This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Vu Thi Hanh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRC) is a technique that uses magnetic fields and RF waves to determine the concentration of metabolites in living tissue. Accordingly, magnetic resonance brain spectrum often uses metabolites containing P, Na, K, C, N, F to evaluate the concentration of metabolites to obtain a spectrum with corresponding peaks of the concentration of metabolites. in the survey area.
1. What is magnetic resonance brain spectroscopy?
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRC) is a technique that uses magnetic fields and RF waves to determine the concentration of metabolites in living tissue.
In fact, routine magnetic resonance (MRI) uses proton H+ in water for imaging, while magnetic resonance spectroscopy uses metabolites containing P, Na, K, C, N, F for evaluation. concentrations of metabolites, magnetic resonance spectra obtained spectra with corresponding peaks being the concentrations of substances in the survey area. Pathological processes associated with alteration of these metabolites.
The basic steps in surveying magnetic resonance spectroscopy are sampling, locating the measurement area, choosing a pulse sequence with TE time, suitable volume, and acquiring the spectrum. The results of the magnetic resonance spectroscopy are analyzed as line histograms. Each peak of the spectrum is characterized by frequency, height, width, and the area, height, or area below the peak represents the relative concentration of the metabolite. Each substance has a certain position on the spectrum, depending on the precession frequency. The basic metabolites commonly imaged on the spectrum are choline, creatine, NAA, lactate.
2. Purpose/meaning of spectral magnetic resonance
The purpose of magnetic resonance spectroscopy is to evaluate the concentrations of metabolites and changes that have diagnostic significance.
Specific metabolites are as follows:
NAA (N-Acetylaspartate): An indicator of density and viability of axons and neurons. NAA is reduced in most cases of brain damage. Cr (Creatine): A marker for energy metabolism in brain tissue. Cr decreases in brain tumors, infections, necrosis, acute disseminated sclerosis... Cho (Choline): Is a component of phospholipid metabolism and an indicator of tumor cell membrane proliferation. For increased in tumor, trauma, inflammation, increased osmotic pressure, loss of myelin... Lac (Lactate): Is an indicator of anaerobic sugar metabolism. Lac is elevated in hydrocephalus, hypoventilation, hypoventilation, cerebral hypoxia, acute and subacute cerebral infarction, necrosis, cystic lesions, abscesses, tumors, demyelinating, mitochondrial metabolic disorders .
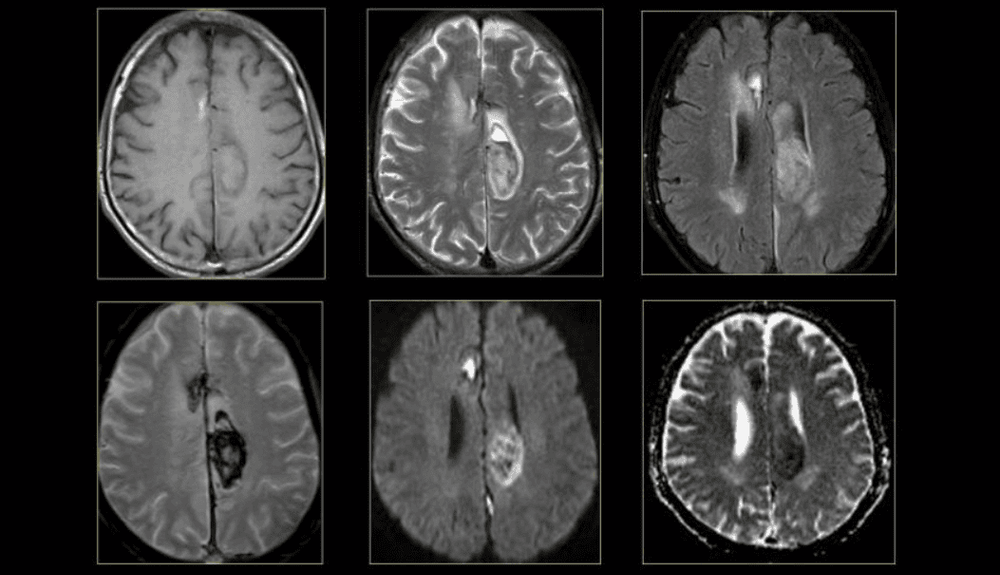
Cộng hưởng từ phổ giúp đánh giá các chất chuyển hóa như Lac (Lactate) gây nhồi máu não cấp
