This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Bui Thi Hang - High-Tech Unit for Treatment of Cerebral Palsy and Autism, Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Meningeal hernia is a birth defect in the nervous system because the baby's spinal canal is not perfected during the fetal period. In order to help children recover soon and develop normally, as soon as they detect symptoms or suspect that their child has this disease, parents need to quickly take the child to the hospital for an accurate diagnosis and treatment. timely treatment.
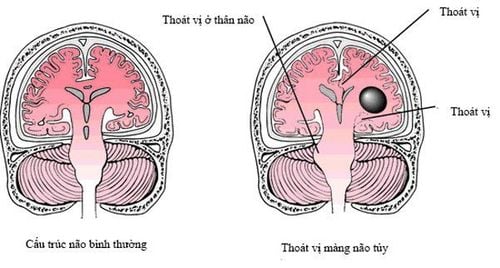
1. What is meningeal hernia?
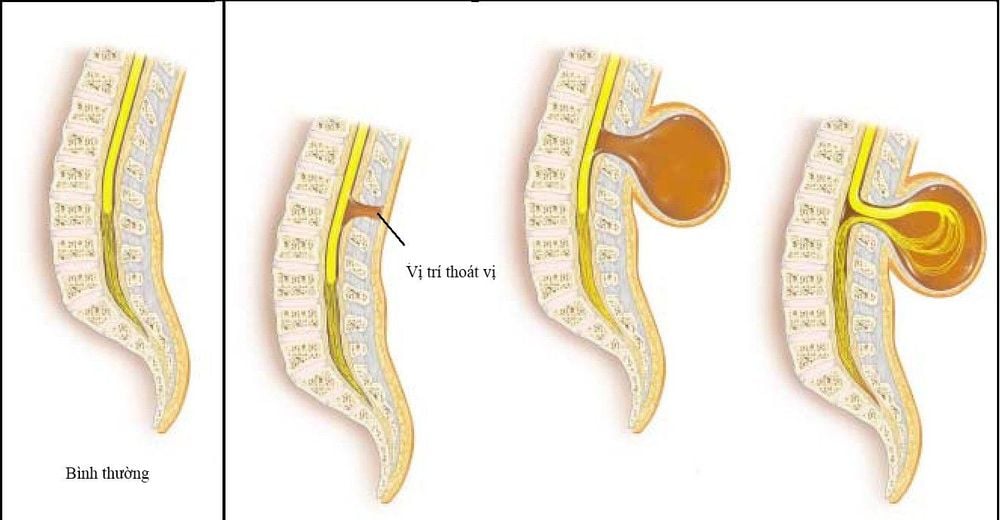
Meningeal hernia is a disease that occurs due to a defect in the posterior arch of the spine, also known as a vertebral cleft, a consequence of the child's neural tube not developing normally during the fetal period, making the spinal canal communicates with the extra-vertebral soft tissue and leads to the spinal dura easily bulging and forming a hernia sac. Normally, the neural tube is formed early in pregnancy and it must be completely closed around day 28 of pregnancy to create a complete spinal system that protects the spinal cord.
Meningeal herniation has many levels, from mild to severe depending on the degree of herniation of the nervous system through the vertebral cleft. Currently, according to the world's treatment recommendations, the hernia should be operated on as soon as possible to minimize the damage to the child.
After surgery, the child's condition will improve, but in cases of severe nervous system damage, the child may still have the following sequelae:
Weakness, paralysis of both legs Foot deformity: variable crow's foot shape, feet crooked inside, outside, drooping feet Muscle atrophy in both legs Decreased, loss of feeling in both legs Loss of feeling of needing to urinate and defecation Incontinence (also known as round muscle disorder due to crow's feet) meningeal hernia) Recurrent urinary tract infections Small bladder vesicoureteral reflux Inflammation of the kidneys, pyelonephritis, pyelonephritis, body failure Skin ulcers due to decreased sensation, loss of sensation in both legs and feet. butt. Other serious complications
Ventricular dilatation Chiari syndrome type II: causes the part of the brain just above the spinal cord to drop down through the occipital foramen, leading to swallowing disorders and breathing disorders Meningitis Low spinal cord Syndrome Sleep apnea Psychological changes, cognitive disorders.
2. Diagnosis and evaluation of sequelae of meningeal hernia
Children are taken obstetric history, medical history Clinical examination: children are assessed for motor status, sensation in both legs, measurement of leg circumference on both sides, assessment of foot deformity and gait Assessment Urinary tract disorders Evaluation of anal sphincter status Evaluation of urinary tract infections, degree of vesicoureteral reflux Measure head circumference Assessment of cognition, language, respiratory system, cardiovascular and general health Laboratory tests to be performed: MRI of the spine to determine damage to the spinal cord system, MRI of the brain to evaluate the degree of ventricular dilatation, Chiari syndrome and other abnormalities in the brain X-ray vesicoureteral retrograde, abdominal ultrasound - urinary system: evaluate urinary system and degree of vesicoureteral reflux if present Blood test, urinalysis Measurement of urodynamics and urogram Assess bladder function and bladder sphincter Measure anorectal manometry to assess sensation and ability to defecate.
3. How is rehabilitation treatment after meningeal hernia?
Rehabilitation for children with meningeal hernia should be carried out soon after surgery to maximize the body's function and limit the sequelae due to damage to the nervous system due to the disease.
Depending on the function of the child after surgery, the doctors will plan rehabilitation exercises for each patient. Commonly used methods:
Physical therapy
For children who are weak, paraplegic, deformed, and atrophied in both legs, they will be trained to exercise their legs with exercises to strengthen the muscles and stretch the leg area. deformation due to shrinkage.
At this unit, the doctor will appoint the child to make a brace to support the legs in necessary cases.
In addition, for children with brain damage due to severe consequences of meningeal hernia, delayed treatment, two-hand movements may be poor, or exhibit motor development retardation. most effective way to improve the level of movement of the body.
Physiotherapy
Children can be prescribed electric pulses to stimulate the legs depending on the muscle groups that are atrophied and weak to increase muscle strength and improve muscle atrophy.
Rehabilitation of defecation and urination
Children are trained to do exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, electrical stimulation of the anus, electrical stimulation of the nerves in the lumbar region, and abdominal interference to treat urinary disorders. convenient.
Other treatments
Guidelines for intermittent catheterization.
Instructions for proper defecation control.
Intervention of cognition, behavior, language in children with disorders due to severe consequences of meningeal hernia affecting the brain.
Unit of Regenerative Medicine Clinic and Educational Psychology of Center for Regenerative Medicine, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is one of the prestigious addresses in the field of rehabilitation exercises for children with cerebral palsy , sequelae of encephalitis, brain damage due to drowning, meningeal hernia ...
Along with specialized equipment and tools for modern physical therapy and rehabilitation, the Unit has the presence of Experienced doctors include:
Master, Doctor Vu Duy Chinh: Over 17 years of experience in examining and treating pathologies in the Physiotherapy/Rehabilitation specialty, especially those in fields: neurology, trauma and pediatrics... Dr. Le Thu Huong: Nearly 5 years of experience in Rehabilitation. In 2017, Dr. Huong obtained the degree of Resident Doctor of Rehabilitation. Doctor Bui Thi Hang: 8 years of experience in Pediatrics. In 2013, Dr. Hang obtained a resident doctor degree and a master's degree in pediatrics.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.