This is an automatically translated article.
White blood cells are generally part of the immune system, which plays a role in fighting infectious diseases and foreign bodies in the blood. Leukocytes are classified into three main types as granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes. In general, the types of white blood cells in the body are divided into 3 types: granulocytes, monocytes and lymphocytes. Each type has a different role in the body.1. Granulocytes
1.1 Characteristics of granulocytes Granulocytes are characterized by differently stained granules in the cytoplasm observed under an optical microscope, having the following characteristics:Capable of changing shape, penetrating vessels through the intercellular wall and directional movement with a prosthetic (amoeba-like) speed of 40 mm/min toward the inflamed side. Capable of phagocytosis and moisture. Able to respond to chemical stimuli such as certain substances produced by inflamed tissues or by bacteria, or chemicals introduced from the outside into the body. Positive chemotaxis means attracting and concentrating leukocytes to the inflammatory site, while negative chemotaxis means driving leukocytes further away. Capable of responding to thermal stimuli. 1.2 Classification of granulocytes There are three types of granulocytes, named for the staining properties of each granule, which are:
Neutrophils; Basophils; Eosinophils. eosinophil 1.3 Normal index of granulocytes Normal index of granulocytes is:
Neutrophils: 1700 - 7000 cells/mm3, rate 60 - 66%. Basophils: 10 - 50 cells/mm3, rate 0.5 - 1%. Eosinophils: 50 - 500 cells/mm3, rate 2 - 11%.
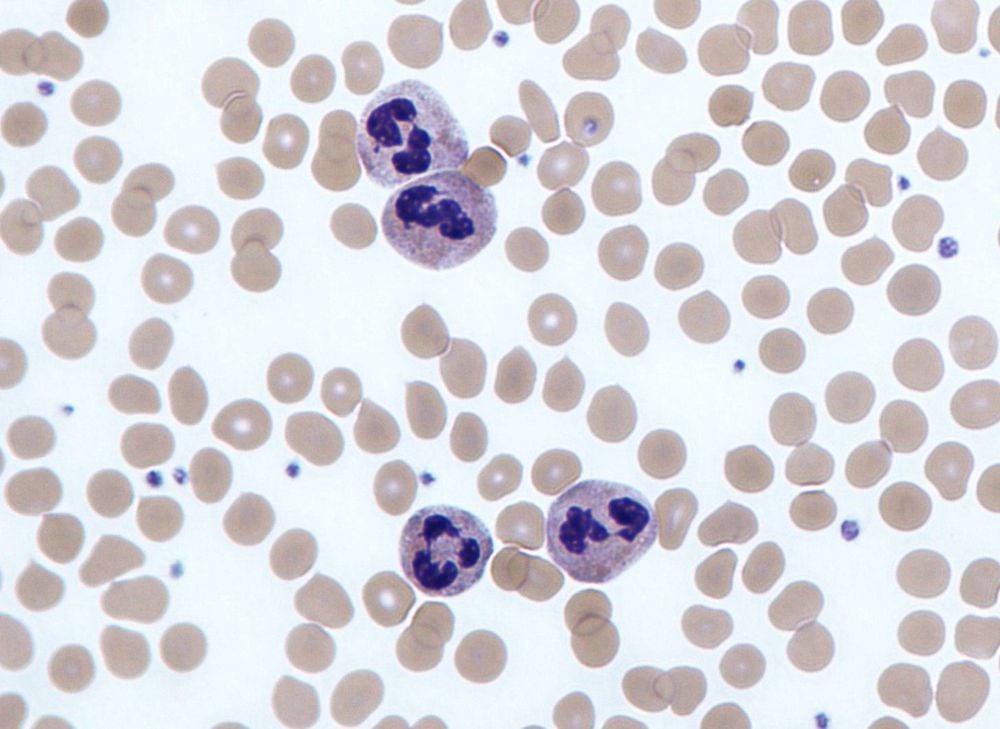
Bạch cầu hạt
2. Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are specialized cells of the immune system and are very common in the lymphatic system.2.1 Characteristics of Lymphocytes Has the ability to change shape, to penetrate vascular walls between cells and to move with prosthetic legs (amoeba-like) at a speed of 40 mm/min towards inflammation. Capable of phagocytosis, moisture cells. Able to respond to chemical stimuli such as certain substances produced by inflamed tissues or by bacteria, or chemicals introduced from the outside into the body. Positive chemotaxis means attracting and concentrating leukocytes to the inflammatory site, while negative chemotaxis means driving leukocytes further away. Capable of responding to thermal stimuli. 2.2 Classification of lymphocytes In the blood, there are three types of lymphocytes, which are:
B cells: produce antibodies that bind to pathogens to facilitate their destruction. T cells: CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) that coordinate the responses of the immune system (this type of white blood cell is often impaired when the body is infected with the HIV virus or has immunodeficiency syndromes) natural). Natural killer (NK) cells: CD8+ (cytotoxic) T cells and natural killer cells are capable of killing the body's cells infected with intracellular pathogens. . 2.3 Normal index of lymphocytes Normal index of lymphocytes is: 1000 - 4000 cells/mm3, rate 20-25%.
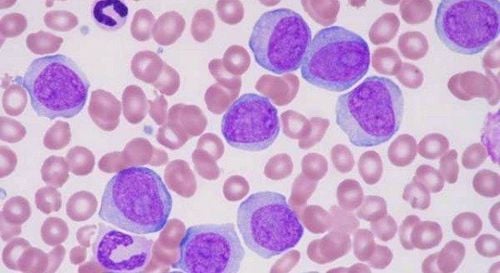
Bạch cầu lympho
3. Mononucleosis
3.1 Characteristics of monocytes They have the ability to change shape, penetrate the vascular wall between cells, and move in a prosthetic (amoeba-like) direction at a speed of 40 mm/min towards inflammation. Capable of phagocytosis, moisture cells. Able to respond to chemical stimuli such as certain substances produced by inflamed tissues or by bacteria, or chemicals introduced from the outside into the body. Positive chemotaxis means attracting and concentrating leukocytes to the inflammatory site, while negative chemotaxis means driving leukocytes further away. Capable of responding to thermal stimuli. 3.2 Role of monocytes Monocytes have a similar effect to neutrophils, but they last longer because they have different complementary roles. Blood monocytes as well as their copies in tissues - phagocytosis plays a role in delivering antigens of pathogens to T cells. Mature monocytes can differentiate into macrophages cells in different tissues in the body. 3.3 Normal index of monocytes Normal index of monocytes is: 100 - 1000 cells/mm3, ratio 2 - 2.5%.White blood cells (or white blood cells) play an important role in increasing the body's resistance to pathogens. An increase or decrease in white blood cells is a warning of health problems. So when you see abnormal signs of the body related to an abnormal change in the number of white blood cells, you should see a doctor for the most accurate diagnosis.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.