This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, endoscopic surgery to destroy the arachnoid cysts of cerebrospinal fluid is the most important treatment method. This surgical method is less invasive and effective because it is used endoscopically to open the cyst wall to communicate with the subarachnoid space, or to communicate with the ventricles.
1 What is a cerebral arachnoid cyst?
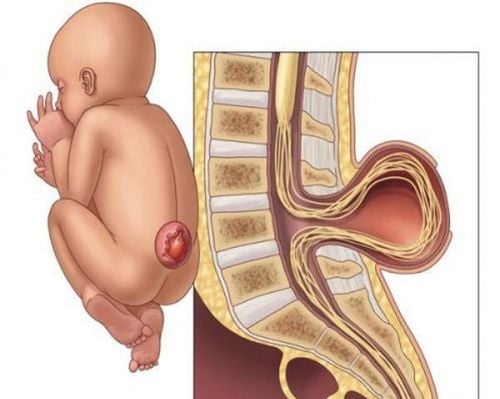
A cerebral arachnoid cyst is actually a water cyst in the spinal cord or brain containing cerebrospinal fluid, with or without communication with the subarachnoid space. According to statistics, more than 50% of arachnoid cysts are located in the middle cranial fossa. In addition, cysts can be found in the pontine-cerebellar angle about 11%, the suprapubic region about 9%, the posterior fossa and even the spinal canal.The cause of this cyst is congenital, stemming from the separation of the arachnoid membrane in the fetus, usually a benign lesion. The cyst is delimited by two layers of membranes, an inner and an outer membrane, which is made up of the leaves of arachnoid cells, a few other small layers of endothelial cells, other glial cells...
Nang màng nhện não là tổn thương lành tính xảy ra từ trong bào thai
Symptoms of arachnoid cysts depend on many factors and often have the following manifestations:
Epilepsy The cyst will increase in size causing symptoms of compression of the cranial nerves, brain, or spinal cord . Clinical progress in the patient suddenly worsens Increased intracranial pressure includes symptoms such as: Headache, nausea, dizziness, ...
2. Laparoscopic surgery to destroy arachnoid cysts with cerebrospinal fluid
2.1 Indications for laparoscopic surgery We can perform laparoscopic surgery for the following types of arachnoid cysts:
Arachnoid cysts in the pituitary fossa Arachnoid cysts in the cerebellar angle of the cerebellum. occipital (large cistern area) Paraventricular arachnoid cyst Temporal arachnoid cyst 2.2 Contraindications to laparoscopic surgery There are no contraindications to endoscopic methods of treating arachnoid cysts. This endoscopic approach will be about 50% successful for temporal arachnoid cysts and 95% successful for pituitary arachnoid cysts.
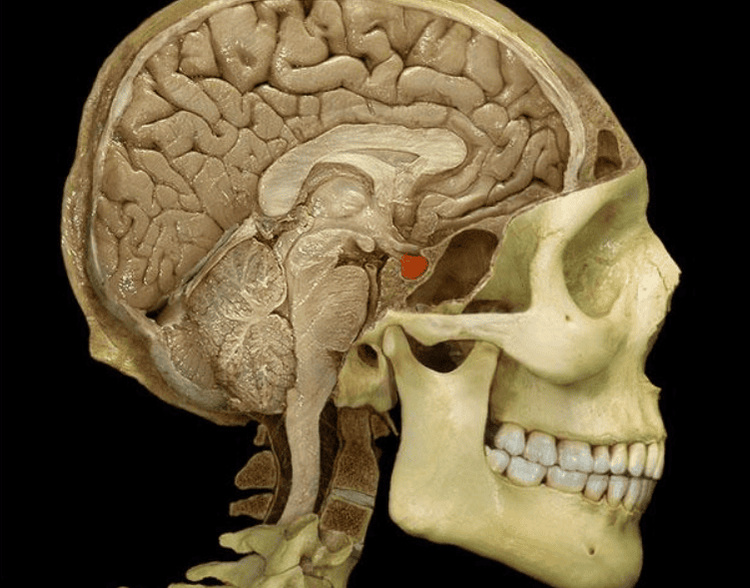
Phẫu thuật nang dịch màng nhện vùng hố yên có tỷ lệ thành công lên tới 95%
2.3. Steps to carry out surgery Step 1: Prepare the necessary neuronavigation positioning system for computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging CD printing; endoscopes, light sources, placement of endoscopes, optical cables, screens. Step 2: Prepare for surgery according to surgical procedures (hygiene, prophylactic antibiotics); anesthesia resuscitation. Step 3: Open the skull cap: Make skin incision, expose the skull bone, drill and open the skull cap; The position of skin incision and opening of the skull depends on the position, size of the fluid cyst and the incision. Step 4: Open bone: The shortest path from the skin incision to the cyst, not through the functional area, not through the infected area. Open the dura and access the arachnoid cyst. Expose the anterior wall of the cyst in such a way that it is wide enough that the endoscope and other instruments can be inserted into the lumen of the cyst through the part of the wall that will be opened. Step 5: Cut the cyst or open the cyst. Open the anterior wall of the cyst and then aspirate the cerebrospinal fluid. Then, insert the endoscope into the cyst and assess the cystic surface, wall structure, nerves, cerebrospinal fluid, blood vessels, and ventricles adjacent to the subarachnoid cyst. Step 6: Determine where the cyst wall will open or the cyst wall will be removed; In cases where it is difficult to locate the cyst wall, the cyst will open and need the help of a neuronavigation system. In case of large cyst wall, partial resection of cyst wall; Thorough examination in the cyst prior to epidural closure. Step 7: Closing the incision: including closing the dura, fixing the skull cap and closing the skin.
Phẫu thuật nội soi phá nang màng nhện dịch não tủy
3. Follow-up after surgery
Immediately after surgery, we need to monitor respiration, circulation, consciousness, paralysis, pupils, paralysis of cranial nerves, sensory disturbances. In case of surgical wound bleeding: Change dressings, pressure bandages, stitches regularly. Intracranial bleeding: Consciousness worsens, paralysis increases, pupils dilate. Infection: Fever, elevated white blood cell count, high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, cerebrospinal fluid test, antibiotic use for the patient. In case of intracranial bleeding, increased intracranial pressure necessitates taking tomography. Emergency surgery to remove internal hematoma, stop bleeding if the hematoma is pressing. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely rest in peace. Center for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.