This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Van Sang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has 18 years of experience in the field of Dermatology.Hemangiomas appear in many places on the body, mainly in the head, face, and neck. Currently, hemangiomas are often classified based on tumor organization or clinical features.
1. Advanced stages of hemangioma
Hemangioma is a common benign tumor in young children, formed by the proliferation of blood vessels (including arteries, veins and capillaries). 59% of hemangiomas occur in neonates, 40% at full month, and 30% in premature infants weighing less than 1.8 kg. According to statistics, 60% of hemangiomas appear on the head, face and neck. Few appear in viscera.Hemangiomas progress in 3 stages:
Proliferative phase: Usually occurs in about 3-6 months for superficial hemangiomas, 8-10 months for deep hemangiomas. At this stage, 80% of hemangiomas double in size, of which 5% grow quickly, affecting organ function, aesthetics and even life-threatening. Stable stage: After the proliferative phase, the hemangioma gradually stabilizes in size and clinical signs, lasting when the child is 18-20 months old. Regression stage: The progression is quite slow, at first the skin color in the hemangioma fades, then the subcutaneous hemangioma gradually collapses but more slowly. This regression occurs in 70-80% of cases of hemangioma over 6 years of age. The regression of subcutaneous hemangiomas is usually slower than that of subcutaneous hemangiomas. However, through follow-up, if the hemangioma does not regress but continues to grow and invade organs, the doctor will offer the most appropriate treatment options for the patient.

2. Classification of hemangiomas
2.1 According to histology, hemangioma is the most common type, accounting for about 60% of cases of hemangioma. In patients with hemangiomas, capillaries proliferate and dilate the skin but no proliferation of endothelial cells. Capillary hemangiomas contain capillaries of various stages of development, with empty capillaries, full capillaries, wide and irregular like normal capillaries.
Cavernous hemangioma This form of hemangioma accounts for about 30% of hemangiomas. Cavernous hemangiomas are organized like erectile organs, consisting of small, blood-filled, interconnected cavities and often have a fibrous sheath that can press on hard tissues below. Sometimes the hemangiomas in a cavernous hemangioma are separated by collagenous septa that are rich in reticular tissue and lack elastic. In cavernous hemangiomas, the capillaries are very dilated.
This form of hemangioma can be combined with other lesions, especially with lymphangiomas, forming hemangiomas - lymphangiomas. In addition, it can also combine with other organs such as muscle, bone, cartilage,... to form hemangioma in muscle, hemangioma in bone,...
2.2 Clinical In clinical terms, There are the following types of hemangiomas:
Superficial subcutaneous hemangioma is a type of hemangioma located close to the skin, with the form of a tumor containing enlarged, proliferative, and blood stasis capillaries accompanied by cavernous organization. Superficial subcutaneous hemangiomas appear later, progress slowly, and are usually only discovered when they are quite large. This type of hemangioma can reach the size of an orange, appear singly or in 3-4 scattered tumors on the face, especially in the neck area. Superficial hemangiomas may be normal in color or pale purple, have superficial veins running above them, and enlarge during strenuous work or when bending over.
Superficial hemangioma under the skin is soft to the touch, painless, can be deflated and re-inflated after a few seconds. This type of hemangioma does not cause dysfunction, only causes problems, difficulties when working and affects aesthetics.
Deep subcutaneous hemangioma is a type of hemangioma deep in the soft tissue, deeper than the fat layer, which can infiltrate muscles and deep-lying organs such as salivary glands and nerves. Manifestations of deep hemangiomas are quite similar to superficial hemangiomas under the skin, but the skin is often more infiltrated, there are veins running above the tumor, the skin is slightly wrinkled, pink or purple. The tumor rarely protrudes from the skin, mainly spreads deep. Hemangiomas deep under the skin also swell up when bending the head or doing heavy work, partially deflated.
This type of hemangioma develops slowly, greatly affects aesthetics and causes organ dysfunction depending on the location of distribution. Specifically, a hemangioma deep under the skin can press on the underlying bone, causing deformation, abrasion, lime loss, leading to osteoporosis,... In particular, the tumor can invade the bone and cause internal hemangioma. the bone.
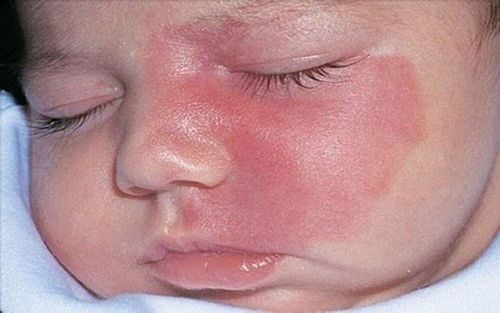
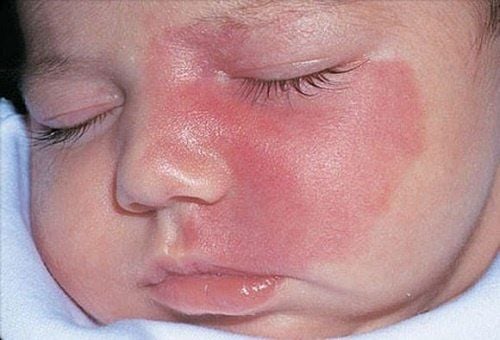
Port-wine stain Flat hemangioma is a congenital disease with malformed lesions in the capillaries of the skin. In it, the capillaries are dilated and there is no proliferation of endothelial cells. The manifestation of flat hemangioma is the appearance of dark spots on the skin, which are pale pink, light red or crimson, not thicker than the surface of the skin, elastic and soft (with the same properties as normal skin, only different in color). ).
