This is an automatically translated article.
Lymphoma is one of the most common clinical pathologies, which can occur at any age from infants, young children to the elderly. Lymphoma also has many different forms, each type has its own symptoms. Lymphoma if detected early can be treated. Depending on the condition and size of the tumor to choose to treat lymphoma with drugs or by surgery.
1. What is a Lymphoma?
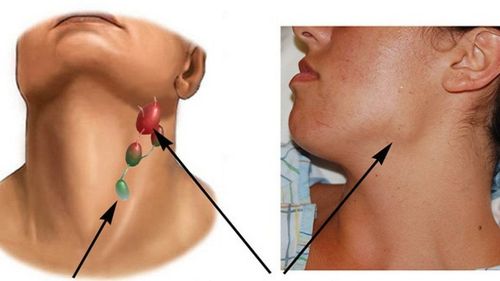
Lymphoma or lymphoma , which is one of the common malformations of the lymphatic system, the disease can occur at any age, in any location on the body. Research on clinical data shows that approximately 50% of lymphomas occur in infancy and 90% of lymphomas occur in children under 2 years of age.
Lymphoma can be congenital or acquired:
Congenital lymphoma: Most are diagnosed prenatally through pregnancy ultrasound. Acquired Lymphoma: Common after trauma, inflammation, or problems that block the lymphatic system. The disease can be discovered incidentally or when the patient presents with mild pain in the affected area. Lymphoma has 3 different types:
Lymphoma: This is a lemon-yellow tumor that is filled with protein-rich fluid inside. Lymphoid cysts come in many different sizes and are often composed of many cysts. Capillary lymphangioma: Usually occurs in small lymphatic vessels due to abnormalities in vascular structure. The tumor is located in the epidermis of the skin in the form of small clusters of pink to dark red bumps. This is a benign lesion. Cavernous lymphangiomas: Usually present at birth, most often in the neck of the tongue and lips. Lesions are located deep under the skin in dilated lymphatic vessels, raised above the skin surface and often have a tendency to invade surrounding tissues. Clinically, depending on the location and size of the tumor, each patient will have different symptoms. Lymphoma is mainly diagnosed based on clinical symptoms, ultrasonography and cytology aspiration from tumor sites.

U bạch huyết thường gặp ở trẻ nhỏ và trẻ sơ sinh
2. Lymphoma treatment
In fact, most people don't pay much attention to the treatment of lymphoma until the tumors get bigger and cause cosmetic problems or complications such as compression of the lymph nodes appear. breathing...
Depending on the type of tumor, the size of the tumor, different treatment methods will be given:
For capillary lymphangioma: Mainly using the lymphatic drainage method. hematologic or surgical excision of the lesion, or laser treatment. For lymphatic cysts: Sometimes surgery is also an option for treatment, but it is difficult to completely remove the affected area because the surgical method is difficult to assess the tumor margin leading to easy relapsed. For cystic form, when treating mainly using non-invasive methods: sclerotherapy, ie injecting drugs directly into the cyst. Lymphoma injection is a relatively safe, highly effective, non-invasive method of treating lymphoma. This method uses drugs (tetradecyl sulfate, doxycycline or alcohol) injected directly into the lymph node lesions causing destruction of the epithelial lining in the tumor spaces, and at the same time reducing the secretion of these cells. lymph fluid, then the tumor size will gradually shrink.
Indications of the injection method to treat lymphoma:
Apply to all cases of lymphoma in children type 1,2. Cases of type 3 lymphoid cysts. Superinfected or compressed lymphatic cysts. Contraindications:
Lymphatic cysts in the abdomen or mediastinum Pediatric patients with a history of allergy to doxycycline, interstitial pneumonia or pulmonary fibrosis Pediatric patients with blood diseases such as coagulation disorders Children with family The family does not agree to be treated with injections.

Bệnh nhi viêm phổi không được chỉ định tiêm thuốc
Procedure:
Check medical records.
Check the patient's current health status, if necessary, then administer the injection.
Carry out the injection according to the following steps:
Anesthesia of the whole body Place the patient in a lying position on the opposite side Mix the medicine according to the standard ratio of the Ministry of Health Using the 18th needle to poke the lower lymph nodes guidance of the ultrasound system. Aspirate fluid from the lymphatic follicles for testing, and then proceed to inject drugs directly into the tumor through the placed needle. Note, after injection, the patient should be kept in the hospital for at least 24 hours to monitor the subsequent symptomatic reactions. Discharge the patient after 1 day if there is no abnormality. Some side effects may occur for patients treated for lymphoma by injection method:
Pain at the injection site, maybe slight redness and swelling. In some cases, the tumor is so large that it will put pressure on the surrounding tissues, then it is necessary to prescribe pain medication. Some children will have diarrhea, fever especially in the first days after injection. After 2 weeks of injection, it is possible to see an increase in the size of the tumor, the density is harder at first but then it will gradually decrease. Especially, for cases of very slow response or no response to the injection method after 3 times of use, it is necessary to change the surgical method for more effective treatment. Remind and advise patients to re-examine after 1-6 months after injection.
Lymphoma is not an acute disease, but it can also be harmful to the patient's aesthetics and health, even in some cases, it may develop into cancer due to the impact on the tumor. right way. Please go to the doctor immediately if you find that your health has abnormalities for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment, to avoid affecting your health.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
MORE
Diagnosis of lymphoma by ultrasound Is hemangioma in children dangerous? Common types of subcutaneous hemangiomas