This is an automatically translated article.
Thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease, also known as immune thrombocytopenic purpura, is a disease belonging to the immune group, that is, the state of thrombocytopenia caused by antibodies that are able to self-produce and attach to the blood. Platelet membrane antigens cause symptoms of thrombocytopenia in the peripheral blood. The disease needs to be detected and treated properly to avoid causing some dangerous complications.
1. How much platelet reduction is dangerous?
Blood is defined as a fluid in the body, consisting of two main components, plasma and cells. Among cells such as red blood cells and white blood cells, platelets play an important role in blood clotting, if the body has a wound, then platelets will stop bleeding from the wound. In clinical practice, there are many cases where the number of platelets in the blood decreases due to many different causes, causing many complex diseases, including thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease.
When the amount of platelets in the blood decreases, there will be a dysfunction of hemostasis when there is a certain damage to the blood vessels appearing in the body. A person with a platelet count below 150000 cells/mL will be diagnosed with thrombocytopenia, which poses certain dangers to the patient's body.
Lượng tiểu cầu giảm mạnh ảnh hưởng đến chức năng đông máu
2. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombocytopenic purpura, also known as immune thrombocytopenic purpura, is a disease caused by the destruction of platelets in the peripheral blood, reducing the number in the endothelial reticular system with the underlying cause. caused by antiplatelet autoantibodies.
Normally, if a foreign agent enters the human body, such as a bacteria, virus or parasite, white blood cells will produce antibodies to fight this invasion. But for patients with autoimmune diseases such as immune thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease, the body will have abnormalities, errors when recognizing an organ in the body as an invading foreign agent, so it automatically produce antibodies to fight against the platelets in the blood.
The mechanism of action of these antibodies is explained that the autoantibodies will attach to platelet cells, causing platelets to break down in the spleen, leading to a lower number of platelets in the blood. , which causes bleeding and does not form clots when the patient has extremely mild effects. In addition, in some cases of immune thrombocytopenic purpura without the presence of autoantibodies, it is the case that T lymphocytes are responsible for this thrombocytopenic purpura.

Tế bào lympho T là nguyên nhân gây xuất huyết giảm tiểu cầu miễn dịch
Thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease can occur in adults or children, in which the rate of thrombocytopenic purpura is higher in children, especially between the ages of 2 and 5 years old. In addition, when considering the issue of gender, the rate of women infected is often higher than that of men. This disease can be discovered by accident when performing blood tests or has some symptoms such as easy bleeding, which can be mild or severe, specific manifestations such as the appearance of punctate bleeding under the skin, bruising. , bleeding in the brain, bleeding gums, nose bleeding, signs of menorrhagia, hematuria, vomiting blood,...
Especially, when a patient has thrombocytopenia bleeding, anemia will occur. In addition, including signs such as pale skin, pale mucous membranes, headache, dizziness... In addition, to confirm whether a patient has immune thrombocytopenic purpura or not, clinical test results readiness is extremely important.
Specifically, when performing a total peripheral blood cell analysis test, the platelet count in the blood will decrease below 100G/L, red blood cells and hemoglobin may also decrease if bleeding is heavy, white blood cells and white blood cells may also decrease. in the normal value.
For the myelogram, patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura patients will have an increased or within normal range of myelocytic densities, platelets will also be elevated or normal, with no presence of cells. malignant. In addition, when the bleeding time test will take longer than usual, the clot is unlikely to contract or may contract but not completely. In particular, testing for specific antibodies against GPIIb-IIIa in platelets or serum will give a positive result. The treating physician needs to combine the different laboratory findings and the clinical symptoms present in the patient to rule out other conditions, thereby confirming the diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
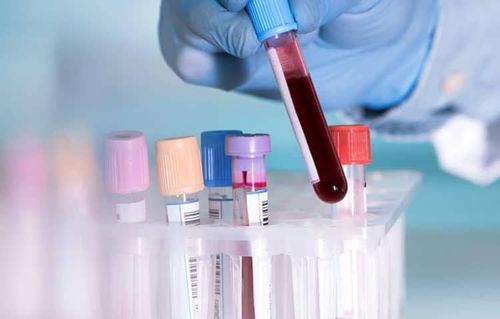
Xét nghiệm kháng thể chẩn đoán bệnh xuất huyết giảm tiểu cầu
3. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura treatment regimen
Depending on the level of bleeding of each patient, the doctor will have appropriate immune thrombocytopenic purpura treatment regimens. For thrombocytopenic purpura in children, there is almost no treatment in most cases. As for adults, the common treatment in those regimens is steroids, besides intravenous immunoglobulins can be used for patients if steroids are not effective. For more severe cases, patients may need to undergo splenectomy if both drugs are ineffective. However, there are also patients in the group of adults who do not need treatment for which thrombocytopenic purpura is automatically cured
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura is an autoimmune disease common to everyone, although The most common occurrence is thrombocytopenic purpura in children. Thrombocytopenia hemorrhagic disease needs to be clinically examined, performed paraclinical tests and assessed the extent to be able to give the most appropriate treatment for the patient.
For detailed advice on immune thrombocytopenic purpura, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Diagnosis and treatment of Immune thrombocytopenic purpura Symptoms and complications of Immune thrombocytopenia Hemorrhagic fever How do platelets decrease?