This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Resident Doctor, Master Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Ovarian tumors are very common in women and can cause many dangerous complications because of their high rate of malignancy. To diagnose and detect the disease early, doctors have applied transvaginal ultrasound according to IOTA.
1. Importance of ultrasound in the evaluation of ovarian tumors
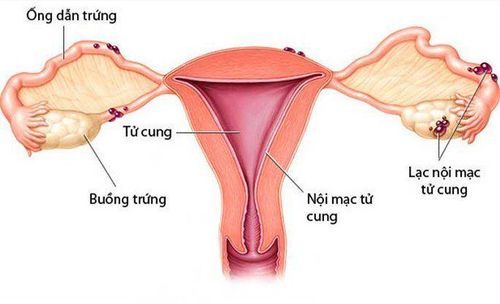
1.1 Understanding Ovarian Tumors and Ovarian Cancer Ovarian cancer is one of the most common types of tumor, accounting for 30% of all tumors of the female reproductive system. Among them, ovarian cancer has a relatively high incidence.
Common symptoms of ovarian cancer are pain, abdominal pain, abdominal distension, abdominal enlargement, change in urination, defecation, indigestion, nausea,... These symptoms are quite vague. , like many diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, ... so patients are often detected late. Ovarian cancer is the most invasive and malignant gynecological cancer. Only 40% of patients can live more than 5 years. The most important prognostic factor in the survival of ovarian cancer patients is the stage of the disease. Therefore, there is a need for a screening method, early detection of the disease at an early stage to reduce the risk of death for patients.

1.2 Learn the ultrasound method of ovarian tumor Ultrasound is the most widely used technique in diagnosing ovarian tumors because this method gives accurate, fast results, can be performed many times and has low cost. reasonable fees. Ultrasound not only detects ovarian tumor early, but also continuously monitors the growth of the tumor, thereby providing timely treatment options for each specific case. Thanks to ultrasound, patients have many conditions to apply the best treatment methods, thereby minimizing unfortunate risks.
However, showing the common image in ultrasound with the characteristics of each type of ovarian tumor, evaluating the value of ultrasound in the diagnosis of ovarian tumors is still inconsistent. Therefore, this article explores more closely the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) classification in the evaluation of ovarian tumors by transvaginal ultrasound.
2. Ultrasound assessment of ovarian tumors according to IOTA
Many types of benign and malignant ovarian tumors have very specific features on ultrasound, which help doctors make an almost accurate diagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to have a uniform descriptive and diagnostic terminology to be able to diagnose and evaluate the risk of malignancy of the tumor. And diagnostic criteria according to IOTA were applied.
2.1 Terms to describe ovarian tumor on ultrasound according to IOTA Tumor size: Measure the size in 3 dimensions (on 2 planes perpendicular to each other); Echo Density: Blank, Poor, Mixed, or Thick (homogeneous or heterogeneous); Wall: Measure the wall thickness (the ultrasonic wave cross section is perpendicular to the wall); Buds: Count the number of shoots, measure the 2-dimensional dimensions (including height and width); Wall u: The inner border is even or irregular; Color Doppler: There is flow on color doppler in tumor wall, bud, wall, solid part; Ascites: Yes or No. 2.2 Classification of ovarian tumors according to IOTA Unilocular cyst: One-lobed cyst, without walls, without buds or without solid tissue. The rate of malignancy is only 0.6%; Unilocular-solid cyst: A cyst with a solid part or at least one bud. The rate of malignancy is up to 37%; Multilocular cyst: Cyst with at least 1 wall and no solid component and no buds. The rate of malignancy is about 10%; Multilocular-solid cyst: The cyst is multi-lobed, with a solid part or with at least one bud. The rate of malignancy is quite high at 43%; Solid: The tumor has a solid component of more than 80%. The highest rate of malignancy, up to 65%. 2.3 Common types of ovarian tumors can be diagnosed with certainty on ultrasound
Simple cyst 1 lobe; There are back shadows; Presence of solid tissue with a maximum diameter of no more than 7mm; Smooth multilobed cyst less than 100mm in size; There is no vascular proliferation. Malignant ovarian tumor
Presence of ascites; Have at least 4 buds; Non-homogeneous solid tumor; Multilobed cyst - irregular solid, over 100mm in size; Increased blood vessel proliferation. This rule is applicable in 78.2% of cases with a sensitivity of 96.2% and a specificity of 88.6%.
Vaginal transvaginal ultrasound to evaluate ovarian tumors according to IOTA has high accuracy, helping to increase the likelihood of successful treatment for patients.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital systems have been using modern generations of color ultrasound machines. One of them is GE Healthcarecar's Logig E9 ultrasound machine with full options, HD resolution probes for clear images, accurate assessment of lesions. In addition, a team of experienced doctors and nurses will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the body in order to provide timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.