Genital pimples in both men and women can cause uncomfortable symptoms and may lead to serious complications if left untreated. Therefore, when pimples appear in the genital area, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
1. Types of Genital Pimples in Women
The common types of genital pimples in women include:
1.1 Folliculitis
Folliculitis in the genital area is one of the causes of pimples in women. Folliculitis pimples typically contain pus and are located at the base of the hair follicles. These pimples cause redness and swelling in the genital area, and if rubbed excessively, they can rupture, causing pain and increasing the risk of infection.
Causes of folliculitis include:
- Poor or improper hygiene.
- Overuse of harsh cleaning products or feminine washes.
- Wearing tight clothing or undergarments for extended periods.
- Improper shaving or hair removal techniques.
1.2 Genital Herpes
A characteristic symptom is the appearance of genital herpes pimples. Initially, they appear as small red or pink spots, growing separately and filled with fluid. Over time, they cluster together like grape bunches. These pimples can rupture, causing pain, discomfort, and itching, which significantly affects daily life.
1.3 Genital Warts
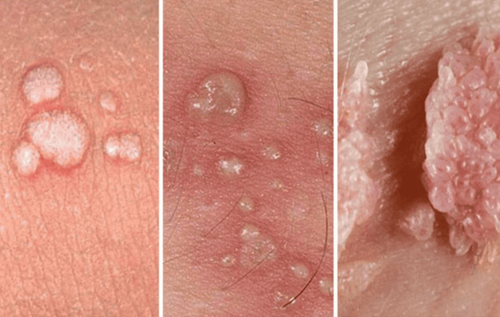
Among the various genital pimples, genital warts caused by the HPV virus are quite common. Symptoms typically appear 6–8 months after HPV exposure, starting as small red pimples. Over time, they form cauliflower-like clusters.
If untreated, genital warts can cause infections and lead to cervical cancer. The most effective prevention method is HPV vaccination.
1.4 Chemical Allergies
The genital area can also develop pimples due to chemical allergies. Cleaning agents such as soap, shower gel, fabric softeners, feminine washes, or sanitary pads may contain ingredients that irritate the sensitive genital skin. Symptoms include pimples, red spots, and itching.
1.5 Other Causes
Hormonal changes during different stages of life can stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to clogged pores and pimples.
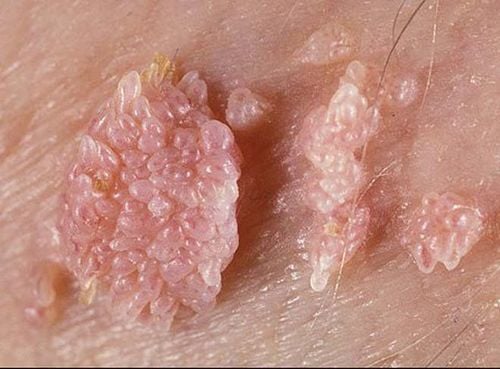
2. Types of Genital Pimples in Men
Pimples can appear on the head, shaft, scrotum, or foreskin of the penis. Common types of genital pimples in men include:
2.1 Genital Warts
This dangerous sexually transmitted disease caused by the HPV virus spreads rapidly and is difficult to treat. If untreated, it can lead to penile cancer or anal cancer.
Symptoms include soft pimples that may appear singly or in clusters resembling cauliflower. These pimples are white, have an unpleasant odor, and often cause itching and discomfort.
2.2 Balanitis (Inflammation of the Foreskin)
If untreated, balanitis can progress to infertility or penile cancer. Causes include:
- Overly long or tight foreskin.
- Poor hygiene.
- External irritants.
Symptoms include itching, discomfort, and small pimples that may spread and rupture, worsening the inflammation.
2.3 Genital Herpes
Genital herpes caused by the Herpes Simplex Virus starts as tiny pimples on the penile shaft. These pimples gradually cluster into blisters, which are prone to rupture, causing itching, pain, and ulcers. In severe cases, the ruptured pimples may discharge fluid or blood with an unpleasant odor.
2.4 Other Causes
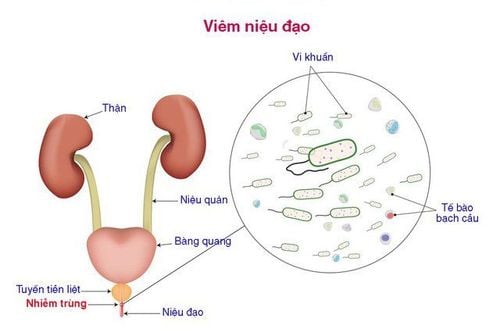
- Infections such as urethritis or urinary tract infections.
- Skin issues: acne in the genital area, folliculitis, fungal infections, or scrotal eczema.
- Poor hygiene or use of inappropriate cleaning products.
- Pearly penile papules: This condition involves small, harmless bumps around the penile head, common in men aged 20–30.
3. Complications of Genital Pimples in Men and Women
Many individuals feel embarrassed and choose to endure genital pimples silently or self-medicate with over-the-counter creams. While some cases may resolve on their own, most worsen over time and can lead to severe complications:
Severe complications:
- Impact on sexual life: Genital pimples may cause self-consciousness, reduced sexual desire, and strain in relationships.
- Increased risk of infections and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
- If untreated, advanced cases may affect reproductive health, potentially leading to infertility or even cancer.
4. Treatment of Genital Pimples in Men and Women
Patients with genital pimples need thorough examinations by specialist doctors to identify the underlying cause. Depending on the severity, patient health, and specific cause, treatment options include:
- Medication: Mild cases may be treated with anti-inflammatory medications. Topical creams may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Patients with known drug allergies must inform their doctor.
- ALA-PDT Therapy: This photodynamic therapy uses high-frequency light to target genital warts caused by HPV. It effectively halts the progression and eliminates the virus.
- Oxygen Therapy: This method is effective for severe or recurrent genital pimples. Oxygen penetrates deeply into the genital tissue to kill harmful bacteria and fungi, improving inflammation and preventing recurrence.
Most genital pimples in men and women affect overall health and can be signs of serious conditions, such as STDs or cancer. Therefore, early medical consultation and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
If symptoms of genital herpes or other forms of genital pimples appear, patients should promptly visit medical facilities for proper diagnosis, advice, and treatment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.