This is an automatically translated article.
Usually, cases of Mast cell disease are diffuse generalized pigmentary urticaria or can be solid and papule Mast cell disease in children, which is not dangerous. It is very rare to see a pattern with a combined systemic lesion. However, adults are more likely to develop UP or diffuse vasculitis of the skin and are at risk of developing systemic Mast cell disease. And the acute form of Mast cell diffuse agranulocytosis will affect the life of children due to acute shock.
1. Is Mast Cell Syndrome (Mastocytosis) dangerous?
Mastocytosis, also known as mast cell disease syndrome, is mast cell infiltration of tissues, skin and other organs, characterized by proliferation of mast cells and infiltration of the skin , other organs, or in some cases including 2.
Mastocytosis is primarily caused by the release of mast cell mediators, including leukotrienes, histamine, heparin, and other inflammatory cytokines together. In which Histamine causes the most symptoms, including stomach symptoms.
However, organ infiltration can lead to organ dysfunction. In addition, some patients with mast cell syndrome may be associated with an activating mutation (D816V) in the gene encoding the stem cell receptor c-kit, which is a cell found in mast cells. . Thus, autophosphorylation of the receptor leads to uncontrolled mast cell proliferation.
Usually, cases of Mast cell disease are diffuse generalized pigmentary urticaria or can be solid and papule Mast cell disease in children, which is not dangerous. It is very rare to see a pattern with a combined systemic lesion.
However, adults are more likely to develop UP or diffuse vasculitis of the skin and are at risk of developing systemic Mast cell disease. And the acute form of Mast cell diffuse agranulocytosis will affect the life of children due to acute shock.
2. Classification of mast cell disease syndromes
Mast cell syndrome includes 2 types as follows:
Skin mast cell disease syndrome Skin mast cell disease syndrome is common in children and most children present with pigmented urticaria, maculopapular lesions brown distribution is localized or diffuse. Nodular and plaque-type lesions may progress and, less commonly, diffuse percutaneous mastocytosis, which is an infiltration of the skin in the absence of discrete lesions and mastocytoma.
Systemic mast cell disease syndrome Systemic mast cell disease syndrome is common in adults and it is characterized by multifocal bone marrow damage in many other organs such as the skin, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract, liver or spleen.
Systemic mast cell disease syndrome consists of inactive systemic mast cells and does not cause organ dysfunction, so this syndrome usually has a good prognosis; systemic mast cell disease associated with hematologic pathology such as myelodysplastic disorder, lymphoma ; Invasive mastocytosis, which is characterized by poor organ function and ultimately mastocytosis, can cause multiple organ failure and the prognosis is often poor.

Hội chứng bệnh tế bào mast ở da thường gặp ở trẻ em và đa số trẻ có biểu hiện mày đay sắc tố
3. Symptoms of mast cell disease syndrome
Mast cell disease syndrome often causes a variety of symptoms according to the classification of the disease. Specific symptoms are as follows:
Nodular Mast cell disease For this syndrome, there will be signs with lesions ranging from macules to papules and finally lumps, solids, many concentrated lesions. Lesions are usually yellow at first, then pink-brown and become red, with Darier's sign. In some other patients this syndrome may present with bullae.
Diffuse Mast Cell Disease This form of the disease is rare and occurs in people of all ages. Symptoms of diffuse Mast cell disease are usually the appearance of large, dark yellow skin lesions on soft, smooth, irregularly convex and convex surfaces. Lesions often appear in the skin folds, especially in the armpits and groin. After trauma, large blisters may appear, or in some cases, blisters may appear on their own.
Vascular maculopapular rash The lesions of vasodilating maculopapular rash are red or brown maculopapular accompanied by vasodilation for a long time. Lesions may be more concentrated and distributed in the trunk than in the limbs.
After rubbing trauma, urticaria often appears with a positive embossed sign, this symptom is rare but if it occurs, it often occurs in adults.
Pigmented urticaria The lesions of pigmented urticaria are yellow-brown macules, sometimes pale yellow-brown. Pigmented urticaria is usually a diffuse systemic lesion. In children, bullae may be present.
Besides, the disease often causes symptoms of swelling, this symptom often appears spontaneously or after rubbing on the skin, after drinking alcohol, taking some drugs to disrupt Mast cells.
