This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Tuan - Pediatrician - Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Children who are malnourished due to protein deficiency will be stunted in both physical and mental development. So, what is protein-energy malnutrition? What causes malnutrition due to lack of protein?
1. What is protein-energy malnutrition?
Protein-energy malnutrition is a condition that occurs when a diet low in protein and energy causes both physical and mental retardation.Although malnutrition is caused by protein-energy deficiency, it is not only a deficiency of protein and energy, but also a deficiency of many other nutrients combined, especially micronutrients .
Protein-energy malnutrition is common in young children, but it can also affect adolescents and adults, especially women of pregnancy and childbirth age.
2. Causes of protein energy malnutrition
Poor nutrition, lacking in quantity and quality. Children are in the period of rapid development, have high nutritional needs but do not eat enough nutrients. Improper breastfeeding or inappropriate complementary feeding. Infections cause digestive disorders and lead to malnutrition, while undernutrition reduces resistance and leads to infections. Children are underdeveloped from the time they are still in the womb.
Chế độ nuôi con bằng sữa mẹ không đúng có thể gây suy dinh dưỡng protein năng lượng
3. Types of malnutrition
3.1. Clinical classification Includes the following types of severe malnutrition:Atrophic malnutrition (Marasmus): This is a very severe form of malnutrition caused by a lack of protein and energy, which is common in clinical practice, due to a lack of diet. both protein and energy.
Atrophic malnutrition can occur in babies during the first year of life. Mothers weaning their babies too soon or giving them inappropriate foods are common causes of this type of malnutrition. At that time, children often fall into poor eating habits and encounter infections, creating a vicious cycle with diarrhea and respiratory diseases.
Kwashiorkor: This is a form of malnutrition caused by protein deficiency less common than atrophy, common in children over 1 year old, especially children in the period 1-3 years old. Rare in adults, however, in poor countries it can still occur in women during famines.
The cause of edematous malnutrition is usually due to a severe and temporary lack of protein or a slight lack of glucose (the diet is mainly based on cassava).
Edema is often associated with moderate to severe infections. Children with edematous malnutrition often have micronutrient deficiencies such as vitamin A or severe iron-deficiency anemia.
Marasmic-Kwashiorkor malnutrition: This is an intermediate form between the two and is more common than the two above in a milder degree.
3.2. Community-based classification Based on the criteria of weight and height of children compared with the standards of the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2006, there are the following types of malnutrition:
Mild malnutrition Weight: Children with a weight lower than the standards of children of the same age and sex.. Malnutrition stunting : Children with reduced body growth and chronic malnutrition, possibly due to The mother is deficient in protein and nutrition leading to fetal malnutrition. Stunting malnutrition is defined when a child has a height lower than the standards of children of the same age and sex. Malnutrition and emaciation: Children have atrophy of muscle and fat. This is an acute state of malnutrition due to its short duration. Underweight malnutrition is defined as the child's weight for height below -2SD.
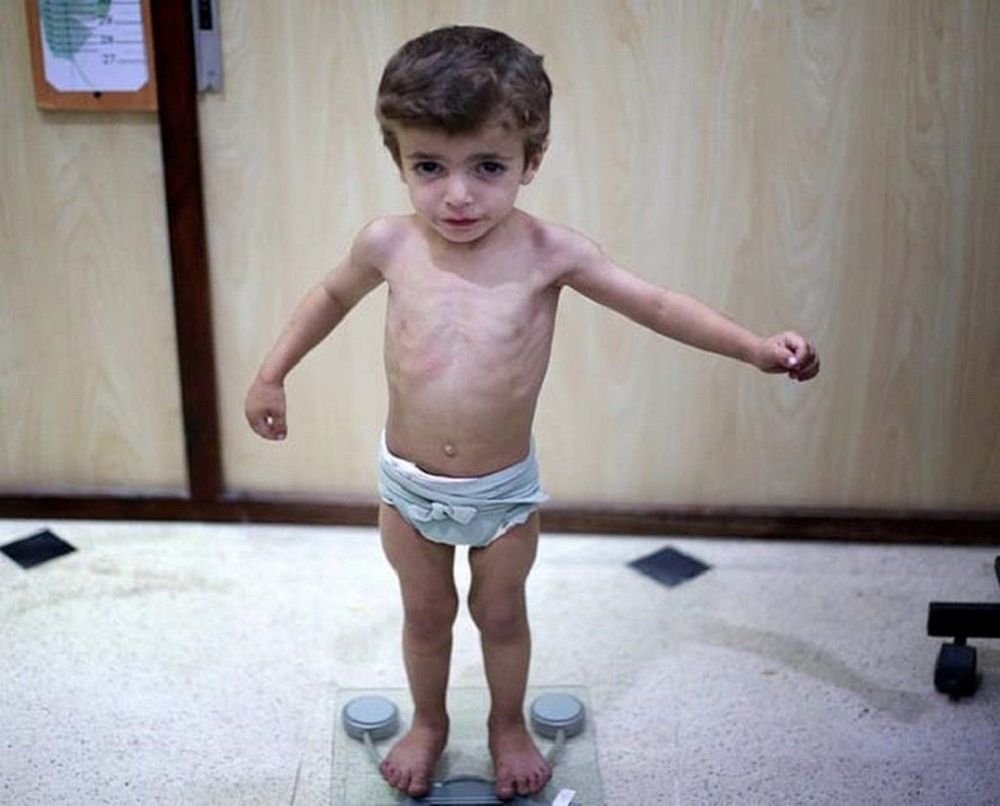
Suy dinh dưỡng do thiếu protein năng lượng gây chậm phát triển về cả mặt thể chất lẫn tinh thần.
4. Treatment of malnutrition due to lack of energy protein
Principles of treatmentTreatment of comorbidities. Change your diet accordingly. Supplement with micro-minerals and vitamins. Treatment of malnutrition due to mild or moderate protein energy deficiency
Patients are cared for, monitored and treated at home. Advice on dietary modification. Monitoring and prevention, early detection for timely treatment of infections. Monitor the patient's weight for timely advice. Treatment of malnutrition due to very severe protein-energy deficiency
For people with very severe or severe acute malnutrition and complications or comorbidities, they need inpatient treatment according to WHO guidelines .
Children who are malnourished due to lack of protein energy will show signs of retardation in physical and intellectual development, affecting their ability to study and work later. The disease can occur at any age, however, can be prevented with a proper and nutritious diet.
To prevent and improve malnutrition in children, parents should supplement with supporting products containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins to help meet meet the nutritional needs of the child. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well. Parents can also apply dietary supplements and functional foods derived from nature for easy absorption by the baby. The most important thing is that the improvement of the baby's symptoms must take place over the long term. Combining many types of functional foods at the same time or changing many types in a short time can make the baby's digestive system unable to adapt and completely not good. Therefore, parents must be really persistent with their children and regularly visit the website vimec.com to update useful baby care information.
Reference source: National Institute of Nutrition (Vietnam)














