This is an automatically translated article.
In the early stages of infection, oral syphilis may appear as sores, called chancres. Oral syphilis begins as small red patches that develop into larger sores. If oral syphilis is not treated properly, the sores can heal, but the patient still recurs and infects others.
1. How does syphilis grow in the mouth?
Syphilis is a systemic bacterial infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. The incubation period is usually 21 to 30 days after exposure, although can vary from 10 to 90 days, depending on the number and virulence of Treponemas and host response.
Regarding the route of transmission of syphilis, the infection is mainly sexually transmitted, but it can also be hematological or longitudinal. Signs and symptoms vary according to the stage of the disease. In many cases, oral manifestations of syphilis are the first sign for an accurate and early diagnosis, which is very important for the cure of syphilis.
In general, the clinical features of syphilis are diverse as follows:
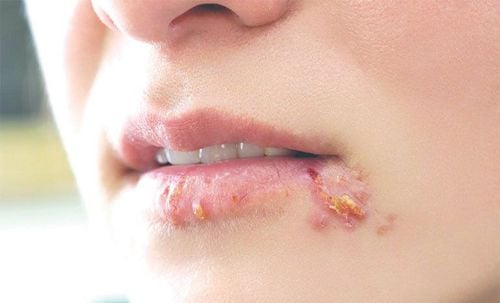
In cases of primary infection characterized by mucosal skin lesions; Secondary or late-stage infection presents with various signs and symptoms, such as vascular damage. In which, oral syphilis is the most important with the lesion being syphilis gum, a form of granulomatous inflammation in the secondary state. Patients with primary syphilis may present with painless and non-inflammatory bilateral satellite lymphadenopathy of the lymph nodes. Lips represent the most common site of oral syphilis, followed by the tongue and tonsils. An important feature of oral syphilis lesions is the absence of painful symptoms, so this condition must be distinguished from squamous cell carcinoma, a common malignancy in this anatomical region. .
People with secondary syphilis will present with headache, watery eyes, runny nose, sore throat, joint and muscle pain. Disease at this stage is characterized by systemic manifestations and a diffuse but painless maculopapular rash. Occasionally, in addition to oral syphilis lesions, the condition may also be associated with palmar lesions.
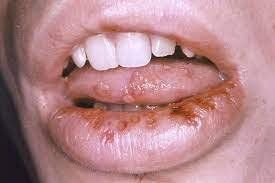
Môi là đại diện cho vị trí giang mai ở miệng phổ biến nhất
2. Approach to Diagnosing Oral Syphilis
Clinically, oral syphilis, commonly referred to as canker sores, presents as a self-limiting nonspecific ulcer that primarily affects the tongue, lips, and oral mucosa. These are the hallmarks of primary syphilis.Meanwhile, secondary syphilis is associated with hematogenous dissemination and clinical manifestations of the disease can be heterogeneous and nonspecific. For diagnosis, small, pinkish-oval macules covered with a fibrous pseudomembranous membrane or mucosal papules should be observed, with or without skin involvement. In addition, oral syphilis may also present as a papule, which is characterized by firm, nodular lesions or distinct raised mucosal patches that may be superficially eroded or ulcerated. However, in most cases, oral syphilis can eventually develop to manifest as an ulcerative granuloma of the palate or syphilis glossitis.
Thus, by observing the lesions, oral syphilis can be suspected, staged, and definitively tested, especially in the setting of occult syphilis. At the same time, the patient also needs to be ruled out the possibility of mouth damage due to other causes, especially malignant causes.
3. The main principles for curing oral syphilis
Syphilis that grows in the mouth in particular or the primary stage in general has the ability to be treated effectively in the early stages. The standard treatment for most oral syphilis is the antibiotic Benzathine penicillin G. Both in the primary and secondary stages, the treatment is an injection of an antibiotic. In the later stages and of unknown duration, the dose of antibiotics will be the same but the person will need multiple injections. In the case of HIV-associated syphilis, the patient will not need to prescribe any additional antibiotic therapy.
During the treatment of oral syphilis, a CSF test to detect neurosyphilis is recommended in grade 3 patients with consistent neurologic signs or no symptoms with high blood pressure. Serum levels did not decrease appropriately after treatment.
In addition, it is important for the patient to complete the full treatment regimen if diagnosed with oral syphilis. Because if left untreated, syphilis sores may clear up on their own after a few weeks, but that doesn't mean the infection has gone away. The bacteria remains in the body and other symptoms are likely to appear later. Furthermore, untreated syphilis can cause long-term damage to other organs, such as the heart and brain, which can eventually be fatal.
During treatment, women with oral syphilis should abstain from sex with their sexual partners until the sores have completely healed and the doctor has confirmed that the bacteria are no longer present in the blood. To confirm this, your doctor may order a blood test every six months.
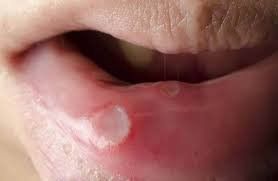
Tổn thương giang mai ở miệng là không có triệu chứng đau đớn
Unprotected oral sex can lead to infection and development of syphilis. Identifying oral syphilis is often difficult, especially in atypical cases. However, it is an important decisive step in the treatment of syphilis, based on a combination of clinical, histopathological, and serological features.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.