This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the spine using radio waves, a magnetic field and a computer. It produces clear, detailed images of the spine and surrounding tissues. An MRI does not use radiation and may require an injection of a gadolinium contrast agent. Gadolinium is less likely to cause allergic reactions than iodine contrast agents.
1. What is an MRI of the spine?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive test used to diagnose medical conditions.
MRI uses a strong magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to create detailed images of internal body structures. An MRI does not use radiation (X-rays).
Detailed MR images allow doctors to examine the body and detect diseases. The images can be viewed on a computer screen. They can also be sent electronically, printed or copied to a CD, or uploaded to a digital cloud server.
Currently, MRI is the most sensitive imaging test available for the spine.
2. What are the commonly used cases of this method?
MR imaging is used to evaluate or detect:
Spine anatomy and alignment. Birth defects in the vertebrae or spinal cord. Injury to bones, discs, ligaments, or spinal cord. Disc and joint disease. Both are frequent causes of severe lower back pain and sciatica (back pain that radiates down the legs). Compression or inflammation of the spinal cord and nerves. Infection of the vertebrae, discs, spinal cord, or its covering (meninges). Tumors in the vertebrae, spinal cord, nerves, or surrounding soft tissues. A spinal MRI is also used to help plan procedures such as decompression of a pinched nerve, spinal fusion, or steroid injections. Steroid injections relieve pain and are usually done with x-ray guidance. MRI of the spine detects other possible causes of back pain such as compression fractures and bone swelling. It is also used to monitor changes in the spine after surgery, such as scarring or infection.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ (MRI) là một xét nghiệm không xâm lấn
3. How should I prepare?
You may need to wear a hospital gown. Or, you may be allowed to wear personal clothing if it's loose and doesn't have metal fasteners.
Instructions for eating and drinking before an MRI vary between specific exams and settings. Unless your doctor says otherwise, take your food and medicine as usual.
Some MRI tests use contrast injection. You may be asked if you have asthma or are allergic to iodine contrast agents, medications, foods, or the environment. MRI exams often use a contrast agent called gadolinium. Gadolinium may be used in patients with an iodine contrast allergy. A patient is less likely to be allergic to gadolinium contrast than to iodine contrast. However, even if the patient has a known allergy to gadolinium, it may be used after appropriate premedication. For more information on allergic reactions to gadolinium contrast, please refer to ACR Guidelines on Contrast Media.
Tell the technician or radiologist if you have any serious health problems or have recently had surgery. Some conditions, such as severe kidney disease, may require the use of specific types of gadolinium contrast that are considered safe for patients with kidney disease. You may need blood tests to determine if your kidneys are working properly.
Infants and young children often require sedation or anesthesia to complete the MRI examination without movement. This depends on the child's age, intellectual development, and the type of test. Sedation may be provided at many facilities. A specialist in pediatric sedation or anesthesia should be available during the scan for your child's safety. You will be told how to prepare your child.
Some facilities may have staff members who work with children to help avoid the need for anesthesia or sedation. They prepared the children by showing them a dummy MRI scanner and playing noises they might hear during the exam. They also answer any questions and explain procedures to reduce anxiety. Some facilities also provide goggles or headphones so the child can watch the movie while the scan is being done. This keeps the child still and allows for good quality images.
Leave all jewelry and other accessories at home or remove them prior to the thoracic mri. Metal and electronic items can interfere with the magnetic field of the MRI unit and they are not allowed in the exam room. They can cause burns or become harmful objects in the MRI scan room. These items include:
Jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids, all of which can break Pins, hairpins, metal zippers and similar metal items, can do image distortion MRI Dental equipment Pens, pocket knives and eyeglasses Earrings, metal objects on the body Cell phones, electronic watches and tracking devices.
MRI cột sống phát hiện các nguyên nhân có thể khác của đau lưng
In most cases, thoracic spine magnetic resonance imaging is safe for patients with metal implants, with some exceptions. People with the following implants may not be scanned and should not enter the MRI scanning area without first being evaluated for safety:
Some cochlear (ear) implants Certain types of clips are used for aneurysms brain arteries Some types of metal coils are placed in blood vessels Some older defibrillators and pacemakers Tell the technician if you have medical or electronic devices in your body. These devices may interfere with the exam or may pose a risk. Many implantable devices will have a book to explain the MRI risks for that particular device. If you have the book, bring it to the person who booked your appointment. MRI cannot be performed without confirmation and documentation of implant type and MRI compatibility. You should also bring any information booklets related to your exam in case the radiologist or technician has any questions.
If there is any question, X-ray can detect and identify any metal object. Metal objects used in orthopedic surgery usually pose no risks in an MRI. However, a recently placed artificial joint may require the use of another imaging test.
