This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Bui Tien Dat - Emergency Medicine - Cardiology - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Heart valves are important organs in the heart that help blood flow smoothly. Due to the continuous work, the heart valve is very susceptible to diseases, damage and no longer guaranteed to do its job well. At this point, the request to repair the heart valve or replace the heart valve will be made.
1. What is a heart valve?
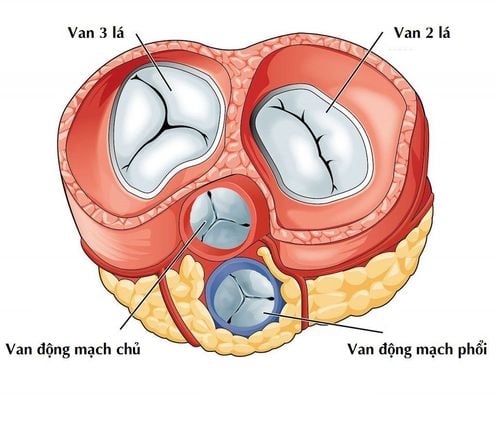
The heart is like a "pump" with the task of pumping blood throughout the body. During each minute, the heart beats an average of 70 beats, a beat pushing about 70 ml of blood into the circulation. Thus, the heart must expel approximately 4900 ml of blood per minute. That is a huge number if calculated in the time of a lifetime. Accordingly, in order for the blood to be circulated rhythmically in the heart, it needs the help of the heart valves.The heart has 4 chambers with 4 heart valves that help separate the heart chambers and the great arteries, including: mitral valve, tricuspid valve, aortic valve and pulmonary valve. The valves of the heart keep blood flowing in one direction from the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles into the great arteries. The heart valve apparatus has a solid structure, including: valve leaflets, annulus, ligaments and papillary muscles. The valve leaves are very soft, flexible and open and close rhythmically according to the heartbeat. Valve rings help keep the heart valves in place in the heart chambers. Ligaments and papillary muscles help to open and close the valve leaflet according to the movement of the heart muscle. Any damage or deformation of these parts will cause heart valve disease.
2. What is heart valve disease?
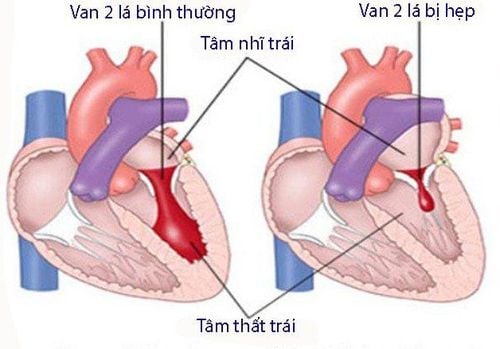
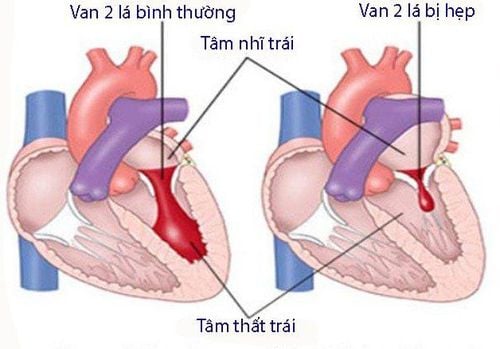
When the heart valves are changed in structure and function for any reason that no longer fulfill their physiological function, valvular disease will occur. Because the left side of the heart works harder and has to push blood into the general circulation of the whole body, mitral valve and aortic valve disease will be more noticeable than the tricuspid and pulmonary valve.Common heart valve disease is stenosis and regurgitation. Heart valve stenosis is when the valve leaf opens incompletely, the blood flow does not escape completely to go out, so it will stay behind. Heart valve regurgitation is when the heart valve fails to close properly, causing backflow of blood, causing the posterior chambers of the heart to expand.
When suffering from heart valve disease, the patient will feel tired, nervous, heart palpitations, shortness of breath when exerted or lying down, sudden shortness of breath at night while sleeping, chest pain, dry cough, coughing up blood or sometimes faint. Your doctor will take your pulse and listen to your heart, detecting an abnormal murmur; From there, echocardiography will be indicated to make a definitive diagnosis.
In some cases, if transthoracic echocardiography is not clear, it is necessary to use transesophageal echocardiography to accurately observe and evaluate the mechanism of heart valve damage, thereby giving indications for treatment. treat.
3. When to repair or replace the heart valve?
Depending on different heart valve disease, different types of heart valves will have different indications for intervention. At the same time, depending on the patient's condition, their choice as well as the accompanying diseases in the heart, the doctor will orient drug treatment or intervention, in the intervention there is surgery to replace the heart valve, repair the heart valve. or percutaneous valvular intervention without surgery.For mitral stenosis, if the valve stenosis is severe, the heart valve damage is complicated, the patient has many symptoms, then surgery to replace the heart valve; If the damage can be repaired, then surgical repair. If the valvular injury is not complicated, the patient cannot tolerate surgery, then intervene by balloon dilation.