Mast cell disease of the skin papule type Mast cell disease of the skin is papule, the symptoms of which are yellow-brown patches, in some cases dark yellow, the size is usually 2 - 5cm , the edges are clear but uneven. Darier's sign is positive, does not scab, and blisters may appear after rubbing. Mast cell disease of the skin as papules is common in children and young children.
In addition to the above signs and symptoms, other symptoms appear in patients including epigastric pain due to peptic ulcer, nausea and vomiting, chronic diarrhea, joint pain with bone pain and neuropsychiatric changes Psychiatric symptoms such as excitability, depression... Some cases of portal hypertension manifest as ascites if there is an infiltrate in the liver and spleen.
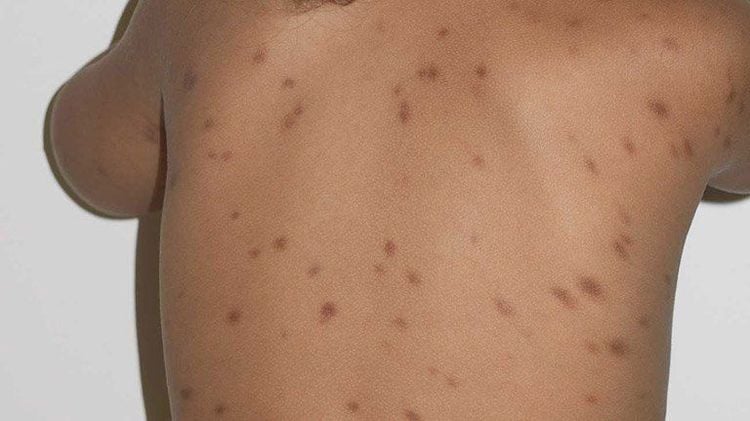
Bệnh tế bào Mast ở da dạng sẩn mảng tường xuất hiện các triệu chứng là thương tổn mảng màu vàng nâu
4. Diagnosis of Mast cell disease
Diagnosis of Mast cell disease is usually based on clinical manifestations. However, to confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy of the skin lesions and in some cases a bone marrow biopsy is required.
Tests may be done to rule out disorders that cause similar symptoms, such as an adrenal adenoma, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. These tests include:
Serum gastrin levels : This test is intended to rule out Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome in patients with ulcerative symptoms. Urinalysis: Urinary excretion of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid is intended to rule out carcinoid syndrome in patients with erythema. Tests to evaluate the concentration of free metanephrines in the blood plasma or metanephrines in the urine are intended to rule out an adrenal tumor. Assessment of mast cell-mediated concentrations: If the diagnosis is uncertain, this method and its metabolites in plasma and urine can be used for diagnosis. If laboratory tests show elevated levels of these substances suggestive of mast cell disease syndrome. Bone radiographs, GI investigations, and identification of the D816V c-kit mutation may also be used in cases where confirmation of the diagnosis is required.
5. Treatment of Mast cell disease syndrome
The treatment of the disease is usually based on the classification of the disease and the symptoms that the disease brings. Specific treatment is as follows:
Treatment of cutaneous mast cell disease H1 blockers are effective for the symptoms of cutaneous mast cell disease. However, if children have skin manifestations, no further treatment is needed because most cases resolve on their own.
For adults with skin manifestations, they are treated with psoralen in combination with ultraviolet irradiation or using topical corticosteroids once a day or twice a day. But most mast cell tumors develop spontaneously and do not require treatment.
Systemic mast cell disease For people with systemic mastocytosis, they should be treated with H1 and H2 blockers and preferably carry a syringe, a syringe of self-injecting epinephrine. Aspirin should not be used in children to control erythema because it can increase leukotriene production, which contributes to mast cell symptoms, and increases the risk of Reye's syndrome.
Besides, it is possible to use Cromolyn 200mg with a dose of 4 times a day (note, 100mg for children aged 2-12 years old and not more than 40mg/kg/day), this drug has a preventive effect. destruction of mast cells. In patients with advanced disease, interferon alfa-2b 4 million units s.c. once a week up to a maximum of 3 million units/day is recommended for the purpose of reducing bone lesions. Corticosteroids are also indicated or in some cases splenectomy to improve survival.
To improve the effectiveness of treatment, patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct an examination as soon as there are signs of Mast cell disease syndrome. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.