This is an automatically translated article.
Post by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
The drugs Nifedipine, Botox ® and GTN may improve flow through the sphincter of Oddi and minimize symptoms of sphincter of Oddi disorder, but efficacy remains to be demonstrated in sufficiently large, randomized and have a witness. Therefore, endoscopic sphincterotomy remains the treatment of choice for a number of patients correctly diagnosed with sphincter of Oddi disorder.
1. Overview of the sphincter of Oddi . disorder
The sphincter of Oddi is a muscular valve that opens and closes, allowing digestive juices, bile, and pancreatic juice to flow properly through the ducts that lead from the liver and pancreas to the small intestine. These digestive juices are necessary for the digestive process.When the sphincter of Oddi is not working properly, it will not open as needed. There is an actual obstruction at the sphincter level, possibly due to fibrosis, inflammation, or increased sphincter tone. This prevents bile and pancreatic juice from flowing properly to the small intestine, leading to prevention of digestive juices that can cause severe pain in the abdomen.
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD) is a term used to refer to a variety of biliary, pancreatic, and liver disorders caused by constriction, tightening, and dilation of these valves at inappropriate times.
There are two types of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD). One case occurred when digestive juices refluxed back into the bile ducts in the liver, causing “biliary dysfunction”. The other type occurs in the pancreas, causing an inflammation known as "pancreatitis".
These two types of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction can be divided into three categories. With type I, the patient has pain, abnormal blood test results, slow contrast drainage during ERCP, and abnormal findings on imaging (dilated common bile duct and dilated pancreatic duct for type I). With type II, the patient has pain and only one or two of the previous criteria. With type III dysfunction, with no obvious laboratory findings or abnormalities, the only sign of a problem is abdominal pain.
It is more difficult to diagnose type III sphincter dysfunction of Oddi than other types and can be more difficult to treat, as the proportion of patients who improve after therapies is lower.
2. Treatment of sphincter of Oddi disorder with drugs
Some exogenous agents relax the sphincter of Oddi, reducing its pressure and resistance. This includes calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, Botox®, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), and somatostatin.
Nifedipine has been shown to reverse opiate-induced effects on the sphincter of Oddi and improve pain associated with sphincter of Oddi disorder in a short-term study. Injection of Botox® into the sphincter of Oddi via sclerotherapy needles resulted in a 50% reduction in sphincter pressure over 4 months followed by a 50% improvement in bile flow in two patients with post-cholecystectomy pain and hypertension. sphincter of Oddi force. GTN has been used to assist in the removal of common bile duct stones formed without endoscopic dilatation or endoscopic papillary resection and to reduce both the basal sphincter of Oddi pressure as well as the amplitude and frequency of the sphincters. sphincter of Oddi contractions in a controlled, non-randomized clinical trial. Intravenous somatostatin has been shown to reduce mean sphincter of Oddi basal pressure in patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis.
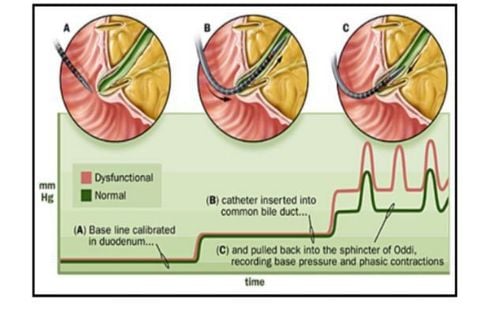
3. Treatment of sphincter of Oddi disorder by procedure Non-drug treatment for sphincter of Oddi disorder is commonly used, especially endoscopic sphincterotomy for patients with biliary sphincter of Oddi disorder. 1 and 2 and pancreatic sphincter of Oddi disorders. Analgesia has been demonstrated in 90% of patients with biliary sphincter of Oddi type 1 and 70% of patients with type 2. However, it is ineffective and may be harmful in type 3 patients. predictor and intervention in sphincter of the Oddi dysfunction trial is a landmark study for the treatment of type 3. This was a multicenter, sham-controlled, randomized trial in The patient had post-cholecystectomy pain, no imaging abnormalities or laboratory studies, and no prior sphincter of Oddi treatment. Participants underwent sphincterotomy or pseudosphincterotomy because of abdominal pain. The investigators concluded that performing sphincterotomy in patients with sphincter of Oddi type 3 was ineffective. Therefore, endoscopists are transitioning to performing sphincterotomy in these patients.
4. Conclusion Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction denotes impaired fluid flow through the sphincter of Oddi, either due to fixed stenosis or disordered muscle control (dyskinesia). Gallbladder function appears to play an important role in the sphincter of Oddi mechanism and patients without a gallbladder are more likely to have sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Other potential contributing factors include female gender, hypothyroidism, irritable bowel syndrome, pre-existing pancreatitis, and exogenous medications. The data demonstrating the association between opiates and sphincter of Oddi disorders are clear and reproducible. The clinical syndromes that result, especially in patients after cholecystectomy, include abdominal pain accompanied by abrupt but reversible elevations of liver enzymes as well as acute pancreatitis. Different opiate agents appear to have different effects on basal and phased contractions of the sphincter of Oddi. While exogenous mu opioid agonists negatively affect flow through the sphincter of Oddi. Although there is some evidence that nifedipine, Botox ® and GTN may improve flow through the sphincter of Oddi and minimize it sphincter of Oddi symptoms, but the efficacy of these agents remains to be demonstrated in sufficiently large, randomized, controlled trials. Endoscopic sphincterotomy remains the treatment of choice for a number of patients correctly diagnosed with sphincter of Oddi disorder. However, increased caregiver awareness of the risk factors for sphincter of Oddi disorder offers opportunities for diagnosis and intervention, including avoidance of potential precipitating agents, especially in case without gallbladder.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References:Elham Afghani. Sphincter of Oddi Function and Risk Factors for Dysfunction. Front Nutr. 2017; 4: 1. Williamson JB. Effect of morphine after cholecystectomy. Br Med J (1941) 1:215.10.1136/bmj.1.4179.215-a [CrossRef] [Google Scholar] Smyth MJ. Exploration of the common bile duct for stone. Drainage with T-tube and cholangiography. Br Med J (1941) 1:111–26.10.1136/bmj.1.4177.111 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar] Eichhorn EP, Jr., Boyden EA. The choledochoduodenal junction in the dog; a restudy of Oddi's sphincter. Am J Anat (1955) 97:431–59.10.1002/aja.1000970305 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]