For mitral regurgitation, if acute valve regurgitation requires emergency surgery; Depending on the cause and structure of the valve apparatus, repair or replace the valve. For primary chronic regurgitation, if left ventricular function is good, valvular surgery or valve replacement should be considered. Particularly with secondary chronic mitral regurgitation, caused by cardiomyopathy, with proper treatment, the valve function will recover, so it is rarely intervened.
In aortic valve disease, when aortic valve stenosis and symptoms are present, valve repair, surgical or percutaneous valve replacement should be carried out as soon as possible, the more beneficial the patient will be when the constriction function. heart beat is still good. For aortic regurgitation, only emergency surgery for acute regurgitation or surgical intervention if chronic regurgitation is severe, the patient is symptomatic and the ejection fraction is reduced.
All heart valve disease with indications for intervention, if not done, will affect the function of the whole heart chamber in the long run, causing irreversible progressive heart failure.

4. Methods of heart valve repair and heart valve replacement
4.1 Heart valve replacement surgery The damaged heart valve apparatus will be completely removed from the heart chamber. The surgeon then replaces the old heart valve with an artificial heart valve. The choice of an artificial heart valve, a biological heart valve or a mechanical heart valve, depends on the risk of taking anticoagulants. Accordingly, young patients will be selected for mechanical valve replacement and lifelong anticoagulation, while elderly patients will be replaced with biological valves with a shorter duration.4.2 Heart valve repair surgery This is also a method of interventional heart valve disease through an open incision on the chest and on the heart chambers. However, instead of having to replace a new valve, the patient's natural heart valve is regenerated and adjusted accordingly. Specifically, separating the valve edges, re-slicing the valve edges, creating ligaments in case the valve is narrow or narrowing the valve ring, sewing the valve leaves together partially if the valve is open.
4.3 Balloon valvuloplasty This method uses an artery that is threaded under the skin into the heart. At the position where the valve leaflets are stuck to the edge, narrowing the flow through the valve, the inflatable balloon will be inflated, separating the valve leaves. After that, the balloon will be deflated to shrink before being withdrawn. From there, the blood flow through the heart will be opened without very limited intervention on the patient, the hospital stay is significantly shortened.
4.4 Clamping the valve flap Similar to balloon dilatation, this method is also performed transarterial. The valvular opening will be narrowed by clamping again. This procedure is performed while the heart is working. Accordingly, to successfully clamp the valve edge without causing trauma to the heart valve requires skillful technicians and long-term practice experience.
4.5 Percutaneous valve replacement This method is often used for aortic stenosis. In it, the patient's natural valve is retained and a new heart valve is inserted into the arterial line superimposed in the same position. When released, the new heart valve will be fixed and pressed close to the old diseased valve leaf against the heart wall. From now on, the new tricuspid valve will act to replace the old heart valve according to hemodynamic blood flow, improving symptoms due to valve stenosis significantly while the patient does not have to suffer much pain, reducing hospital stay.
5. Why should heart valve repair, heart valve replacement at Vinmec?
Cardiovascular disease is generally a complex specialty, in which interventions to repair or replace heart valves are advanced and sophisticated techniques. Even for open surgery, the decision needs to be carefully considered due to the high risk and difficult postoperative time. Therefore, understanding the benefits and risks of cardiovascular intervention, as well as choosing a reputable place to perform, having good doctors and good equipment is extremely necessary. Hybrid surgery and Cathlab room are built on the 2nd floor of the Cardiology Center. This place is home to state-of-the-art equipment such as DSA angiography machine, anesthesia machine with the most closely integrated patient hemodynamic monitoring software (PiCCO system, entropy,...).Hybrid operating room brings the highest efficiency in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as combination surgery and angioplasty, coronary stenting, aortic stent graft, open heart surgery, heart valve replacement, heart valve repair, and repair. treat congenital heart diseases with the most modern minimally invasive techniques. In addition, with the modern technique of anesthesia in the Hybrid operating room, the level of anesthesia will be guaranteed, helping the patient recover quickly afterwards, reducing the time for mechanical ventilation and hospital stay; Reducing the risk factors of surgery, helping patients save both time, money and most importantly, the effectiveness comes with safety for the patient.
Master. Doctor. Bui Tien Dat received intensive training in the field of cardiology and cardiovascular emergency resuscitation at Hanoi Medical University and Bach Mai Hospital. The doctor has more than 12 years of experience in the field of emergency and cardiovascular resuscitation and is currently a doctor at the Emergency Department of Vinmec Hai Phong International Hospital.
If you notice unusual health problems, you should visit and consult with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.