This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Thao Tram - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Angiography and vascular malformation in the head and neck area under enhanced X-ray is a method applied to treat vascular diseases of the head, face and neck. The procedure to capture and node vascular malformations is often very complex and requires a combination of many different specialties.
1. Overview of vascular malformations in the head, face and neck region
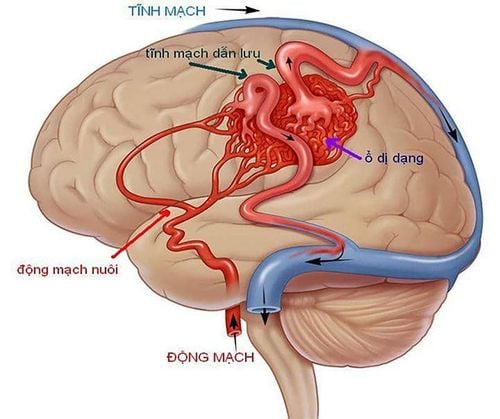
Most cases of head and neck vascular malformations originate from the external carotid arteries, which are the main arteries of the head and neck, or can also be caused by the internal carotid arteries, or the vertebral arteries. It is also the great artery in the neck.
Vascular malformation of the head, face and neck is a very complicated treatment method because it requires a combination of many different specialties. To treat, usually requires endovascular intervention, or direct puncture of the vascular malformation, and then temporarily or permanently occlude the vessel by injecting material. This method can help cure completely, or reduce the size of the focal malformation, or it can also reduce the perfusion to the malformation. In order to completely treat the disease, it may be necessary to combine surgery or sclerotherapy.
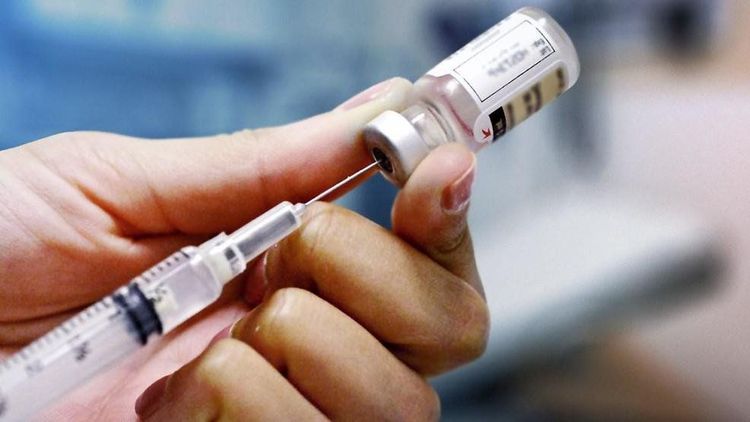
Điểu trị bệnh bằng cách bơm trực tiếp vật liệu vào đường mạch dị dạng
2. Indications/Contraindications for angiography and vascular malformations in the head, face and neck region
Angiography and vascular malformations in the head and neck area under enhanced x-ray are indicated for treatment in the following cases:
Pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous catheterization, ... head and neck area. Reduce tumor size. Help surgery more convenient and more radical such as reducing bleeding, ... Stop bleeding due to trauma or necrosis due to invasive blood vessels The pathology of angiogenesis in the tumor. Angiography and vascular malformations in the head, face and neck area under enhanced x-ray have no absolute contraindications, but are relatively contraindicated in cases of renal failure or coagulopathy, or patients with pre-existing medical conditions. clear history of allergy.
Chống chỉ định tương đối với người bị suy thận
3. Imaging procedure and vascular malformation node in the head, face and neck area under enhanced x-ray
For about 6 hours before the procedure, the patient is asked to fast and drink, only drinking water with a maximum amount of 50ml. In case the patient is overstimulated, sedation may be prescribed.
The procedure to capture and node the vascular malformation in the head, face and neck area under the enhanced x-ray includes the following specific steps:
Step 1: Conduct anesthesia by injecting pre-anesthesia into the intravenous line. In case the patient is a child under 5 years old who is agitated and scared due to lack of sense of cooperation, general anesthesia is required to perform the procedure. Step 2: Apply the Seldinger technique to insert the catheter. In most cases, the catheter is inserted from the femoral artery, if not from the femoral artery, it can be from other arteries such as axillary, brachial, radial or carotid artery. Step 3: The next step in the angiography and node malformation procedure is cerebral angiography. The patient was disinfected and anaesthetized, inserted a needle into the artery and placed an opener. Arterial catheterization to the external carotid artery, internal carotid artery, and vertebral artery, inject the contrast agent through the machine, and record, take series of films focusing on the skull and posterior fossa in the lateral position and completely straight. Depending on the blood supply to the tumor, a 3D scan may be possible. Step 4: Perform vascular malformation plug in the head, face and neck area by inserting a catheter to guide the gill vessel (usually the external carotid artery - internal jaw), then insert the microcatheter to the malformed blood vessel or arteries, which cause bleeding. Next, depending on the characteristics and location of the damaged blood vessel, select the appropriate embolization material. For temporary embolization, Gelfoam, PVA, or Spongel can be used; For permanent embolism can use metal spiral, Histoacryl glue, or Onyx, ... Finally, the end of the procedure is to withdraw the catheter and tube into the vessel lumen, stop bleeding by pressing the rectum with your hand. Continue to the puncture site for a period of 15 minutes, then, apply compression for 8 hours.
Bệnh nhân được gây mê trong quá trình thực hiện thủ thuật
4. Management of complications during and after the procedure
During head and neck angiography and angiography, if bleeding occurs, it may be due to an artery laceration or dissection. To handle, it is necessary to immediately stop the procedure, apply pressure and bandage the wound for monitoring. After 1-2 weeks, when the wound stops bleeding, the procedure can be repeated. Another possible complication during the procedure is vasospasm which, depending on the severity of the spasm, can be injected with a selective vasodilator. In addition, there are complications due to contrast agents.After the procedure to capture and node the vascular malformation of the head, face and neck, some complications such as catheter bleeding, arterial occlusion, venous aneurysm, infection, and vision loss may appear. Depending on the complications, it should be treated promptly and appropriately. In case of catheter bleeding or hematoma, which requires compression, the patient is asked to remain motionless until the bleeding stops. Patients should be examined promptly in cases such as suspected arterial occlusion (due to coagulopathy); arterial embolism (due to dislodged atherosclerotic plaques); broken catheter or wire; an arteriovenous bulge or catheterization; reduced vision, or loss of vision (due to blockage of the branch connecting the ophthalmic artery). Use antibiotics in case of infection.
Capturing and plugging vascular malformations in the head, face and neck is a complicated procedure that requires a doctor with professional qualifications, high skills and experience to treat vascular diseases of the head, face and neck, avoiding complications. Major vascular complications occur.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a general hospital with the function of examining and diagnosing many diseases with modern imaging techniques, a team of well-trained doctors and nurses. will bring optimal treatment results for customers.
For detailed advice on this method, please come directly to Vinmec medical system or book online HERE.