This is an automatically translated article.
Esophageal cancer is a common form of cancer, if the disease is detected early in the early stages, when the cancer cells have not metastasized, and esophagectomy is performed, it can completely treat the cancer. high efficiency.
1. What is esophageal cancer?
The esophagus is part of the human digestive tract, and cancer comes from the esophagus. Esophageal cancer is a malignant disease caused by uncontrolled division of cells in the esophagus, including two main types of cancer, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma originates in the epidermal cells in the wall of the esophagus, and is most commonly located in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus. Adenocarcinoma originates in the glandular cells of the esophagus, usually located in the lower esophagus. Esophageal cancer can invade outside the esophagus, metastasize through the lymphatic system and to other organs, such as liver, spectrum, bone, brain,... In Vietnam, esophageal cancer is one of the most common cancers. The five most common types of gastrointestinal cancer.
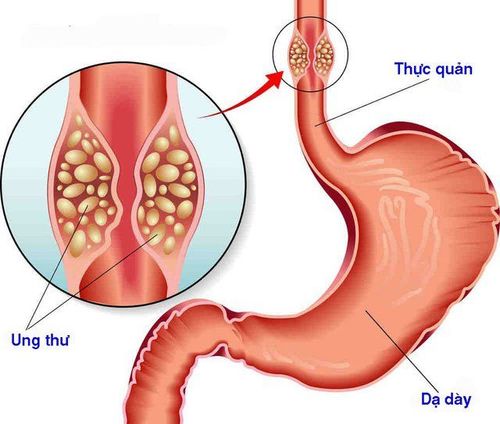
Ung thư thực quản có thể di căn đến các cơ quan khác trong cơ thể
2. Laparoscopic esophagectomy through diaphragmatic slit in the treatment of esophageal cancer
In the treatment of esophageal cancer, surgery is the basic and main treatment, chemotherapy and radiation are adjuvant treatments.
Laparoscopic thoracic and abdominal surgery has the advantage of good lymph node dissection, but it cannot be performed in cases with pleural thickening, or in cases where there is a tumor in the lower 1/3 but not capable of assessing the problem of spreading to the center of the gastric aneurysm, so endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit was born to overcome the above-mentioned situations.
2.1 Indications for endoscopic esophagectomy through diaphragmatic slit:
Patients with esophageal cancer located 1⁄3 lower, stage T1 - T3, regardless of metastasis (N0 or N1) Patient Cardiac cancer type I and type II according to the classification of Siewert in 1987. 2.2 Contraindications Contraindication of transdiaphragmatic endoscopic esophagectomy:
Patients with cervical and thoracic esophageal cancer in the location 1⁄3 top or 1⁄3 middle. The patient has esophageal cancer in the lower 1/3rd position but the tumor is large. The patient has many serious systemic diseases, such as: respiratory failure, heart failure, kidney failure, ...
Bệnh nhân có nhiều bệnh lý nặng không được chỉ định phẫu thuật
There is a history of peritonitis requiring surgery, intestinal obstruction, ascites, umbilical hernia, abdominal wall hernia, local infection of the abdominal wall, coagulopathy,... Indications for peritoneal inflator: Coronary artery disease, heart valve disease, chronic heart failure. The patient did not agree to perform the treatment by transdiaphragmatic endoscopic esophagectomy.
3. Preparation steps before the patient undergoes endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit
Patients need to complete the following issues before performing endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit:
Be explained and consulted by the doctor about the current medical condition as well as the actual surgical method. endoscopic administration through the diaphragmatic slit for cancer treatment. Complete basic tests, endoscopy, ultrasound, X-ray, computed tomography chest - abdomen and other necessary tests and techniques. The patient's condition is well nourished to ensure that he can respond to surgery, and the results of pre-anesthesia examination are favorable. Use prophylactic antibiotics before surgery.
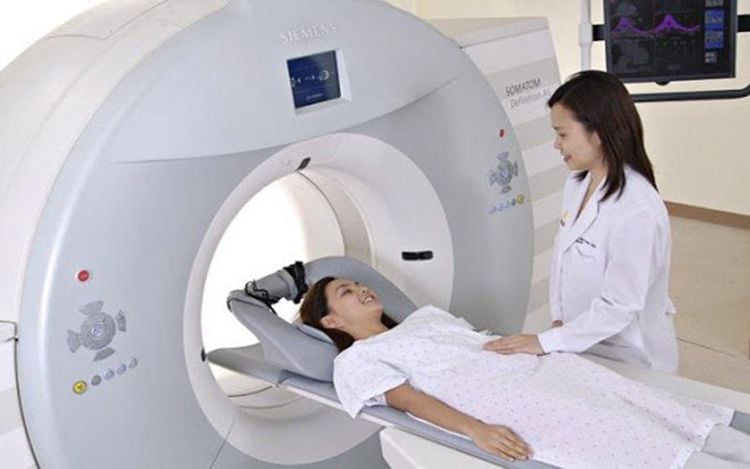
Bệnh nhân tiến hành chụp cắt lớp trước khi phẫu thuật cắt thực quản nội soi qua khe hoành
4. Care and monitoring of patients after endoscopic esophagectomy through diaphragmatic slit
After performing endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit, the patient care and monitoring steps include:
Monitor the patient's vital signs. Monitor pleural drainage and intraoperative drainage. Use of antibiotics after surgery. Replenish water and electrolytes. Nutritional recovery.
5. Risks and complications that may be encountered when performing endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit
Like other types of surgery, the process of performing endoscopic esophagectomy through the diaphragmatic slit also has certain risks and complications, such as:
Esophageal perforation. Bronchial tear. Large blood vessels are damaged. Bleeding after surgery. Respiratory failure . Leaky connection, probing for maintenance. If there are complications like the above, it is best to immediately notify the treating doctor, and at the same time choose the nearest and reputable medical facilities for timely emergency and treatment.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.