This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. Nguyen Ngoc Phuong Nam - Emergency Medicine Doctor, Emergency Department - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalHBV has 3 types of antigens HBsAg, HBeAg and HBcAg, corresponding to the 3 above antigens are 3 types of antibodies anti-HBs, anti-HBc and anti-HBe. The presence of these antigens and antibodies is important in determining the disease, the disease form as well as the course of the disease. There is now a prophylactic vaccine, which significantly reduces the number of people newly infected with HBV.
1. Overview of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B virus is a common global disease, caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The disease can be transmitted by blood, sex, and from mother to child. If the mother is infected with HBV and has HBeAg (+), the chance of transmitting it to her baby is more than 80% and about 90% of the baby will be born with chronic HBV.
Hepatitis B can have an acute course, in which more than 90% of cases are completely cured, nearly 10% turn to chronic hepatitis and the final result is cirrhosis or liver cancer.
HBV belongs to the family Hepadnaviridae, has a DNA structure. Based on the sequence of nucleotides, HBV is divided into 10 different genotypes with symbols from A to J.
2. Meaning of Hepatitis Virus Test
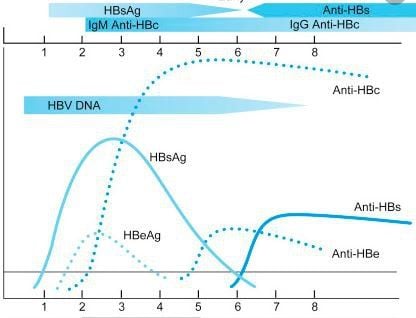
2.1 HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen) HBsAg (+) is evidence of persistent positive HBV infection, reaching high levels from 1-10 weeks and then gradually decreasing until June, then becoming negative If HBsAg (+) > 6 months, is considered chronic hepatitis B. In rare cases, HBsAg reappears in people who already have anti-HBc and anti-HBs when immunocompromised or due to use immunosuppressive drugs or chemotherapy.
2.2. HBsAb or Anti-HBs Anti-HBs appears soon after HBsAg disappears (or later, 1-10 weeks after HBs disappears; or 3 months from onset). Why there is Anti HBs: The body recognizes HBsAg as a foreign antigen → produces antibodies against the HBsAg antigen.
HBsAg (-), Anti HBs (+) test proves that you have immunity to HBV:
Hepatitis B has been cured Have been vaccinated against HBV → the body only produces anti-HBs ==> Anti-HBs is closed role in protecting the body against HBV re-infection.
2.3. HBeAg (Hepatitis B evelope antigen) HBeAg (+) appears right after HBsAg (+), HBeAg (+) for about 3 months and then disappears (because the new phase of virus penetration will increase). very strong) and with very high HBV DNA
HBeAg is not used to diagnose HBV infection, but is valuable in terms of the staging of chronic hepatitis B.
HbsAg and HBeAg (+) reflect how the virus is multiplying in the body.
2.4. Anti HBe (specific antibody against HBeAg) Anti HBe appears at the end of the acute phase (HBsAg concentration decreases, HBeAg disappears) ==> Anti HBe (+) indicates that viral replication has decreased or stopped during the acute phase. acute or acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B but is effectively treated.
Some patients with HBV still duplicating despite HBeAg seroconversion are due to HBV having a pre-core mutation called mutated HBV. This type of HBV does not produce HBeAg, although HBV still duplicates. HBV that does not mutate is called a wild type.
2.5. HBcAg (Hepatitis B core antigen - VR VGB core antibody) This antibody is located in liver cells, serological tests cannot detect it, so it is not mentioned much in the diagnosis of hepatitis B and the stages of hepatitis leading to no commercial value. But in serum HBcAg (+) when hepatocytes are destroyed.
2.6. Anti-HBc (Anti hepatitis B core - Anti-HBc core antibody) Anti-HBc begins to appear during the incubation period (from the 2nd month) and is positive for a long time ==> Depends on the time of testing which Anti-HBc reflects:
The patient is in the acute stage. The patient is a chronic carrier of the virus. People with a history of HBV infection have now recovered. ==> Anti-HBc has no role to protect the body.
In addition to specific tests as mentioned above, there are other tests to monitor and assess the status of patients infected with hepatitis B virus such as: liver enzymes (AST, ALT, GGT), hepatitis B virus levels in the blood to decide on treatment, evaluate treatment and monitor hepatitis B.
3. Conclusion
In order to conclude or provide treatment and follow-up for people infected with hepatitis B virus, doctors need to examine many times, perform specialized tests, possibly many times over time to diagnose and decide on treatment. treatment and even follow-up treatment. Patients infected with hepatitis B virus should follow up with their doctor's appointment to be monitored in the best way.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/cause liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory, subclinical; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.