Tell the technician or radiologist about any shrapnel, bullets, or other metal that may be in your body. Foreign objects near and especially in the eye are important because they can move or heat up during the scan and cause blindness. The dye used in tattoos may contain iron and may heat up during an MRI scan. This is rare. Fillings, braces, eyeshadows and other cosmetics are generally unaffected by magnetic fields. However, they can distort images of the face or brain area. Tell the radiologist about them.
Anyone accompanying the patient into the clinic must also be examined for metal objects and implanted devices.
4. What does the device look like?
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a round magnet. You will lie on a table that slides into the center of the magnet.
Some MRI units, known as short drill systems, are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround you. Some newer MRI machines have larger diameter bores, which may be more comfortable for larger patients or those with claustrophobia. "Open" MRI units are opened on either side. They are particularly useful for examining older patients or those with claustrophobia. Open MRI units can provide high-quality images for a variety of tests. Some tests cannot be done using an open MRI. For more information, consult the performing radiologist.
Đơn vị MRI truyền thống là một ống hình trụ lớn được bao quanh bởi một nam châm tròn
5. How does the testing process work?
Unlike X-ray examinations and computed tomography (CT) scans, MRI does not use radiation. Instead, radio waves rearrange the hydrogen atoms that naturally exist in the body. This does not cause any chemical changes in the tissues. When the hydrogen atoms return to their usual alignment, they emit different amounts of energy depending on the type of body tissue they are in. Scanners capture this energy and create visualizations of how to use it.
In most MRI units, a magnetic field is created by passing an electric current through a coil. Other coils are placed within the machine and, in some cases, placed around the part of the body being imaged. These coils send and receive radio waves, generating signals that are detected by the machine. The electric current must not come into contact with the patient.
The computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each showing a thin slice of the body. These images can be studied from different angles by radiologists.
MRI can tell the difference between diseased and normal tissue better than X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasound.
6. How is the procedure done?
Thoracic spine mri can be done on an outpatient basis.
You will be positioned on a moving exam table. Straps and washers can be used to help you stay still and maintain your position.
Devices containing coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves can be placed around or next to the area of the body being scanned.
The MRI scan usually involves several runs (sequences), some of which can last several minutes.
Depending on where your symptoms are, only part of the spine may be scanned. For example, the cervical (neck), thoracic (thoracic) or lumbar (lower) spine. Gadolinium contrast agents may be used when looking for infections, tumors, or recurrent disc problems after surgery.
If contrast is used, the doctor, nurse, or technician will place an intravenous catheter (IV line) into a vein in your hand or arm that will be used to inject the contrast.
You will be placed on the magnet of the MRI unit. The technician will perform the test while working at a computer outside the room.
Once the examination period is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist examines the images in case of further need.
Your IV line will be erased once the scan is over.
The whole process is usually completed within 30 to 60 minutes. This will depend on whether part or all of the spine is scanned. If contrast material is used, multiple images will be taken after the injection. This will add another 15 to 20 minutes to the total scan time.
Chụp mri cột sống lưng có thể được thực hiện trên cơ sở ngoại trú
7. What will be done during and after the test?
Most MRI exams are painless. However, some patients experience discomfort while standing still. Others may feel tight (suffocating) while in the MRI scanner. Scanners can be noisy. Sedation can be arranged for anxious patients, but less than one in 20 require it.
It is normal for the area of your body to be photographed to feel some warmth. If you feel any discomfort, tell the radiologist or technician. It is important that you remain completely still while the images are being taken. This is usually only a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. You will know when the image has been recorded because you will hear and feel loud or loud sounds. They are generated when coils that generate radio waves are activated. You will be provided with earplugs or headphones to reduce the sound produced by the scanner. You can relax between sequences of images. However, you will be asked to stay in place without moving as much as possible.
You will usually be alone in the shooting room. However, the technician will be able to see, hear and talk to you at all times using the two-way intercom. Many facilities allow a friend or parent to stay in the room if they have also been screened for safety.
Children will be given earplugs or appropriately sized headphones during the shoot. The MRI scanner is air-conditioned and well-lit. Music can be played through headphones to help the time pass faster.
In some cases, an IV injection of contrast agent may be given before images are obtained. The IV needle may cause you some discomfort and you may experience some bruising. There is also a very small chance of skin irritation at the IV tube site. Some patients may have a temporary metallic taste in the mouth after contrast injection.
If you don't need sedation, there's no need for a recovery period. You can resume your usual activities and normal diet right after your MRI. On very rare occasions, a few patients experience side effects from the contrast material. These may include nausea, headache, and pain at the injection site. Very rarely, patients develop urticaria, itchy eyes, or other allergic reactions to the contrast material. If you have symptoms of an allergic reaction, tell the technician. A radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance.
