This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
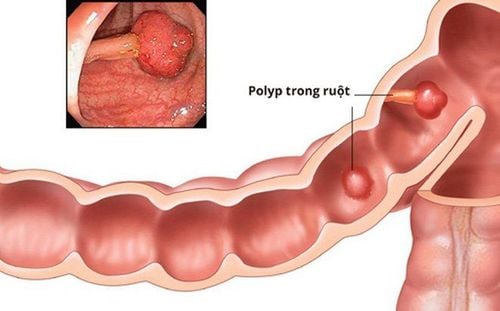
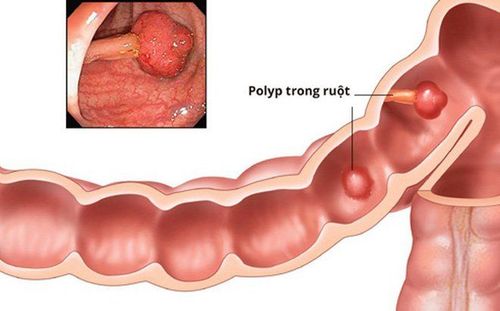
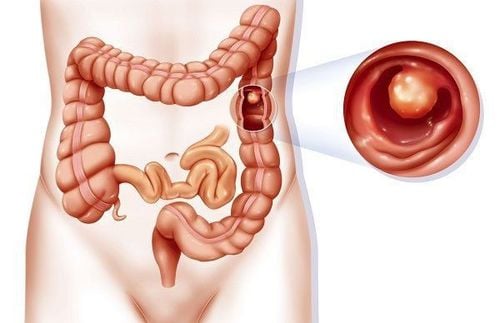
Endoscopic polypectomy and endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) are established treatment standards for colorectal polyps. Nose nose polypectomy technique – Cold snare resection is the emerging standard for the treatment of smaller polyps (<5mm) and may also be appropriate for removal of polyps non-cancerous up to 9 mm. This approach avoids thermal injury, reduces procedure time, and may reduce the risk of late bleeding.
1. Remove polyps faster and safer with cold biopsy
The disadvantage of the conventional current-using noose cutting method is the damage caused by heat. Possible complications are delayed bleeding and heat damage leading to post-polypectomy syndrome and late perforation. Recently, cold nose resection has been introduced as a possible alternative. This method involves catching polyps - mainly with specialized equipment - without the additional use of electrocautery. It is mainly applied to small polyps (up to 5mm) but has recently been extended to larger lesions. This approach offers the possible advantage of reducing procedure time and postoperative complications while maintaining the same efficacy as conventional hot ablation.
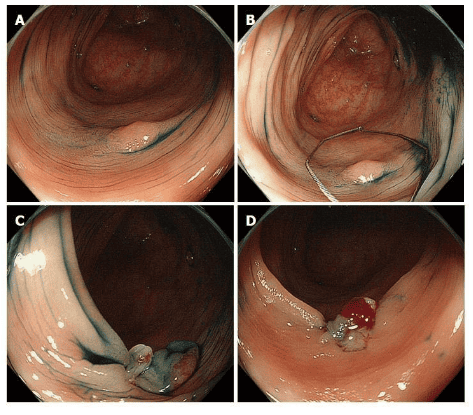
In summary, cryo-nose resection is becoming the standard of care for small tumors (up to 5 mm) and also for small (up to 9 mm) sessile noncancerous tumors. Larger studies will need to determine the exact role of cold noose resection in polyp removal.
2.Expanded indication to treat larger colon polyps with ESD
The main advantages of EMR are the relatively short procedure time (approximately 35 minutes for larger lesions) and an acceptable complication rate, with late bleeding of 0.9% and perforation rate from 0. 4% to 1.3%. It should be emphasized that the complication rate depends on the size and location of the resected lesion. Therefore, a late bleeding rate of 6.7% was reported in a recent multicenter study including >2000 EMR. Risk factors for bleeding include lesion size, polyp location in the right colon, and comorbidities. The frequency of perforation after EMR is between 0.4% and 1.3% and depends on the size and location of the resected lesion.
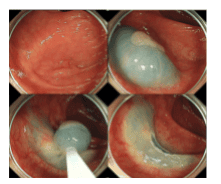
The disadvantage of EMR is the size limit of about 20 mm. Larger lesions cannot be pieced together block-by-block and must be removed piece by piece (array EMR technique). This fragmentation implies that complete resection cannot be confirmed by histopathology, and partial EMR is associated with a recurrence rate of approximately 15%-20% in the retrospective series and more than 30% in one study. Recent prospective study of endoscopic partial resection of 252 adenomas >20 mm in size. Multiple risk factors for recurrence have been identified, including lesion size, number of resected fragments, and more advanced histology (tubulovillous adenoma or high-grade intraepithelial carcinoma). Furthermore, multiple relapses are not a rare occurrence (approximately 20%-40%), although most of them are treatable endoscopically. Notably, incomplete endoscopic resection of adenomas is thought to be responsible for 20%-25% of cancers. The recurrence rate implies the need for endoscopic control and follow-up endoscopic compliance.
The advent of ESD submucosal dissection
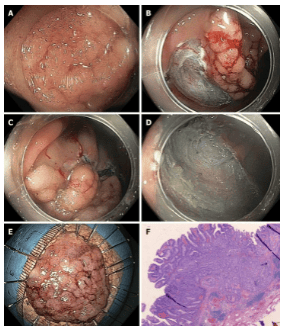
While EMR of larger polyps or pedunctal lesions will lead to fragmented resection, ESD - developed in Japan for the treatment of early gastric cancer - endoscopic submucosal dissection. This method consists of mucosal incision followed by submucosal dissection below the lesion to produce a mass specimen of unlimited size.
