This is an automatically translated article.
Whole blood contains all components of blood, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma components. Transfusions of blood and blood products must be used in the right type, in the right patient, and at the right time.
1. Benefits of blood transfusion and use of blood products
Like other medical therapies, blood transfusion brings many effects in the treatment and support of patients' treatment. The role and benefits of blood transfusion can be mentioned as:
Restore hemoglobin to maintain the oxygen-carrying function of the blood; Restore blood volume to maintain the body's vital functions; Restore the ability to clot and stop bleeding, avoiding the risk of continued blood loss; Helps the body's ability to fight infections. Each patient will have different treatment needs and indications for blood transfusion or blood product use. Therefore, blood transfusion and blood products need to be used properly and rationally in order to maximize effectiveness and minimize blood transfusion complications.
Chế phẩm máu cần được sử dụng đúng đắn, hợp lý
2. Possible blood transfusion complications
Some risks and complications that patients may encounter when receiving blood transfusions and using blood products:
Being infected with viruses, parasites, spirochetes through blood transfusion; Blood transfusion complications: Due to immunocompromise, overload, contaminated blood or intermediate substances formed during storage; Iron overload due to blood transfusion.
3. Indications for use of blood and blood products
3.1 Whole blood
Indication: Patient has lost a lot of blood (lost ≥1/3 of body blood). Contraindications: Not for people with kidney failure, heart failure or just anemia. Whole blood is effective in restoring the lost blood volume, the red blood cell mass in the blood helps to alleviate the circulatory burden while maintaining the effectiveness of the treatment of red blood cell deficiency.
3.2 Red blood cells
Red blood cells are obtained from whole blood that has been centrifuged and plasma fraction separated. Depending on the method of extraction, there are different types of red blood cells such as:
Concentrated red blood cells: Indicated for use in cases of anemia. However, because it is concentrated, the infusion is slow, especially at the beginning of the transfusion, there are many white blood cells, so it can cause transfusion reactions and cause premature hemolysis due to substances released from leukocytes and plasma. contain antibodies; Red blood cell block with preservative solution: Indicated for use in cases of anemia due to heart failure, kidney failure; Leukocyte-poor red blood cell mass: Indicated when the patient has pure anemia. This blood product helps to reduce the reaction caused by leukocytes (anti-leukemic antibodies, lymphocytes, mediators) and reduce the risk of disease transmission where the agent resides in the leukocytes; Washed red blood cells: Indicated for transfusion in patients with autoimmune hemolytic anemia; White blood cell filtration and irradiated red blood cells: Indicated for anemia patients with severe immunosuppression, especially patients undergoing organ transplantation or preparing for organ transplantation; 3.3 Platelets
Platelets are one of the important components involved in the clotting process to stop bleeding to prevent bleeding. A lack of platelets causes a variety of bleeding conditions. There are two types of platelets:
Platelets separated from whole blood: Indicated for use in the treatment of diseases causing thrombocytopenia, especially thrombocytopenia after treatment for malignancy; Platelet Extract: Indicated for use in the treatment of severe thrombocytopenia such as dengue fever with severe thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenia after chemotherapy, thrombocytopenia in patients with marrow failure or disorders. marrow physiology.
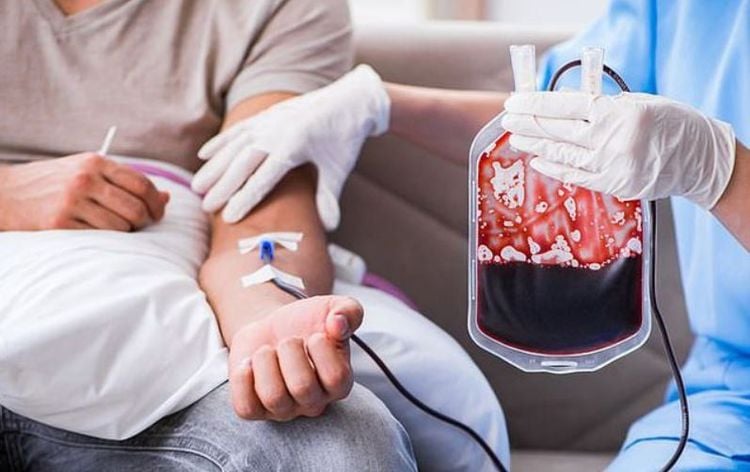
Truyền máu mang lại nhiều hiệu quả trong việc điều trị và hỗ trợ điều trị bệnh lý
3.4 Fresh frozen plasma
Plasma is the component found in whole blood. Fresh plasma after being extracted from blood stored frozen is called fresh frozen plasma. Fresh frozen plasma is indicated for use:
Plasma replacement; Blood clotting disorders; Hemophilia A & B; Complications of overdose of vitamin K antagonists; Compensate plasma components and volume, burn shock; Loss of blood due to trauma, surgery (combined transfusion of red blood cells and platelets). 3.5 Precipitation (cryo)
After freezing fresh plasma at a temperature of 4 degrees Celsius and centrifugation will obtain precipitates (cryo). This product is indicated for use in patients with coagulation disorders (fibrinogen loss, DIC) and hemophilia A patients.
3.6 Fresh plasma precipitated
Indicated for use in patients with plasma loss, anemia blood volume.
3.7 Granulocytosis
Indicated for use in patients with severe infections, no granulocytopenia, antibiotic treatment does not bring desired results.
Thus, in cases where the patient needs to receive a blood transfusion or use blood products, the doctor will base on each person's medical condition to give the most appropriate indications to use blood and blood components. for the treatment.
Customers wishing to visit and treat at Vinmec Health System nationwide can contact directly or book an online appointment HERE.
MORE:
Blood transfusion: When should it be done? Basic principles of blood transfusion To ensure safety in blood transfusion