This is an automatically translated article.
Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine are branched chain amino acids (BCAAs). They form an important group of amino acids. Of these, Leucine is the most well-studied because of its higher oxidation rate than isoleucine or valine.
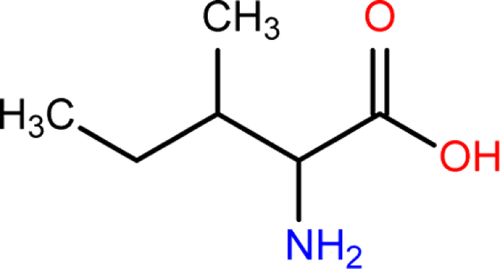
1. What is Leucine?
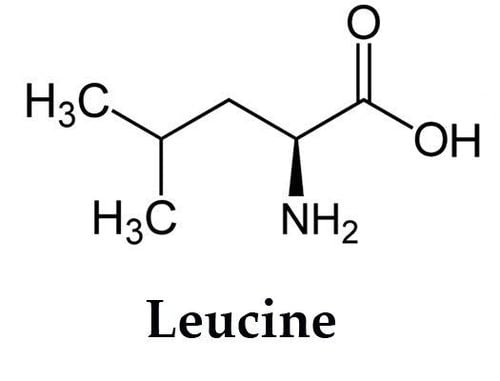
Leucine là một trong những axit amin được tìm thấy trong protein
Leucine is one of the amino acids found in proteins. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid. This is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized on its own, but must be obtained from food.
Leucine is found in meat, fish, and poultry. Leucine has the ability to stimulate protein synthesis, which helps the body to build muscle and is closely related to the release of gluconeogenic precursors such as alanine.
Leucine levels decrease significantly after aerobic exercise (range 11-33%) or exercise (30%). During aerobic exercise, leucine levels decrease and glycogen stores decrease.
2. Benefits of Leucine
Build muscle : Athletes need Leucine supplements due to its strong impact on muscle gain. This is an important amino acid for muscle synthesis, helping to trigger muscle building to optimize athletic performance. The consumption of protein produces an increase in muscle protein synthesis. Protein stimulates the building process in muscle. The amino acid leucine was most associated with increased protein synthesis.
Slows down muscle loss with age: According to some studies, Leucine is thought to slow down the decline of muscle due to the effects of aging, helping to improve muscle synthesis in humans. old. The addition of leucine also contributes to limiting weight loss due to malnutrition in the elderly. Improved exercise performance: Subjects who regularly exercise or are new to exercise also often supplement with leucine to increase exercise performance.

Bổ sung Leucine hiệu suất thể dục được cải thiện
One study showed that leucine supplementation for six weeks significantly improved endurance and strength, and this amino acid also increased muscle tissue mass and improved performance. exercise performance in the elderly.
Fat loss: Leucine supports muscle building while reducing excess body fat. Leucine stimulates the body to burn subcutaneous fat to build muscle tissue. Using leucine for weight loss will preserve muscle mass and at the same time you will lose body fat. Research has shown that leucine reduces fat accumulation during aging and prevents the development of obesity.
Promote muscle recovery: You will feel sore and tired after exercising with high intensity, sometimes you can't continue to practice because of the pain. Several studies suggest a potential role for leucine in muscle recovery. Consuming leucine after work can stimulate recovery and protein synthesis.
Leucine helps maintain muscle tissue by maintaining nitrogen balance, the body is supplied with energy even during exercise, and muscle glycogen is conserved to use for muscle contraction.
Stable blood sugar: High blood sugar can affect your health causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss... the situation will become more serious if blood sugar is not controlled. control. Several studies have shown that leucine can maintain normal blood sugar levels. In addition, leucine has been shown to facilitate insulin signaling and glucose absorption to control blood sugar.
Support patients with cirrhosis: Cirrhosis can lead to serious complications such as internal bleeding, jaundice, yellow eyes... more dangerous than liver cancer and can be fatal. BCAAs are clinically proven to be effective in improving blood albumin levels in patients with cirrhosis and reducing the dangerous complications of cirrhosis. With low blood albumin levels, patients with cirrhosis have a higher mortality rate.
Patients with cirrhosis, if too much protein is added, the liver will work harder. Using the BCAA arm will be better for patients with cirrhosis, inhibiting the protein destruction pathway that causes muscle atrophy.
3. Leucine side effects
Consumption of leucine in food is considered safe. High doses of leucine supplements may increase the risk of side effects such as fatigue.

Bổ sung leucine liều cao có thể làm tăng nguy cơ tác dụng phụ như mệt mỏi
Leucine may affect vitamin B3 production. In addition, leucine can reduce the production of serotonin, which is involved in mood regulation.
High doses of leucine can be toxic and increase blood ammonia levels. Several studies have shown that leucine should be limited to less than 50 mg/kg body weight to reduce the risk of side effects.
For people with syrupy urine disease, caution should be taken when supplementing with leucine because indiscriminate use of leucine can cause symptoms such as coma, weight loss or possibly nerve damage.
4. Leucine in which foods?

Leucine có trong nhiều loại thực phẩm mà chúng ta đang sử dụng hàng ngày
Leucine is present in many foods that we are using every day.
Here are some foods rich in leucine:
Eggs Beef Pork Cheese Sesame seeds Chicken Oats Peanuts Almonds ...
Besides, leucine can also be obtained from milk. High doses of leucine supplementation can cause adverse effects and toxicity. Therefore, to get the best results, you should eat a variety of leucine-rich foods combined with a reasonable diet to be able to take full advantage of the benefits of this amino acid.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
The article references the source: ncbi.nlm.gov; drugs.com; webmd.com; nld.com