This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hong Phuc - General Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.1. Learn about the infectious disease typhus
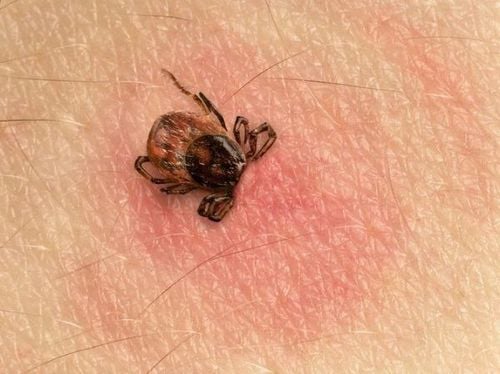
Scarlet fever is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. This bacteria originates from wild animals such as rodents, mainly mice, rabbits, pigs, birds, or dogs, pigs, chickens... The disease is characterized by fever, sores and sores. skin, rash, swollen lymph nodes, damage to many organs and viscera. The disease occurs mainly in the rainy season due to high humidity creating favorable conditions for the larvae to develop. The disease occurs mainly in rural areas, people living on the edge of forests and mountains, people working in agriculture and forestry. How is the disease transmitted? Bacterial mites from wild animals lay their eggs in moist soil and develop into larvae before becoming red mites. Therefore, red-billed larvae are present in many places, especially in wet and humid areas. The larvae then develop into pupae and adults. Humans are infected when bitten by the larvae. After burning, the larvae return to the ground, mature and reproduce the next generation.
+ Some cases are not treated, the patient may have no fever after 10-14 days, the disease is usually completely cured. Fever in pregnant women can cause pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, stillbirth, or low birth weight.
2. Clinical symptoms
The incubation period ranges from 6 days to 21 days. Then there may be onset after a few days such as fatigue, headache, low-grade fever. Full-fledged period: common fever, skin sores, rash, swollen lymph nodes, lesions in organs and viscera. Fever: high fever continuously, malaria shivers or chills in the first stage, after that, mainly hot fever. Accompanying symptoms are headache, pain behind the eye socket, body aches. Skin ulcers are round or oval in shape, shallow, with raised margins, painless, and little inflammation. Ulcers usually reside in soft and closed skin such as inguinal folds, external genitalia, anus, armpits, folds under breast, chest, ears, eyes, etc. Swollen lymph nodes and enlarged liver and spleen. Swollen lymph nodes near the ulcer usually appear by the end of the first week of illness; Generalized lymph nodes usually appear later and are smaller in size. Then appeared splenomegaly and hepatomegaly. A maculopapular or maculopapular rash, sometimes with purpura . The rash first appears on the trunk, spreads to the extremities, or grows all over the body, lasts about 4-5 days. The facial skin is often red, the sclera of the eyes is red, which may be accompanied by burning sensation and photophobia.
3. Diagnosis of infectious disease typhus
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the specific clinical symptoms found characteristic sores caused by larva stings . Clinical diagnosis includes: Serological tests. It is a specific diagnostic method to help detect resistance. Serological tests include indirect immunofluorescence (IFA), enzyme-linked immunosorbent antibodies (ELISA), and rapid tests. Several polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests help diagnose typhus infectious disease.
4. Specific treatment
Fever patients need to be treated with specific antibiotics for typhoid fever according to the doctor's prescription. However, the disease can recur after stopping treatment, especially when using short-term regimens and starting early, during the first week of illness. Therefore, treatment of infectious diseases should be strictly according to the doctor's prescription.5. Prevention
Avoid going to areas where typhus is spreading. People in the fever area need to apply anti-larvae measures such as wearing tight clothes, wearing clothes impregnated with insect repellent chemicals. Kill rats, kill insects, kill weeds or burn weeds. Use preventive medicine in high-risk subjects as directed by a physician. Basic investigation to detect outbreaks in suspected and inhabited areas (catch small rodents, detect, classify, isolate R.orientalis, find antibodies, detect patients). Avoid sitting and drying clothes, placing backpacks on the lawn, near the edge of dust, tree stumps; When going to clear fields for farming, field trips, scouts into the forest, they need to wear shoes and socks, and close their pants to kill them in the environment: residual spraying on wet soil, under 20 cm tall bushes around the house where the sex is located. cool medicine diazinon, fenthion, malathion, lindane, dieldrin, chlordane. Clearing vegetation around the house selects clumps of plants with many mite larvae.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.