This is an automatically translated article.
Pericarditis is a disease that occurs in the pericardium and needs to be treated urgently because if not timely intervention will lead to rapid death due to pericardial effusion causing acute cardiac tamponade.1. What is pericarditis?
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium. Clinical forms of pericarditis include:
Acute pericarditis; Recurrent pericarditis; Constrictive pericarditis; Pericardial effusion causes acute cardiac tamponade.
2. Causes of pericarditis
Bệnh Lupus ban đỏ hệ thống có thể là nguyên nhân gây viêm màng ngoài tim
Infections: Due to viruses (Coxsackie A and B, HIV, adenovirus, Influenza,...), bacteria (tuberculosis, Staphylococcus, pneumococcus,...), fungi (Candida), parasites (amoeba, candida, ...); Autoimmune diseases: Systemic lupus erythematosus, drug-induced lupus, post-cardiac syndrome (after myocardial infarction, after cardiac surgery), rheumatoid arthritis; Tumors: Mediastinal tumors, metastases, tumors near the heart, direct invasion; Long-term thoracic irradiation; Metabolic disorders: Increased urea causes pericarditis, cholesterol deposition in the pericardium; Ischemic heart disease ; Renal failure , severe heart failure ; Consequences of anticoagulation therapy; Cardiac trauma: Thoracic trauma causes pericardial hemopericardium, ruptured thoracic duct causes pericardial chylous effusion.
3. Diagnosis of pericarditis
Chụp X-Quang ngực để tìm nguyên nhân gây ra viêm màng ngoài tim
Confirm the diagnosis of pericarditis when the patient has at least 2/4 of the following criteria:
Chest pain; ECG changes; There is pericardial rubbing; Pericardial effusion. If pericarditis is suspected or certain, the cause of the condition should be investigated using diagnostic techniques such as chest X-ray, echocardiography, cardiac enzyme testing, and electrocardiogram. ..
4. How to treat pericarditis
With idiopathic pericarditis: About 70-90% of cases will heal on their own. The treatment includes:
Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Use ibuprofen 600 - 800mg orally 3 times a day, stop taking when pain ends and usually use for 2 weeks; Hospitalization if the patient shows signs of not responding to treatment. Signs include extensive effusion, suspected pericarditis; In case of slow response or incomplete response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, additional narcotic pain relievers, colchicine or prednisone should be used at the dose prescribed by the doctor; Acute pericarditis after myocardial infarction: Occurs in 24-96 hours after myocardial infarction, the incidence is 10-15%. The treatment includes:
ASA high dose: Dose 650mg x 4 times/day; Avoid using ibuprofen; Use Colchicine and ASA if symptoms recur; Use Prednisone at a dose of 1mg/kg/day if symptoms are severe or resistant to initial treatment, not more than 4 weeks; Stop taking Heparin; Dressler syndrome: Occurs 1 to 8 weeks after myocardial infarction.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade
chụp MRI có thể chẩn đoán tràn dịch màng tim gây ép tim cấp
5.1 Pathophysiology The accumulation of fluid under high pressure compresses the chambers of the heart, while reducing the diastolic filling of both ventricles. This leads to:
Reduced stroke volume, decreased cardiac output, decreased blood pressure, shock, reflex tachycardia; Increased systemic venous pressure leads to distended neck veins, hepatomegaly, abdominal distention, and peripheral edema. 5.2 Diagnosis of pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade Symptoms: Shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, pale skin, sweating, palpitations, palpitations, abdominal bloating, dizziness, cough, dyspnea, hoarseness language,...; Clinical examination: Paradoxical pulse, signs of shock, hypotension, distended neck veins, faint heart sound; Chest X-ray : Enlarged heart shadow; Electrocardiogram: Low voltage, alternating voltage, tachycardia; Echocardiography: The inferior vena cava is dilated, not completely deflated, the mitral and tricuspid valve velocity changes with respiration, there are signs of right ventricular collapse in early diastole and right atrium systolic; Other diagnostic methods: CT scan, MRI scan, pulmonary artery catheterization, laboratory tests (leukocyte formula, cardiac enzymes, thyroid function, electrolytes,...). Note: Need to differentiate acute tamponade pericardial effusion from acute right heart failure, myocardial hypertrophy, ischemia/myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema, pulmonary embolism.
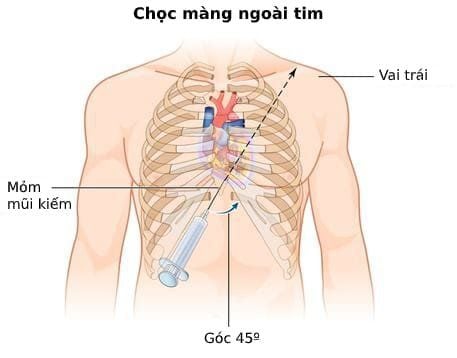
Hình ảnh mô tả quá trình chọc dịch màng ngoài tim
5.3 Management of pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade If pericardial pressure is not lowered by blood or fluid removal, the patient will die. Management measures include:
Medical treatment: Including intravenous fluids to maintain filling pressure, avoid diuretics, vasodilators, avoid slowing the heart rate. This method has a rather limited effect; Pericardial puncture under ultrasound guidance. This method is quite safe and effective for patients. However, this method also carries risks of complications such as: myocardial puncture, coronary artery puncture, arrhythmia, pneumothorax - hemothorax, hemorrhagic peritonitis, liver or gastrointestinal injury chemistry, infection, cardiac arrest, pulmonary edema,...; Pericardial drainage using a catheter; Surgical drainage of pericardial fluid in cases of recurrent or localized effusion is not safe when performing pericardial aspiration. It is necessary to treat pericarditis and pericardial effusion causing acute tamponade as quickly as possible to avoid leading to a poor prognosis, even death. To do so, when there are warning signs of these conditions, the patient should immediately notify the doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment intervention.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.