ESD is much more technically demanding than EMR and requires a longer process time, with an average procedure time of shift of 70 min in a recent meta-analysis. The duration and complexity of the procedure depend mainly on the endoscopic approach to the lesion and the access to the submucosal space. This approach is not considered standard in Europe, but it has been included in Japanese guidelines as the standard technique for larger cancerous lesions where resection of the tumor is desirable.
ESD techniques require highly specialized training
Most clinical data on colorectal ESD are from Asia. Larger retrospective or prospective observational studies (>500 patients) reported resection rates and R0 resection rates of 84% to 94.5%, with very few recurrences. In contrast, experience with colorectal ESD is very limited in the Western world.
This is mainly due to the lack of training opportunities, the high level of skills required to perform colorectal ESD and the fact that this method has a longer procedure time and perhaps a lower complication rate. higher than partial EMR. However, it is possible to achieve competence in colorectal ESD without prior expertise in gastric ESD, particularly if training is conducted under the supervision of ESD specialists.
Thus, data from Western endoscopy are rare, with smaller case series and only two publications in larger (n > 150) series, which mainly include lesions local to the rectum . Both monolithic resection rates and R0 in these publications were lower than in studies from Asian populations, which is especially true for larger lesions in the ascending colon. Adverse events are more common for ESD than for EMR, with a reported perforation rate of approximately 4.8% (2%-14%) for the former. However, most perforations are small and can be closed with standard forceps during or at the end of the procedure, and the incidence of emergency surgery is relatively low (about 0.5%). Bleeding retardation was observed after 1.5%-2.8% of the intervention. Tightness is observed only occasionally, for example, after resection of a circular line in the rectum
3.Treatment options for difficult or invasive neoplasms, fibrosis - Total gastrointestinal resection (EFTR)
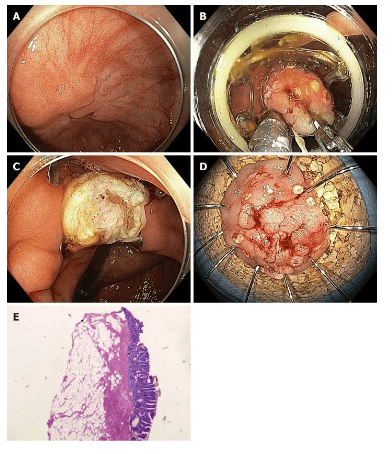
Conventional laparoscopic resection may not be technically feasible in cases of severe fibrosis, for example, due to scar formation in adenomas that have recurred after previous resection or in cases of adenomas in specific anatomical sites, eg, close to the diverticulum or at the orifice of the appendix. In these situations, EFTR can be a useful alternative. This method consists of full-thickness flattening of the bowel wall, fixed with an endoscopic forceps, followed by resection of the bowel wall above the forceps. The full-thickness cutting device system (FTRD®) (Ovesco, Tübingen, Germany) is a safety-range full-wall cutter with an integrated noose. After marking the lesion, the colonoscope is withdrawn and the FTRD is attached to the tip of the scope and guided to the lesion. The lesion is then pulled onto the ablation flap, and after clamp deployment, the noose is closed and the tissue is excised. Additionally, a tissue puller is used to pull the tissue inside the cap (CAP) prior to firing the clip.
4.Advantages and disadvantages of the method of removing the entire digestive tract containing polyps
EFTR is particularly useful for resection of smaller lesions (up to 15-20 mm). To date, only limited data are available on the effectiveness of the method, which is typically performed with an FTRD device. The duration of the procedure depends mainly on the location of the lesion (sometimes moving to proximal sites can be difficult or even impossible). It takes more time than EMR and the size of the lesion is limited by the size of the flap. In the largest prospective study published to date, the R0 resection rate was 77.7% for 127 patients with non-moving adenomas. The overall complication rate was 9.9% and included perforation, fistula, bleeding and appendicitis; emergency surgery rate 2.2%.
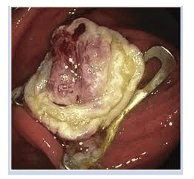
Conclusion
Polypectomy and EMR remain the standard treatment options for the removal of most colorectal neoplasms. They are relatively easy and quick to perform technically and have an acceptable complication rate. New developments are underway with cryo-nose resection as a method that may be associated with an even shorter procedure time and lower complication rates. In addition, the ESD technique has the potential for resection of larger monolithic lesions; it should probably be reserved for larger lesions suspected of high-grade dysplasia or early invasive cancer. Finally, small lesions that are difficult to resect can now be effectively treated with the EFTR technique.
Vinmec International General Hospital has invested in the most modern and advanced equipment in the world today to maximize the performance of endoscopic digestive polyps.
Vinmec is being equipped with the most modern digestive endoscope of Olympus. Endoscope Olympus HQ 190, Argon VIO 200 D - APC 2 ablation machine, Olympus synchronous endoscope washing machine. This is one of the best machines in the world for early detection of lesions and timely intervention, clear images...
Gastrointestinal endoscopy with Narrow Banding Imaging (NBI) has been creating a breakthrough for the screening and diagnosis of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach, duodenum, colon, rectum) at early and very early stages. NBI endoscopic images have high resolution and contrast, so it is easy to detect small changes in color and morphology of cancerous and precancerous lesions that are difficult to detect and intervene with conventional endoscopy. correct injury site.
The synchronous machine washing system is used with standard RO water and chemicals to ensure maximum safety for the patient.
Vinmec Hospital is gathering a team of experts, medical professionals, experienced professionals in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy and gastrointestinal endoscopy. The doctors have been trained in endoscopic polypectomy techniques and have many years of experience in the profession.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.