3. Indications/contraindications for spectral magnetic resonance?
3.1. Indications for magnetic resonance spectroscopy in brain tumors with cases
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a non-invasive technique that allows the assessment of metabolites in tumor tissue, providing information on tumor composition. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is indicated in brain tumors including: differential diagnosis of neoplastic or non-tumor lesions, suggesting histological nature. Distinguish primary and secondary brain tumors. Assess tumor spread, tumor progression, response to treatment, and determine the ideal site for biopsy. The accuracy of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the diagnosis of tumors and non-tumors is 95-100%. The main signs of brain tumors on MRI are increased choline, Cho/NAA, Cho/Cr, increased lipid, lactate, decreased NAA, decreased NAA/Cr, decreased Cr. Differential diagnosis of brain tumor and brain metastasis: when there are no peaks of NAA and Cr on the magnetic resonance spectrum, there is no increase in the region suggesting brain metastasis. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the assessment of high and low malignancy of brain tumors are 100%, 86% and 96%, respectively. Metabolites used to assess tumor malignancy are Cho, lactate, NAA, CR, and mI. Locating the biopsy site: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is able to identify the areas with the highest Cho increase, the areas with the highest tumor activity, and the bottom is the ideal location for biopsies. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is used in assessing treatment response, identifying recurrent and residual tumors earlier than conventional magnetic resonance imaging, even when patients have clinically improved, distinguishing recurrent and residual tumors. with non-tumor abnormalities after treatment. When Cho increases or there is an increased Cho/NAA ratio suggestive of tumor recurrence.
3.2. Magnetic resonance is contraindicated in the following cases:
Having a pacemaker (pacemaker) Had surgery to replace a heart valve (that valve has a metal component). Carrying magnetic grafting materials. Nerve stimulator. Automatic injection pump implanted in the body. Foreign body in eyeball (in doubtful cases, radiograph should be taken and specialist examination is required) Pair of intracranial blood vessels. Do not use with pregnant patients in the first trimester. Other contraindications that need to be evaluated by radiography: Metal drains in cavities in the body. Vascular Clips Fixed dental fillings. The hearing aid is attached to the cochlea. Artificial joints and osseous materials (screws, splints, etc.) have no contraindications but can damage the magnetic field and will not be able to convert to images.
4. How to perform spectral magnetic resonance
Step 1: Prepare
After being assigned to take an MRI from the doctor, the patient moves to the imaging department and will be greeted by the staff of the magnetic resonance room and instructed to change and remove the objects. use metal on the body to ensure safety during magnetic resonance imaging. When entering the imaging room, guided by the staff to lie in a comfortable position suitable for the shooting unit, the bed will automatically move to the shooting area.
Step 2: Procedure
The technician will place the patient inside the IRM machine. Usually the patient will lie in the denture remover, deaf machine, glasses, jewelry, hairpins, shoes, belt, all the metal in the bag (coins, pens, cell phones, etc.) ATM card...) will be asked to take out.
The time taken for the MRI will range from 40 - 60 minutes. Patients should try to lie still in a position to get the best information, without interference.
In some cases contrast injection is required from the MRI staff who will place a fine needle in the vein in the elbow area and withdraw the needle at the end of the examination.
5. Advantages/disadvantages of magnetic resonance imaging
5.1. Advantage
Patient is not affected by radiation The patient is not biologically affected. Differential diagnosis of tumor due to tumor or non-tumor, suggestive of histological nature. Distinguish primary and secondary brain tumors. Assess the spread of u. Tumor progression, response to treatment, and ideal site for biopsy.
Chụp cộng hưởng từ phổ giúp đánh giá sự lan rộng của u
5.2. Defect
The price is still high. Not usable if patient has claustrophobia or claustrophobia (Claustrophobia) Long exposure time: Difficult if patient is severe or uncooperative Unable to image patient with pacemaker , surgical clips, eye or ear implants Resuscitation equipment cannot be brought into the imaging room. Magnetic resonance brain spectrum is a technique that requires specialized people to perform as well as a system of modern medical machines that can provide the best image quality for medical treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied magnetic resonance technology to medical examination and treatment, and image diagnosis. In particular, the brain magnetic resonance imaging technique at Vinmec is performed methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, contributing to plays an important role in the identification of disease and disease stage, diagnosis and screening of cancer diseases. From there, come up with the most effective treatment plan for the patient.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.