This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Van Sang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalSome babies are born a few weeks after birth and have a birthmark (a dark area of skin that is bluish-violet, blue, brown, black, pale pink, or bright red) anywhere on their body. body. Birthmarks can be harmless or warn of a number of health problems in the baby that parents need special attention.
1. What is a birthmark?
Birthmarks are an abnormal appearance on the skin of a newborn baby. There are two types of birthmarks: birthmarks made up of blood vessels and birthmarks. Moles can also be considered birthmarks.Birthmarks made up of blood vessels: Incomplete formation, often red. There are 2 types of vascular birthmarks: hemangiomas and wine-red birthmarks; Pigmented birthmarks: Made up of a collection of pigment cells that give the skin its color. They can come in a variety of colors such as tan, brown, gray, black or blue.
2. Harmless birthmarks
Pigmented birthmarks: Dark like black, purple, blue, brown, ... can be a few centimeters small or spread all over the thighs and buttocks. The cause of these birthmarks is the accumulation and abnormal increase of melanin pigment under the skin, which may be accompanied by increased hair. When pressing or rubbing your hand on the damaged skin, the skin remains the same, without losing the birthmark because the fixed pigment is congenital in the dermis and epidermis in the damaged area. As the child grows, these birthmarks will slowly disappear without intervention.
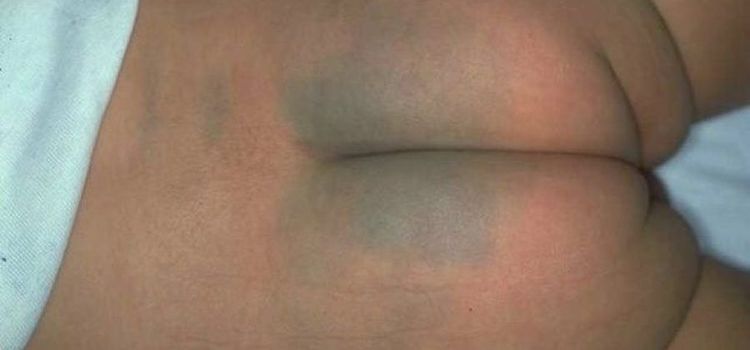
Mongolian birthmarks: Looks like bruises, usually appearing on the baby's hips or lower back. This type of birthmark is completely harmless and by the time the child is 4 years old, the birthmarks will fade away.
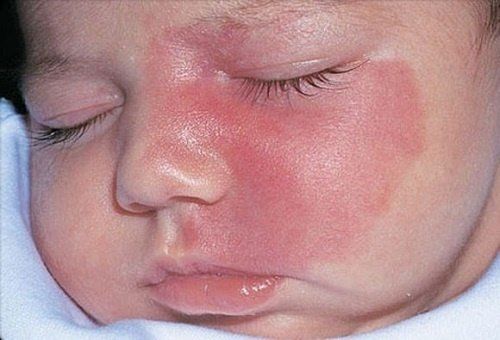
Birthmarks made up of blood vessels: Bright red or pale pink. They often appear during fetal development or after birth. The cause of this type of birthmark is because the small arteries under the skin dilate too much and often, causing a lot of blood to pool in that area.
When you rub the affected area with your hands, the skin will turn pink, light red or normal because at this time the arterioles are pressed, causing blood to be pumped to the surrounding area. On the contrary, when the hand is removed, the blood rushes back and the injured area will be bright red or light pink as before. Those red-pink birthmarks are called flat hemangiomas.
Simple or hairy hypopigmentation, flat hemangioma if not stimulated are all benign lesions. Birthmarks can increase in size but very slowly. By a time like when the child reaches puberty, the birthmark will stop increasing in size, stay fixed for a long time, do not affect the child's health and cause no complications.
However, if hypopigmentation occurs in the eye, malignant degeneration is possible (rare). The most severe effects of melanoma and flat hemangioma are aesthetic loss, making patients lack confidence, affecting psychological development, work and social activities.
3. Birthmarks need attention
Cavernous hemangioma: With birthmarks forming blood vessels, if the arterioles dilate at a higher level, the wall is tufted, clustered or rough on the skin surface, it is called a bulging hemangioma, a cavernous hemangioma. Particularly for cavernous hemangiomas, if scratched, it can bleed smolderingly or massively, causing very dangerous infections and should be handled soon;
Coffee-milk-colored birthmarks: Usually light brown or milky in color, most are oval in shape, can appear right after birth or after a few days or weeks. As the baby grows, the birthmark does not fade.
If your baby has more than 4 coffee-milk-colored birthmarks, it could be a sign of neurofibromatosis, which occurs when a baby's nerve tissue has a proliferative fibrous tumor.
Most diseases are hereditary, in many cases not harmful. However, if the tumor presses on nerve tissue or other tissues, the disease can be dangerous.
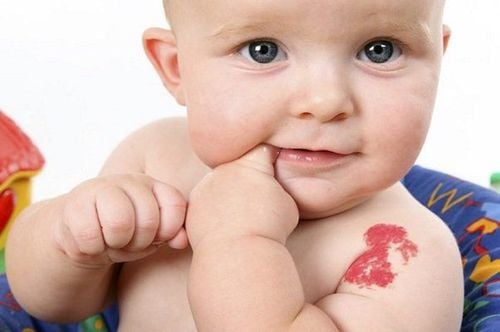
Wine-red birthmark: Like a red or purple dot, a few millimeters to a few centimeters in size, it mainly appears on the face of infants. In addition, it can also appear on other parts of the body, due to leaky blood vessels.
4. Treatment of birthmarks on the skin
In general, for small pigmented or flat hemangiomas, in the closed skin, less prone to trauma, intervention may not be necessary. For birthmarks that are widespread, in open skin, affect aesthetics and psychology, cause guilt, and interfere with social interactions, they can be treated.Depending on the case, age, location and size of birthmark, shallow or deep X-ray, laser, plastic surgery, ... can be used for treatment. Flat hemangiomas in children can be treated with drugs (oral or injected corticosteroids, Interferon alfa-12 to shrink the hemangioma, not to grow further) prescribed by a specialist and closely monitored.
Do not arbitrarily apply medicine, remove birthmarks because it is easy to cause skin burns and infection. Besides, do not shave on the less pigmented hair because the more you shave, the faster and harder the hair grows, causing discomfort.
People with birthmarks should use sunscreen with SPF over 30 when outdoors to prevent complications. At the same time, people with birthmarks should see a dermatologist to determine the type of birthmark and consider treatment in each specific case.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.