This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Doctor Le Xuan Luat - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Vietnam is a tropical country, dengue fever is a common disease in our country. Every year hundreds of thousands of dengue cases are recorded, as in 2019, more than 300,000 dengue cases were reported. Dengue is common in most provinces of the country, concentrated in the Central Highlands, the South and the North. The disease often increases in the rainy season, the months of August, September, October and November every year often have a high number of dengue cases.
Dengue is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted mainly by the Aedes agypti mosquito. Dengue virus has 4 serotypes, designated Den-1, Den-2, Den-3, and Den-4. All four of these serotypes are circulating in Vietnam. Typical symptoms of dengue fever are high fever, continuous fever, and fatigue.
1. Clinical signs that need attention in people with dengue fever
The average incubation period in humans is 3-7 days. The main symptoms in people infected with dengue such as:
Headache, body aches, pain in the eye socket. High fever, possibly continuous fever. Tired a lot. Anorexia. Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting. Rash, petechiae under the skin. Bleeding tooth. Early menstrual period, more than usual.
When having the following warning signs, dengue patients should seek medical attention immediately:
Abdominal pain, increased pain Vomiting a lot

Người bệnh nên nhanh chóng đến cơ sở y tế nếu thấy triệu chứng trở nặng
Mucosal bleeding Fluid retention Confusion Confusion Hepatic enlargement >2cm On tests: hemoconcentration, thrombocytopenia
2. Liver damage in dengue patients
Patients with dengue often have impaired liver function, manifested by elevated liver enzymes, AST and ALT. The mechanism by which dengue virus causes liver damage has not been fully elucidated. However, through histopathology, autopsies have proven that liver cells are the target of dengue virus.
Dengue virus penetrates inside liver cells, causing liver cell rupture. The mechanism of hepatocyte rupture is thought to be by pathways such as the body's immune response, cytokine storm, cytotoxicity, and mitochondrial inactivation. The clinical manifestations of these things make the patient tired, and the liver enzymes are elevated in laboratory tests.
Virus Dengue xâm nhập vào các tế bào và làm tổn thương gan
3. Mechanism of action of Paracetamol
The most commonly used antipyretic is Paracetamol. Paracetamol has antipyretic and analgesic effects. 90% of Paracetamol is metabolized by the liver. In the liver, Paracetamol is metabolized through sulfation, Glucuronidation cycles.
A small part is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system to the alkylating product, NAPQI. Too much accumulation of NAPQI, not eliminated by the kidneys, causes hepatotoxicity, hepatocellular necrosis, and hepatocyte rupture. Subclinical manifestations are increased liver enzymes, there are patients with liver enzymes increased several thousand units, and need dialysis to improve liver function, body function.
4. Paracetamol overdose
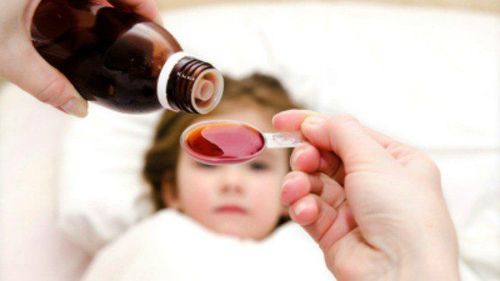
Paracetamol is a commonly used pain reliever and fever reducer. Medicines are easily purchased at pharmacies without a prescription. This contributes to drug abuse. The usual dose for adults is 2-3 grams/day. Dosage for children, depends on weight, age. The interval between two consecutive doses is at least 4-6 hours in adults, in children up to 10-12 hours.
Paracetamol là thuốc giảm đau hạ sốt được bán không cần đơn
Common causes of overdose are headache, body aches, persistent high fever. Dengue fever itself can cause liver damage. Paracetamol overdose increases the risk of more severe liver damage. DHF often causes fatigue.
Liver damage caused by Paracetamol also makes the patient more tired. Therefore, taking too much Paracetamol does not reduce the disease, but on the contrary, aggravates the disease, causing complicated complications.
Patients need to take Paracetamol under the guidance of doctors, medical staff at medical examination and treatment facilities. Do not arbitrarily use Paracetamol at home.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: NCBI