This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Pregnancy with ovarian cysts, if not detected and handled in time, can seriously affect the health of the mother and the fetus. Endotracheal anesthesia is an anesthetic method used in most cases of laparoscopic ovarian tumor surgery on pregnant patients.
1. How dangerous is a pregnant woman with ovarian tumor?
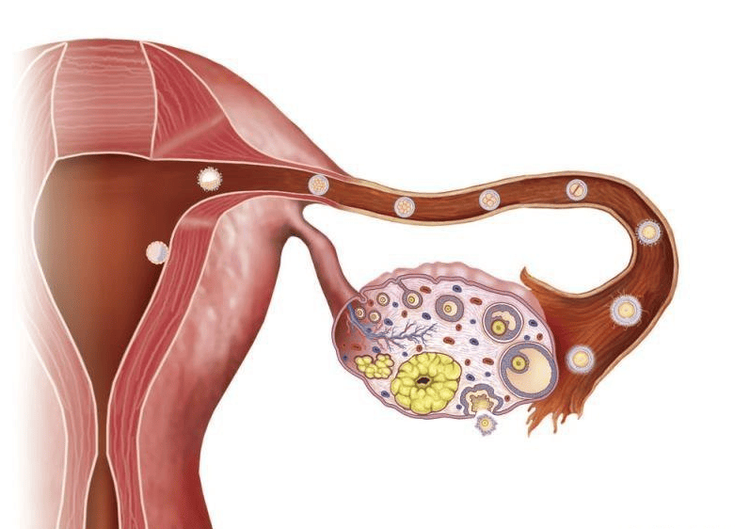
It is not uncommon for pregnant women to have ovarian cysts. These ovarian tumors may be present before pregnancy but go undetected or may appear during pregnancy. Cysts that appear during pregnancy are usually luteal cysts.The corpus luteum is the remains of the follicle after the release of the oocyte. The corpus luteum secretes hormones that help nourish and support the development of the uterine lining, creating favorable conditions for the embryo to implant. When the fetus reaches 10-12 weeks, the corpus luteum will gradually shrink and disappear. A corpus luteum cyst is a condition in which the corpus luteum does not degrade but continues to fill with fluid, present on the ovary.
When pregnant women have ovarian cysts, the level of danger of ovarian cysts to the mother's health and pregnancy depends on the size and type of cyst. The cyst may be small or benign at first, but with the development of pregnancy, the cyst can increase in size and cause dangerous complications such as: : When the tumor grows to a large size, the solid form will press on the uterus, affecting the development of the fetus. Tumors pressing on the uterus can also stimulate the uterus to contract more, causing the fetus to be expelled early. In addition, the tumor can press on the bladder causing urinary retention, on the intestines making constipation worse, the tumor on the ureter can cause pyelonephritis, kidney failure. Difficult delivery: around the 7th or 8th month of pregnancy, the fetus will turn its head down to facilitate birth. But if a pregnant woman has a large ovarian tumor that presses the uterus against the abdominal wall, the fetus cannot turn its head, causing difficulty in childbirth. In addition, during labor, if the tumor is 10cm or more in size and is located in the pelvis, the tumor will prevent the fetus from entering the pelvis to come out, forcing a cesarean section. Torsion: Ovarian tumors with stalk, small and medium size but heavy density often have a high risk of torsion. The time when the tumor is prone to torsion is when the mother has just given birth, the uterus shrinks, the abdomen is spacious, so the tumor has space to move a lot, causing torsion. Malignant neoplasms: Malignant neoplasms are usually those that lie in the abdomen for a long time but are not detected and treated in time. The rate of ovarian cancer during pregnancy is 1/10,000-1/25,000.
2. How are pregnant women with ovarian tumors treated?
Ovarian cysts when discovered need to be operated on as soon as possible. But for pregnant women with ovarian cysts, if ovarian tumors are detected in the first 3 months, the doctor will closely monitor and wait until the end of 3 months to perform surgery to limit miscarriage and fetal malformations. due to drugs...If ovarian tumor is detected in the last 3 months of pregnancy, surgery to remove the tumor will be combined with cesarean section. However, in the process of monitoring the tumor, if a malignant degenerative tumor is suspected, surgery must be performed immediately to save the life and health of the mother. The most commonly used surgical procedure for pregnant women with ovarian cysts is laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy.
This method has many advantages such as high safety, fast implementation time, less pain for the patient. Endotracheal anesthesia is the method of anesthesia used in most cases of laparoscopic ovarian tumor surgery in pregnant women.
3. Procedure for endotracheal anesthesia for ovarian tumors in pregnant patients
3.1. Point
Laparoscopic endotracheal anesthesia for ovarian tumors in pregnant patients is a technique of general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation to control breathing during surgery (possibly in postoperative recovery). Endotracheal anesthesia is indicated in the following cases:Laparoscopic surgery on pregnant women with large ovarian cysts causing compression. Breathing with a mask is difficult or requires close control of the airway, especially in emergency surgery and with a full stomach. Maintain anesthesia with inhalational anesthetic. Endotracheal anesthesia for ovarian tumors is not performed when the patient does not agree or when the medical facility does not have enough anesthesia and resuscitation facilities, and is not proficient in the technique.
3.2. Prepare
The technical team includes: doctors and nurses specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation. Necessary technical equipment includes: system of anesthesia machine with breathing, life function monitor (ECG, SpO2, arterial blood pressure, EtCO2, breathing rate, temperature), hand squeeze oxygen source, defibrillator, aspirators, anesthetics, analgesics, muscle relaxants, antidotes and adjuvants,... Laryngoscopes, endotracheal tubes of all sizes, masks, straws, oropharyngeal catheters, Magill pliers, soft mandrin. Lidocaine 10% spray, Salbutamol spray and means of prevention of difficult intubation such as Cook tube, tracheostomy kit, flexible bronchoscope, laryngeal mask, mouth opener,... Patients : will be examined before surgery to detect, assess the level and offer preventive measures for the risks of difficult intubation, cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine, and embolism risks. , vomiting pain after surgery ... . The patient will be consulted by the medical staff on the purpose of the anesthetic technique and the possible complications during the procedure such as air embolism, subcutaneous emphysema, subcutaneous hemorrhage,... Spirit can be used from the night before surgery if necessary.3.3. Steps to perform endotracheal anesthesia for ovarian tumors in pregnant patients
Patients are instructed to lie supine on the operating table and breathe 100% oxygen at a dose of 3-6 liters/minute at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia.The crew installed a machine to monitor vital signs (EtCO2 parameters are required), set up the transmission line. Then perform pre-anesthesia with Fentanyl 100mcg, can add Midazolam 1-2mg.
Steps to induce anesthesia include:
Sleeping pills: can use intravenous anesthetics such as Propofol, Etomidate, Thiopental, Ketamine, ... or volatile anesthetics such as Sevofluran,... Painkillers: can be used fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine,... Muscle relaxants: succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium,... are used depending on the circumstances. Prophylaxis of gastroesophageal reflux with H2-receptor antagonists (ranitidine, famotidine,...) and/or antiemetic Metoclopramide. The process of endotracheal intubation will usually be done when the patient is in deep sleep with enough muscle relaxation. Oral intubation technique includes the following steps:
The doctor opens the patient's mouth, puts one hand under the neck to keep the neck straight, inserts the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, moves the tongue to the left, and inserts the lamp. Go to the epiglottis, find the epiglottis and the glottis. Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and the Sellick maneuver in case of full stomach. Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 1-2cm through the vocal cords; Gently withdraw the laryngoscope; Intubation of endotracheal balloon; Listen to the lungs and check EtCO2 results to check the position and ventilation status of the endotracheal tube; Secure the tube with adhesive tape. Put the canul in the mouth to avoid biting the tube if necessary; If it is difficult to intubate the patient, the team will switch to the difficult intubation procedure.
