as spastic paralysis on one side (right or left). Often the upper extremities are more severely affected than the lower extremities.
Spastic quadriplegia Patients in this group present with spastic paralysis of both upper and lower extremities along with the trunk axial muscles. Even the muscles of the face are affected, making the child very disabled.
3.2 Cerebral palsy with dance or agitation
About 6% of cerebral palsy patients have this type. The dyskinesia is characterized by erratic changes in muscle tone (increase and decrease). Children often have abnormal movements that cannot be controlled. These movements have a slow rhythm, the amplitude is sometimes wide like dancing, but the child is not aware of this. Due to abnormalities in movement control, the patient has difficulty with normal movement posture, the muscles of the face and tongue are also affected, making it difficult for the child to suckle, swallow, and speak.3.3 Cerebral palsy ataxia
Ataxia accounts for about 6%. In this form, postural balance and coordination are affected, the child has difficulty controlling the wobbly gait, the lumbar region, or swinging. Poor motor coordination makes it difficult for children to perform movements that require rhythm, such as clapping their hands to the beat or writing letters.
3.4 Combined cerebral palsy
Children with combined cerebral palsy often combine 2 of the above types of cerebral palsy, often a combination of spasticity and playfulness, these cases are often severely disabled.Classification by severity:
Mild cerebral palsy Moderate severe Cerebral palsy Severe cerebral palsy
4. Early detection signs of children with cerebral palsy
When born, do not cry immediately or cry weakly. After giving birth, they are usually soft and do not move. Head drooping, unable to lift.

Difficulty holding, bathing, changing clothes for children because young people are stiff Convulsions: unconsciousness, foaming at the mouth Slow to hold head and neck, slow to roll, sit, crawl... Has a disability in using a table Inner hand grasps and performs activities Doesn't recognize mother or loved ones, slows early communication skills Doesn't turn head to respond to sounds, colored toys, doesn't look mother, loved ones Don't know listens to conversation, shows affection, does not turn head to sound Does not show facial expressions, does not use eyes to show pleasure Sucking, sucking difficulty, or choking on milk Or drooling, wheezing, increased nasopharyngeal secretions. .. There are superficial sensory disturbances such as heat, cold, pain Other manifestations: Cross-eyed, drooping eyelids, decrease, loss of vision, hearing loss, mouth distortion... Cerebral palsy is a complex disease, Due to many causes, diverse disease forms, treatment is still difficult. Understanding the causes of diseases helps us to take proactive preventive measures, and at the same time, early detection and timely intervention.
Vinmec Times City International General Hospital has applied stem cell method to successfully treat many cases of cerebral palsy that seemed to have lost all hope. The whole process of stem cell transplantation for cerebral palsy at Vinmec is performed very closely, ensuring safety in accordance with international standards. All surgeries are performed by leading experts and doctors with modern machinery and medical equipment.
In addition, Vinmec has also developed a standard transplant procedure so that it can share experiences with colleagues, creating more opportunities for treatment for children with cerebral palsy across the country.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.