Flat hemangiomas vary in size, from as small as a coin to as large as half the face. This is a congenital form of hemangioma, which tends to grow and spread with age and only affects aesthetics, not causing organ dysfunction. However, flat hemangiomas can also progress to depth, infiltrate layers of the skin or into fat, muscle, mucosa, etc., causing facial deformity and large growth, affecting the function of the agencies. At the same time, the surface of the birthmark may be rougher, more rough, become small lumps, the skin covering it may become wrinkled and turn into a hemangioma (bulb hemangioma).
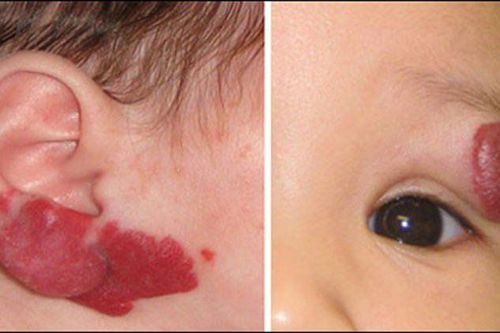
Hemangioma (bulb hemangioma) Hemangioma can be due to progressive flat hemangioma or congenital. Tumors protrude from the skin from a few mm to 1cm or more, dark pink, burgundy, covered with slightly wrinkled skin, easy to bleed when touched, leading to infection. Sometimes hemangiomas form a broad mass on the face or along the neck. This type of hemangioma can grow and spread with age, or stop growing, shrink, and go away on its own.
Hemangiomas that develop from flat hemangiomas are common in middle-aged or elderly people. The tumor manifests as a pre-existing flat, lumpy, crimson hemangioma that is wrinkled.
Hemangiomas progress to a degree that will stop on their own, do not spread further, only increase in volume in place, may cover eyes, nose, lips, ... affecting organ functions, aesthetic and psychological well-being of the patient. In addition, the tumor is prone to infection and bleeding, and the skin under the tumor may be slightly infiltrated but not spread to the underlying muscle layer.
Aneurysms This form of hemangioma usually forms from hemangiomas spontaneously or under the influence of trauma or hormonal changes (due to pregnancy). Occasionally, a tangled aneurysm is an intermediate between a hemangioma and an arteriovenous bulge. Turbulent aneurysms consist of enlarged, uneven, bulging, pulsating, and non-collapsible capillaries.
The clinical appearance of a tangled aneurysm is a bump, as large as a tangerine, the skin on the tumor is dark pink, wrinkled, thin, sometimes with prominent veins, clearly visible pulse, easy to bleed and difficult to stop bleeding. Aneurysms deform the face, can affect the function of organs depending on where they form near the nose, lips or ears. In addition, this type of hemangioma can also affect the functioning of the heart.
Oral mucosal hemangiomas Can be flat or bulbous hemangiomas. Oral mucosal hemangiomas are common in the lips, cheeks, tongue, floor of the mouth, cleft palate, soft palate, and can spread to the tonsils, forming a very dangerous tuberous cyst with the uvula. The mucosa that covers the tumor is dark red or dark purple, slightly rough or numerous, entangled, easy to bleed, and affects eating and communication functions. Oral mucosal hemangiomas usually grow wide in the oral cavity, can infect submucosal tissues, muscles, subcutaneous fat, and extend beyond the skin.
Hemangioma in the jawbone is the most dangerous type of hemangioma, which can lead to death. Usually hemangiomas in the jawbone are tumors of the oral mucosa or gums that invade, gradually destroying the jawbone. More rarely, hemangiomas can develop from the center of the jawbone, gradually destroying gums and teeth,...
Some other special types of hemangiomas:
Combined hemangiomas: In the above diseases, there are many Types of hemangiomas can develop and combine with each other such as flat hemangiomas alternating with rough hemangiomas, mucosal hemangiomas interspersed with deep subcutaneous hemangiomas,...
Rendu and Osler scattered hemangiomas: Hereditary, characterized by scattered hemangiomas on the skin and mucous membranes, dark in color, with black spots, dark blue, bleeding or vasodilatation. This type of hemangioma localized to the lung can cause arteriovenous fistula. In the face, it is often localized in the cheeks, neck, oral mucosa, lips, tongue, floor of the mouth, cleft palate, nasal mucosa, ... easy to cause bleeding; Sturge-Weber-Krabbe syndrome: Also known as diffuse neuroendocrine hemangioma, is a congenital disease. Presented as a flat hemangioma on one side of the face, accompanied by a brain hemangioma on the same side. Patients may have visual disturbances, retinal darkening, glaucoma and epilepsy, headache, hemiplegia,... Klippel-Trenaunay and Parkes Weber syndrome: Belonging to a type of brain-facial hemangioma, with Hypertrophy of the face and skull or atrophy of the half of the face and skull, patients with movement disorders, mental disorders, glaucoma,... Hemangiomas can regress or grow strongly, causing many complications unpredictable. Therefore, when detecting hemangiomas, patients should promptly go to major hospitals for accurate diagnosis, monitoring and the most effective treatment options.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.