8. Who will report the results and how do you get it?
A radiologist, a doctor trained to supervise and interpret the X-ray process, will analyze the images. The radiologist will send a signed report to your primary doctor or referring physician, who will share the results with you.
Further imaging studies may be needed. If so, your doctor will explain why. Sometimes a follow-up is done because of an underlying abnormality that requires further evaluation with additional views or a special imaging technique. A follow-up test may also be done to see if there are any changes in the abnormality over time. Follow-up testing is sometimes the best way to see if treatment is working if abnormalities or changes have occurred.
Máy quét MRI có máy lạnh và đủ ánh sáng
8. How do the benefits compare to the risks?
Benefits:
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not involve radiation exposure. MR images of the spine are clearer and more detailed than those obtained with other imaging methods. MRI can show spinal abnormalities, injuries, and diseases that may not be seen with other methods. MRI is the best method available to visualize the spinal cord and nerves. MRI can detect abnormalities that may be obscured by bone using other imaging methods. The gadolinium MRI contrast agent is less likely to cause allergic reactions than the iodine-based contrast materials used for x-rays and CT scans. MRI is useful for evaluating spinal cord injuries. It helps diagnose or rule out acute spinal cord compression when physical examination reveals muscle weakness or paralysis. MRI is the best method for evaluating ligament injuries. An MRI can detect subtle changes in the spine that could be an early sign of an infection or tumor. MRI is more sensitive than CT scans for evaluating tumors, abscesses, and other soft tissue masses near the spinal cord. MRI is the preferred method for evaluating potential complications of surgery, including bleeding, scarring, infection, and re-occurrence of herniated discs. Risks:
An MRI test poses almost no risk to the normal patient when appropriate safety guidelines are followed. If sedatives are used, there is a risk of using too much. However, your vital signs will be monitored to minimize this risk. Strong magnetic field is not harmful. However, it can cause implanted medical devices to malfunction or cause image distortion. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is a recognized, but rare, complication associated with injection of gadolinium contrast. It usually occurs in patients with severe kidney disease. Your doctor will carefully evaluate your kidney function before considering contrast injection. There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if the contrast agent is used. Such reactions are usually mild and controlled with medication. If you have an allergic reaction, your doctor will be available to assist immediately. The manufacturers of IV contrast media say that mothers should not breastfeed for 24-48 hours after the contrast agent is administered. However, the most recent American College of Radiology (ACR) Guidelines on Contrast Media reports that studies show the amount of contrast absorbed by infants during lactation. suckling is very low.
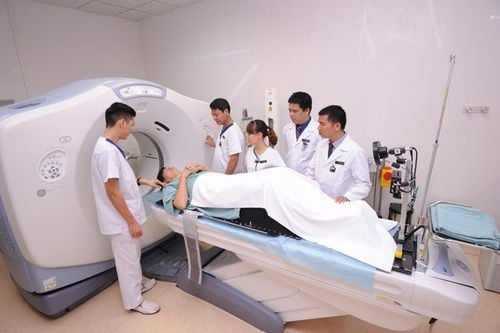
Xét nghiệm MRI hầu như không gây rủi ro cho bệnh nhân
10. What are the limitations of MRI of the spine?
High quality images depend on your ability to stay perfectly still and follow the instructions to hold your breath while the image is being recorded. If you are nervous, confused, or in severe pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during the photo shoot.
Some people with a large weight may not be suitable for certain types of MRI machines. There is a weight limit on the scanner.
Implants and other metal objects can make it difficult to get a clear picture. Patient movement can have a similar effect.
Irregular heartbeat may affect image quality. This is because some imaging techniques are based on the electrical activity of the heart.
MRI is generally not recommended for critically ill patients. However, this decision is based on clinical judgment. This is because traction devices and life support devices can distort MR images. As a result, they had to stay away from the area to be photographed. Some trauma patients, however, may need an MRI.
Although there is no reason to believe that an MRI will harm an unborn baby, pregnant women should not have an MRI exam during the first trimester unless it is medically necessary.
MRI is generally more expensive and may take longer to perform than other imaging methods. Talk to your insurance provider if you are concerned about the cost of an MRI.
In some patients, vertebral fractures may be better detected by CT scan.
Vinmec International General Hospital put into use the magnetic resonance imaging machine 3.0 Tesla Silent technology. Magnetic resonance imaging machine 3.0 Tesla with Silent technology of GE Healthcare (USA).
Silent technology is especially beneficial for patients who are children, the elderly, weak health patients and patients undergoing surgery. Limiting noise, creating comfort and reducing stress for customers during the shooting process, helping to capture better quality images and shorten the shooting time. Magnetic resonance imaging technology is the technology applied in the most popular and safest imaging method today because of its accuracy, non-invasiveness and non-X-ray use. Customers can go directly to the system. Vinmec Health System nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.