This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Tran Thi Huyen Trang - Laboratory Doctor - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Currently, many countries, including ours, are starting to apply a new direction of biomarker testing for lung cancer. The cancer marker test method can help diagnose cancer at an early stage, avoiding the unfortunate consequences of detecting the disease at a too late stage.
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers with 1.8 million new cases each year worldwide and 1.6 million deaths from the disease. Currently, disease rates are highest in Asia, Europe and North America1. Particularly in Vietnam, every year there are about 22,000 new cases and 19,500 deaths from lung cancer, in 2020 the number will increase to 34,000 cases6. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), lung cancer is likely to become more serious, with up to 10 million deaths and 15 million new cases each year3. Tobacco is known as the main cause of lung cancer. However, according to statistics, up to 270,000 new cases every year come from other causes such as radiation, the risk of occupational diseases for people working in certain industries with high risk of exposure to carcinogens, air pollution in urban areas, air pollution in closed areas, frequent use of combustible substances such as coal, wooden cribs... but lack of a system Effective ventilation and other causes.7
Currently, there are many challenges in the management of lung cancer patients from early diagnosis to follow-up treatment. Imaging tests and tissue biopsies are the main diagnostic tools being used by clinicians to diagnose, monitor, and manage patients with lung cancer. However, the sensitivity of these methods is highly dependent on specimen collection method and tumor location 4.
1. Manifestations of lung cancer
Some common symptoms of lung cancer are chest tightness, coughing up blood, shortness of breath/difficulty breathing, prolonged cough. However, this is not a characteristic sign of the disease, so it is easy to confuse it with other respiratory diseases, making the patient subjective.
Not to mention, according to a recent study, 25% of people diagnosed with lung cancer said they did not experience any symptoms until they received their test results. When the disease has progressed, there will be systemic symptoms such as weight loss, fever, loss of appetite, fatigue, chest pain, bone pain, difficulty swallowing, swelling in the face and neck, hoarseness...

2. CT scan detects lung cancer
To make a diagnosis, doctors would have ordered X-rays in the past. When abnormal signs are detected, other tests will be indicated to accurately determine whether lung cancer is present.
Currently, CT scans have become more popular with an average of 1.5 every year. This method is often applied to smokers. However, 20-40% of false-positive results are still present in symptomatic patients, and in asymptomatic patients this rate is even higher.
Trắc nghiệm: Hiểu về phổi của bạn
Phổi là một tạng lớn rất quan trọng và không thể thiếu trong cơ thể. Việc giữ cho lá phổi của bạn luôn khỏe mạnh, tránh khỏi những bệnh phổ biến về phổi là điều bạn cần lưu ý để giúp cơ thể bạn có thể vận hành tốt. Hãy cùng chúng tôi trả lời nhanh những câu hỏi trắc nghiệm sau sẽ giúp bạn hiểu về phổi của bạn hơn.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Nguyễn Huy Nhật , Nội Hô hấp , Khoa Khám bệnh & Nội khoa - Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Đà Nẵng
3. Markers to detect lung cancer
Currently, many countries, including Vietnam, are starting to apply a new direction of testing biomarkers (lung cancer markers or tumor markers) to detect cancer early.
Cancer markers (protein-derived biomarkers) have been known for decades, and are also included in clinical practice guidelines for lung cancer in some countries to Support diagnosis and follow-up during and after treatment. The "Cancer Marker Test" method can help support the diagnosis of cancer at an early stage, avoiding the unfortunate consequences of detecting the disease at a too late stage. Currently, about 70% of lung cancer patients are detected at an advanced stage. This makes treatment very difficult and the patient's 5-year survival is very low. In the management of lung cancer, early diagnosis and treatment are very important. Lung cancer markers help to effectively support diagnosis and follow-up treatment, bring medical values to both doctors and patients, and reduce the medical burden on society.
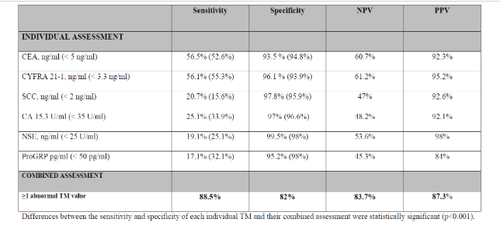
Five common markers for lung tumors are currently CEA, ProGRP, NSE, Cyfra 21-1 and SCC, which are tested based on patient blood samples. If the body is normal, the concentration is low, but when there is a malignant lung tumor, it will be abnormally high. According to Professor Molina's research, if combined (CEA, Cyfra 21-1, SCC, CA 15-3, NSE, ProGRP) sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, predictive value negatives of 88.5%, 82%, 83.7%, 87.3% respectively, much better than using each imprint individually8.
High-risk subjects such as smokers, including passive smokers, families with close relatives (father, mother, brother, sister, brother) with lung cancer, working in an environment with continued risk exposure to carcinogens, polluted environments in big cities... need more extensive testing, depending on age. The older the age, the thicker the frequency.
On August 6, 2018, the Ministry of Health issued Decision No. 4825/QD-BYT on the issuance of a professional document "Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer" in this document. Tumor markers (tumor biomarkers) CEA, ProGRP, NSE, Cyfra 21-1, SCC are used to help diagnose primary lung tumor and other markers such as CA 125, CA 15-3 , CA 19-9, PSA help in differential diagnosis of lung metastases9.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI... biology, immunohistochemistry, genetic testing, molecular biology testing, biomarkers as well as a full range of targeted drugs, the most advanced immunotherapy drugs in cancer treatment. Multimodal cancer treatment from surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, targeted therapy, immunotherapy in cancer treatment, new treatments such as autoimmunotherapy body, heat therapy...
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the cancer treatment is effective or not.
Especially, now to improve service quality, Vinmec also deploys many packages of Lung Cancer Screening Packages that can help customers detect cancer early before there are no symptoms, bringing better results. quality of treatment and the chance of recovery is high.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
1 Kamangar F, Dores G, Anderson W. Patterns of Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Across Five Continents: Defining Priorities to Reduce Cancer Disparities in Different Geographic Regions of the World. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:4.
2 Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit Retal. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International Journal of Cancer doi:10.1002/ijc.29210 PMID:25220842 Published online 9 October 2014
3 Risse EK et al. Diagn Cytopathol. 1985: 1; 286–291
4 D. Morgensztern, Lung cancer: A clinical guide. Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2008
5 Zhi X., Shi Y., Yu J. Chinese guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of primary lung cancer. Chin J Oncol. 2015; 37: 1-19
6 http://vienyhocungdung.vn/70-benh-nhan-ung-thu-phoi-duoc-phat-hien-o-giai-doan-muon-2016091011050038.htm
7 World Health Organization. World Cancer Report 2008 [document on the internet]. Lyon; 2008; [cited 2016 Nov 21]. Available from: http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/wcr/2008/wcr_2008.pdf [Calculation: 960,000 (new cases per year in men) + 390,000 (new cases per year in women) = 1,350,000 (new cases per year) / 1,350,000/100 = 13,500 (1% of cases diagnosed each year) / 13,500 * 20 = 270,000 (new cases per year not linked to smoking)
8 Molina R, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016 Feb 15;193(4):427-37
10 Decision 4825/QD-BYT 2018 Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer