This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Dr. Pham Quoc Thanh - Diagnostic Imaging Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Shoulder joint is an important joint in the movement of the human body. Accordingly, the mobility of the shoulder joint is also greater than that of other joints. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the shoulder joint is considered the most optimal imaging method for diseases related to bones and joints, including the shoulder joint.
1. Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder joint
Shoulder joint is an important joint in movement and activity of the body. The shoulder joint has a greater range of motion than other joints in terms of space and frequency. However, the clavicle joint is less stable than other joints because the socket surface is small and shallow, and the humerus head is larger.
Anatomy of the shoulder joint connecting the socket of the scapula to the crest of the humerus. The socket is a shallow hollow, smaller than the top of the humerus. Around the socket there is rim cartilage.
The joint capsule surrounds the upper alveolus and the lower humerus. The brachial fascia extends from the crow's process to the large and small tubercles above the humerus. The brachial fascia ligaments are thickened portions of the joint capsule that include the superior, medial, and inferior ligaments.
The muscles involved in the shoulder joint area include: subscapular muscle, large round muscle, broad back muscle, pectoralis major, brachiocephalic muscle (in front), supraspinatus, infraspinatus muscle, small round muscle (back), muscle in the shoulder joint. delta (outside). The muscles above the spine, under the spine, in the small round, below the shoulder form the rotator cuff muscles.
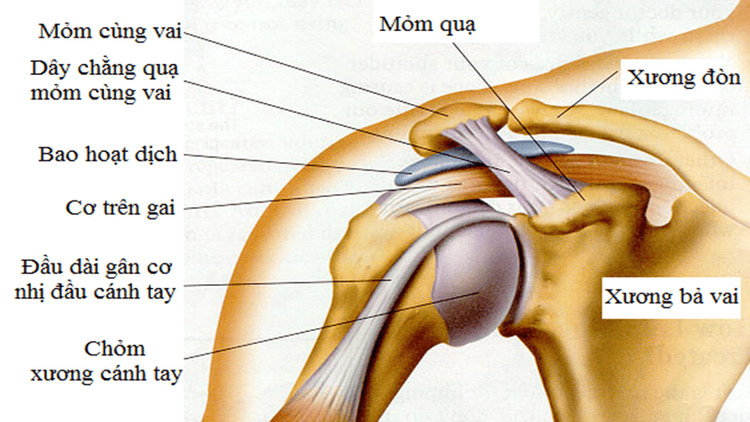
Giải phẫu khớp vai
Anatomical or pathological changes in the bony, ligamentous and soft structures around the joint that affect joint mobility. Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder joint will give good images to assess the pathologies of the shoulder joint.
2. Pathologies in the shoulder joint requiring magnetic resonance imaging
MRI of shoulder joint is indicated in the following cases:
Abnormalities of tendons, rotator cuff muscles Lumbar cartilage Shoulder muscles Disease bursitis Bone marrow disorder Tumor and arthritis of shoulder Disease Vascular management Neurology Injury, fracture and dislocation of the shoulder, shoulder instability, compression syndrome, post-operative examination.
Chụp MRI để kiểm tra phát hiện các bệnh lý vùng khớp vai
3. Procedure and steps for performing magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder joint
Step 1: Prepare the patient
Have the patient go to the toilet before the examination Have a copy of the request from a clinician with a clear diagnosis or complete medical record (if necessary). Explain the procedure to the patient clearly to coordinate well in the examination. Ask the patient to remove anything that contains metal (dentures, hearing aids, hairpins, jewelry, ear rings...) Ensure that the patient understands and completes the consent form. MRI . Provide patient with earplugs or ear protectors, listen to music. If necessary, insert an intravenous line before entering the imaging room. Step 2: Patient position
The patient lies supine on the table with both legs extended, the palm of the side to be taken is supine and extended. Place the shoulder on the side to be covered on the coil, and place the cushion on the opposite shoulder and hip so that the patient's back is at a 20° angle with the table. Secure your hands with a foam padded sandbag.
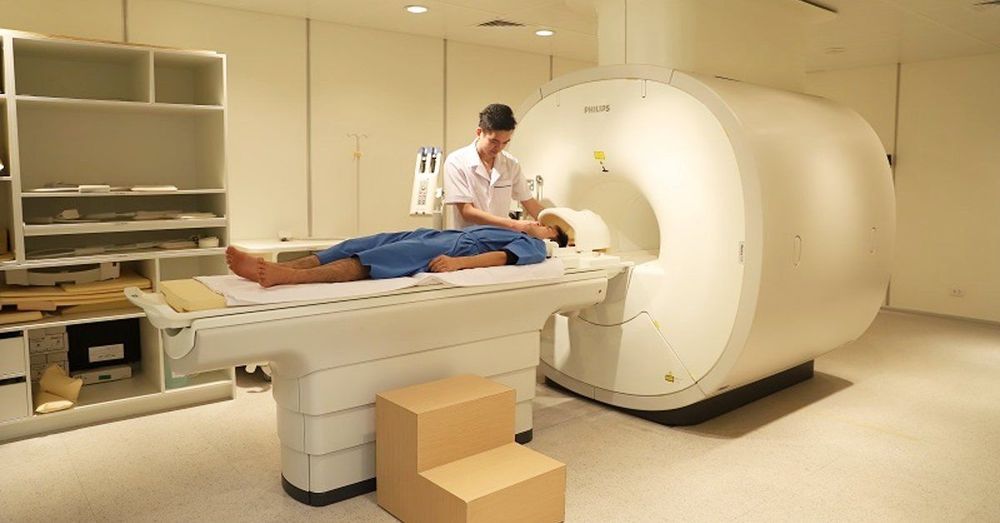
Bệnh nhân thực hiện chụp theo hướng dẫn của nhân viên y tế
Step 3: The technician conducts a scan
Survey the shoulder joint with cross-sections of the fronto-oblique direction parallel to the joint longitudinal axis, the longitudinal-oblique direction perpendicular to the joint longitudinal axis and the horizontal direction. Often examine the SE pulse sequence, with the fat removal pulse sequence. Survey with contrast injection into the joint when evaluating the cartilage around the joint. Investigation with injection of magnetic contrast in the case of evaluation of inflammatory diseases, tumors or after surgery. Step 4: End the examination
Instruct the patient to go out and wait for the doctor to read the results. Film technician MRI scan of shoulder joint can detect bone lesions in trauma such as non-displaced fracture, edematous bone marrow , the trauma cases were X-ray or computed tomography but not detected. Not only that, bone and joint magnetic resonance imaging also helps to evaluate soft shoulder joint injuries, muscle tendons, ligaments, etc. associated with bone injuries.
Chụp MRI có nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội hơn các phương pháp chẩn đoán hình ảnh thông thường
Currently, in order to improve the examination and diagnostic work, Vinmec International General Hospital has put into use a 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging machine with Silent technology. A 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging machine with Silent technology from GE Healthcare (USA) will bring the following benefits:
Silent technology is especially beneficial for patients who are children, the elderly, and the elderly. Weak health conditions and surgery patients Limit noise, create comfort and reduce stress for customers during the shooting process, help capture better quality images and shorten shooting time. Magnetic resonance imaging technology is the technology applied in the most popular and safest imaging method today because of its accuracy, non-invasiveness and non-X-ray use. Customers can go directly to the system. Vinmec Health System nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here.