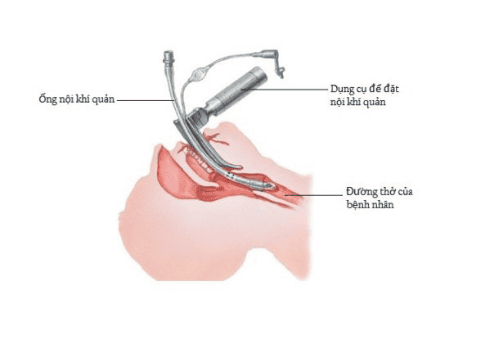
After the end of laparoscopic ovarian tumor surgery, the endotracheal tube will be removed when the following criteria are met:
The patient is awake, breathing evenly, breathing rate, Sp02, normal air volume.. . within normal limits; pulse and blood pressure are stable. No residual muscle relaxant, TOF > 0.9. Arterial blood gas results were within normal limits. There were no complications of anesthesia and surgery.
4. Possible complications during endotracheal anesthesia for ovarian tumors in pregnant patients and how to handle them
4.1. Reflux of gastric juice into the airways
If there is digestive fluid in the oral cavity and airways, the doctor will stop ventilation, put the patient's head down, tilt the head to the side, and drain the fluid. Perform rapid intubation technique and use other drugs if necessary, along with monitoring and prevention of postoperative lung infections.4.2. Hemodynamic disorders
Possible hemodynamic disturbances are hypertension, hypotension, and arrhythmias. Depending on the case and cause, the doctor will have an appropriate treatment.
4.3. Complications due to endotracheal intubation
Possible complications during endotracheal intubation of ovarian tumors in pregnant patients include:If the endotracheal tube cannot be intubated due to difficulties, changes in the anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system during pregnancy, handle difficult intubation procedures or switch to another method of anesthesia; If the endotracheal tube is inserted into the stomach by mistake, there will be no alveolar murmur when listening to the lungs and no measurement of EtCO2. In this case, the endotracheal tube will be reintubated; If laryngotracheal-bronchospasm occurs, the crew will provide enough oxygen, add sleeping pills, muscle relaxants, bronchodilators and corticosteroids to ensure ventilation. If breathing is not controlled, proceed with difficult intubation procedures; Injuries that can occur during endotracheal intubation such as bleeding, broken teeth, damage to the vocal cords, foreign objects falling into the airways, etc. The doctor will handle depending on the specific injury case.
4.4. Respiratory complications
The endotracheal tube can be folded, retracted, the tube pushed deep into one lung, collapsed or open the respiratory system, exhausted oxygen or soda, leading to hypoxia and hypercapnia. Ventilation and 100% oxygen must be ensured immediately, and the cause is found and resolved.4.5. Complications after extubation
After extubation, the patient may experience respiratory failure from various causes, such as sore throat hoarseness, laryngotracheal spasm, upper respiratory tract infection, laryngotracheal stenosis, ... The doctor will treat according to symptoms and specific causes.4.6. Complications in laparoscopic surgery for ovarian tumors
In addition to the complications caused by endotracheal anesthesia, the patient is at risk of complications due to endoscopic ovarian tumors such as air embolism, subcutaneous pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumothorax, arrhythmia, etc. Blood pressure due to hypercapnia, perforation of hollow viscera causing peritonitis,.... Trendelenburg position during endoscopy increases the risk of atelectasis, reduces lung compliance, and reduces visceral blood flow.In order to limit the above-mentioned complications, during endoscopic ovarian tumor in pregnant women, the doctor will limit drugs that affect the fetus, control the pressure of CO2 into the abdomen from 10-12mmHg. , closely monitor hyperextension through Capnography, EtCO2 should not exceed 50mmHg. When performing laparoscopic ovarian tumor with Trendelenburg position, the head should not be lower than 15 degrees. At the same time, closely monitor the patient to prevent atelectasis, subcutaneous emphysema, pneumomediastinum,...
Ovarian cysts during pregnancy have many potential dangers to pregnant women. Therefore, before and during pregnancy, you should check your health regularly to detect the disease early and have timely treatment.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy, including:
Health checkup package Diamond Health Checkup Package Vip General Health Checkup Package Special General Health Checkup Package Comprehensive General Health Checkup Package Standard General Health Checkup Package Patient's examination results will be returned to your home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.