This article is professionally consulted by Doctor Trịnh Lê Hồng Minh, a radiology doctor at the Department of Radiology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Liver cancer is a serious disease and a leading cause of death for both men and women. It is often detected at a late stage, making treatment difficult and resulting in a poor prognosis. Therefore, early detection of the disease plays a crucial role in treatment, monitoring, and prognosis.
1. Overview of liver cancer
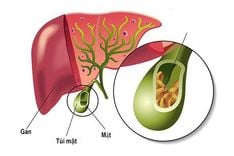
Liver cancer is the condition when liver cells grow abnormally, causing changes in the structure and function of the liver. These cells can invade healthy cells and nearby organs. Additionally, liver cancer can result from abnormal cells migrating from other organs. There are two types of liver cancer:
- Primary liver cancer: refers to a condition where liver cells become abnormal, affecting liver function and potentially spreading to other areas of the liver as well as organs outside the liver. Primary liver cancer includes three main types: hepatocellular carcinoma (originating from liver cells and the most common type), cholangiocarcinoma (originating from the bile duct cells within the liver), and hepatoblastoma.
- Secondary liver cancer: occurs when tumors appear in the liver, but these tumors have originated from cancer cells in other parts of the body. These can include tumors from the stomach, gallbladder, colon, pancreas, breast, lungs, and so forth.
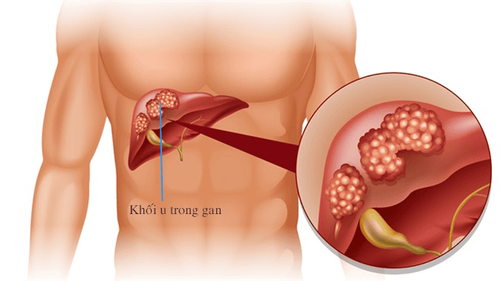
2. Causes of liver cancer
The exact causes of liver cancer are still unclear. Some risk factors are determined to contribute to liver cancer, including:
- Viral hepatitis: Viral hepatitis is a condition in which liver cells become inflamed or necrotic either acutely or chronically, due to viral infections. There are 6 types of viruses that can cause hepatitis, but hepatitis B and C have been found to be correlated with cirrhosis and primary liver cancer. In Vietnam, 60% of hepatocellular carcinoma cases are associated with hepatitis B, and 25% with hepatitis C.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver cells become damaged, leading to the subsequent formation of scar tissue due to various causes. Liver cancer is commonly found in cirrhotic patients, especially those with alcohol-related cirrhosis.
- Exposure to hepatotoxic substances: Regular consumption of aflatoxin-contaminated moldy peanuts and bean sprouts. Toxins, particularly dioxin, carbon tetrachloride, azo dyes, or nitrosamines, have been shown to cause liver cancer in experimental settings.
Heavy alcohol consumption: Alcohol toxins are mostly detoxified by the liver. Frequent alcohol use can damage liver cells, leading to cirrhosis and liver cancer. - Diet: Consuming moldy or unhygienic food, a diet low in protein and vitamin B1, and high in fat.

3. Symptoms of liver cancer
In the early stages, the symptoms of liver cancer are often vague, and patients may exhibit signs such as fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, feeling full quickly or bloating after eating, and pain or discomfort in the right side of the ribcage.
In later stages, the following symptoms may appear:
- Poor appetite, loss of appetite, abdominal bloating, fat in stools.
- Severe pain in the right rib cage that progressively worsens.
- Patients may feel a lump in the liver area.
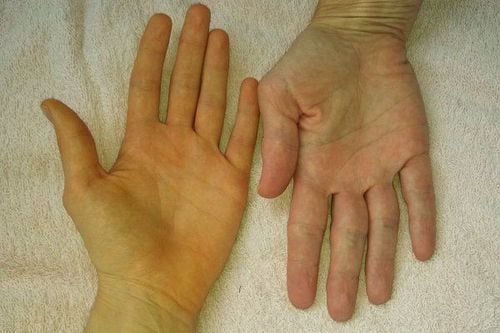
- Jaundice, yellowing of mucous membranes, and conjunctiva, along with itchy skin due to increased bilirubin levels in the blood.
- Pale stools, dark urine.
- Unusual bleeding, such as bleeding gums, and bruising under the skin.
- Sudden, unexplained weight loss.
Swelling or bloating in the abdomen due to ascites.
Liver cancer often shows clear symptoms at a late stage, so patients with pre-existing liver conditions should have regular health check-ups for early detection.
4. Ultrasound images of liver cancer
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging diagnostic method. Through ultrasound, doctors can identify certain characteristics of liver lesions to aid in the early detection of liver cancer, cirrhosis, and portal hypertension.
Ultrasound images of liver cancer lesions include:
4.1. Primary liver cancer
Primary liver cancer presents with diverse lesion shapes:
- Small primary liver cancer lesions less than 3cm often appear as nodules with unclear margins; these nodules can be hyperechoic or hypoechoic compared to the liver parenchyma, but they are mostly hypoechoic. Doppler ultrasound may show increased blood flow within the tumor, typically appearing as a network of small blood flow branches entering the tumor.
- Tumors larger than 3cm: can appear as nodules with clear margins, heterogeneous echotexture, and a hypoechoic halo around the tumor. Typical infiltrative form is characterized by poorly defined tumor boundaries, invasion of surrounding areas, portal vein invasion, and compression of adjacent structures. A diffuse form, featuring scattered small nodules throughout the liver, is rare.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: Less common, the lesion on ultrasound often appears as a large tumor with clear boundaries, diverse internal echo structures, and central calcification nodules.
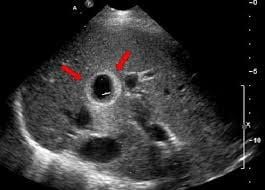
4.2. Secondary liver cancer
The liver is the most common organ for metastatic tumors. Metastatic tumors vary in size and shape.
- Multiple tumors of various sizes are often found to be scattered throughout the liver, which can be either hyperechoic or hypoechoic but are commonly hypoechoic compared to the liver parenchyma. About 40% of these tumors have a surrounding hypoechoic halo. Doppler imaging may show that metastatic tumors have little to no vascular signals. Generally, metastatic lesions are multifocal, especially in patients with a prior cancer diagnosis, suggesting liver metastasis.
- A portal vein thrombosis sign, which can result from tumor invasion, can be detected early through liver ultrasound.
- In some cases, signs of cirrhosis may be observed, such as coarse and irregular liver parenchyma, uneven liver margins, changes in liver size, and increased portal vein pressure.
Additionally, elastography, a relatively new ultrasound technique, can diagnose cirrhosis and liver tumors with up to 90% accuracy compared to biopsy, significantly reducing the need for liver biopsy. This method measures tissue elasticity under compression to determine the pathological condition. Liver elastography determines the stiffness of the tissue, which is then used to assess and categorize the severity into four levels: score 4 indicates malignant tumors; scores 2 and 3 are suspicious and require further assessment; and score 1 represents benign lesions.
Liver cancer is a serious disease, and early detection is crucial for treatment, prognosis, increasing the cure rate, and extending patient life expectancy. Ultrasound is a simple, non-invasive method with high accuracy in guiding the diagnosis of liver cancer. Patients with suspected signs of liver cancer should seek medical evaluation for early detection.

To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.