This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International Hospital
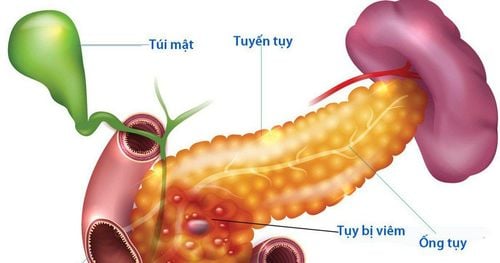
Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation that lasts for a short time. The severity can range from mild discomfort to a serious life-threatening development. Most people with acute pancreatitis make a full recovery after being treated.
1. What is increased intra-abdominal pressure?
Intra-abdominal pressure is the dynamic equilibrium pressure in the abdominal cavity, increasing with inspiration and decreasing with expiration. Normally, intra-abdominal pressure ranges from 0 to 5 mmHg but can be higher in obese people.
Increased intra-abdominal pressure is the value of abdominal pressure greater than or equal to 16 cmH2O on at least 3 measurements spaced 4-6 hours apart.
2. Causes of acute pancreatitis
The most common cause is people abuse alcohol excessively. Mechanical causes: Gallstones, pancreatic stones are the second cause. Metabolic disorders: Hypertriglyceridemia is an increasingly common cause in Vietnam. Hypercalcemia: such as thyroid tumor, hyperparathyroidism... Acute traumatic pancreatitis: After endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatitis. After surgery on nearby organs. After abdominal trauma. Due to allergies when eating foods that are not suitable for the body, drugs, chemicals. Due to overeating, the pancreas is overactive, leading to strong stimulation, secreting an excessive amount of fluid and stagnation in the pancreatic duct. On the other hand, causing severe vasodilatation reflex, especially in a meal with a lot of alcohol, in obese, elderly patients with underlying cardiovascular disease, it is difficult to correct vasomotor disorders after excessive meals and acute pancreatitis. easy to happen. Acute fatty liver in pregnancy. Due to infection: mumps, viral hepatitis, roundworm. Due to drugs: sulfonamide, 6MP, furosemide, ethanol, oestrogen... Linkage pathology: systemic lupus erythematosus, necrotizing vasculitis, Schonlein Henoch...

3. Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
Signs of acute pancreatitis include the following:
Abdominal pain: As the most prominent sign, patients often appear suddenly in the epigastrium, which can spread to the chest, to two networks. flanks on both sides, obliquely behind. Severe abdominal pain that lasts for hours, continuous, may hurt after eating. Sometimes the onset is spontaneous. Vomiting: This is a common symptom in almost every patient, initially vomiting food, then vomiting fluid, after vomiting, the patient may or may not have pain relief. Constipation of defecation: Due to the functional bowel paralysis, the patient does not defecate, does not defecate, the abdomen is distended and full of discomfort. Shortness of breath: Due to pain, pleural effusion, pleural effusion.
When examining the doctor, the patient has the following symptoms:
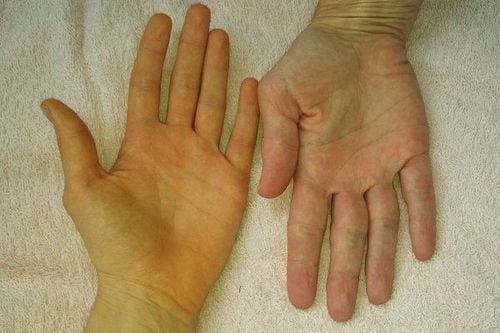
Fever: usually has a mild fever, possibly high fever because of cholangitis caused by stones, worms or extensive pancreatic necrosis. Pulse, blood pressure: Mild acute pancreatitis: the general condition is usually not serious, the patient is tired but awake, the pulse, blood pressure is stable, no shortness of breath. Severe acute pancreatitis: there may be shock, sweating, cold limbs, paleness, mental sluggishness, rapid pulse, low blood pressure, the patient may panic or be agitated or vice versa lying down. tired eyes. Abdominal distension There is abdominal wall reaction or spasticity due to pancreatic juice causing peritonitis, in addition to bleeding, edema, in the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneum. Jaundice is seen in patients with biliary tract disease, especially common bile duct stones
4. Diagnosis
The patient is diagnosed by the doctor for timely treatment with the main signs:
Sudden, severe epigastric pain, stabbing pain in the back accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Blood tests showed blood Amylase and/or lipase elevated more than 3 times the normal value. Serum cytokines increased. Imaging: There is a typical picture of acute pancreatitis on ultrasound or CT scan.
5. Complications of acute pancreatitis
The most dangerous acute pancreatitis complication for patients is multi-organ failure, which is the highest cause of death. The more severe acute pancreatitis with organ failure, the higher the risk of death. Some other local complications such as bleeding, pancreatic abscess and pancreatic pseudocyst.
6. Treatment of acute pancreatitis
6.1. General principles Active medical treatment, close monitoring to have indications for timely surgical intervention.
6.2. Conservative treatment The first stage of acute pancreatitis is edema, medical treatment of patients at this stage is largely successful: even mild edematous acute pancreatitis can be treated. without having to have surgery. Conservative treatment includes:
Reduce pancreatic secretion: Atropin, Sandostatin... Pain relief for the patient. Anti-infective. Emergency resuscitation against shock, respiratory, circulatory, endocrine, electrolyte compensation and other systemic disorders. Fasting, parenteral nutrition. Closely monitor the patient's progress for emergency surgery when indicated by the doctor.
6.3. Surgical intervention Surgery is required in the following cases:
The disease is progressive, with signs of threatening necrosis of the pancreatic tissue, clinically found: Increased toxicity. Pain does not decrease, abdominal muscle reactivity increases. Blood and urine amylase tests did not decrease or even increased despite aggressive medical treatment. It is possible that the blood and urine amylase decreased, but the toxicity increased, the reaction of the abdominal wall increased, which is a bad sign, showing that the pancreatic cells are severely necrotic with a large area. Acute pancreatitis due to biliary tract disease: biliary obstruction with acute pancreatitis. There are doubts in the diagnosis: suspicion of gastrointestinal perforation, suspicion of necrotizing cholecystitis, suspicion of intestinal obstruction (exploratory surgery). Complicated acute pancreatitis: hemorrhagic necrosis, pancreatic abscess.
7. Disease prevention, living mode
Limiting alcohol intake. Go to the doctor for early detection and treatment of gallstones, pancreatic stones. Patients with hypertriglyceridemia need regular treatment and reasonable dietary control. Maintain weight by exercising daily, regularly, fit the body. A happy and comfortable life to avoid stress by practicing yoga and meditation.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.