This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Dr. Tran Ngoc Hoang Anh - Head of Neurosurgery Department, Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
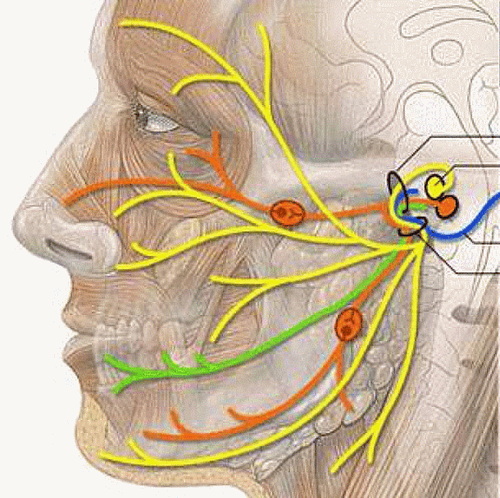
Hemifacial spasm is a painless, involuntary, intermittent convulsion of muscle groups innervated by nerve VII on one side of the face.
I. Overview of hemifacial seizures
The disease is considered a chronic, painless and not life-threatening neurological disease, but it greatly affects the psychology and spirit of the patient, thereby hindering social communication and affecting the health of the patient. activities and work. Especially in severe cases, the patient will have insomnia and limited vision.
The prevalence rate in the United States is 10/100 000 population, male:female ratio is 2:1, mean age is 45 to 55 years, the disease rarely occurs in young people or children. There are currently no studies on the incidence of the disease in our country.
The most common cause of the disease is a blood vessel pressing on the place where the facial nerve originates. In addition, a small number of brain stem tumors are sequelae of traumatic brain injury or a very small number of spontaneous pathologies.
Patients can now choose between two treatment options: Botulinum toxin injection and facial nerve microvascular decompression surgery. However, the radical treatment method is microvascular decompression surgery, which is a cure-all in 85%-90% of cases, and if performed by specialists, the rate of complications and complications. very low less than 1%.
II. Diagnosing hemifacial convulsions
1. Clinical symptoms of hemifacial seizures Hemifacial seizures are a disease of insidious onset, slow progression and chronic progression. However, some patients complain of a rather rapid onset of the disease.
The typical symptom is when the convulsion starts from the lower eyelid and then pulls the entire eye sphincter, then spreads to the cheek muscle groups and jerks the sphincter muscles. The convulsions are painless, involuntary, frequent, widespread, and occur during sleep.
In some severe cases, the muscle groups that attach to the skin of the neck, the muscles of the forehead also twitch. A convulsion can cause one eye to close due to spasm of the sphincter for a few seconds to a few minutes.
Nearly 30% of patients complain of hearing a low, crackling sound in the ipsilateral ear during facial twitching, which is caused by abnormal stapes muscle activity due to irritation of the facial nerve.
However, there is no change in taste, no autonomic symptoms such as watery eyes or runny nose as in cluster headaches. In some cases other than hemifacial convulsions, the patient had episodes of dizziness accompanying the convulsion.
Table 1: Jankovic's severity classification of hemifacial seizures
Functions considered to be caused by hemifacial spasm include: making it difficult to drive a car, read a book, watch TV or watch a movie, as well as cause the patient to feel inhibited and depressed. discomfort as well as shame about the condition, worry about other people's reactions to their facial spasms.
2. Diagnosis of hemifacial seizures a;Defined diagnosis
Diagnosed as primary hemifacial seizures when the following 3 criteria are met:
(1) Not a consequence of ipsilateral facial paralysis
(2) Chronic and self-limiting course
(3) Radiographic studies are normal except for the presence of vascular compression over the origin of the VII nerve
b; Differential diagnosis
blepharospasm Habit facial tics may also be confused with hemifacial seizures

3. The Role of Imaging Certain lesions of the cerebellar pons may also cause hemifacial seizures. Therefore, at the time of diagnosis, the patient is given a contrast-enhanced CT or MRI to rule out these causes.
Sometimes on MRI, dilated and enlarged vertebral arteries can be seen inserted into complexes VII, VIII. Naraghi used CISS-3D MRI to reconstruct the compression survey of blood vessels in the Root exit zone.
The role of imaging in hemifacial seizures is only to rule out causes other than neurovascular compression. In most cases, imaging cannot accurately diagnose the "culprit" blood vessel causing the symptoms.
III. Treatment of hemifacial convulsions
Most patients with hemifacial seizures complain of cosmetic and psychosocial problems caused by facial seizures. Some seriously ill patients are worried that the convulsions can be dangerous when they are operating machinery or vehicles.
Usually medical treatment is very ineffective. Currently, there are two methods of treating the disease that are accepted in neurological centers around the world:
1. Medical treatment with botulinum toxin (botox) Botulinum toxin application in the treatment of hemifacial seizures first in the United States in 1980 and approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1989.
Botulinum toxin inhibits presynaptic acetylcholine secretion at the neuromuscular junction, thereby inhibiting muscle contraction.
The goal of this treatment is to reduce excessive facial twitching activity without weakening the facial muscles. Intramuscular tobulinum toxin injection through this mechanism may provide temporary relief of symptoms for about 2-4 months. The effectiveness of this minimally invasive method is up to 90%. However, the goal of treatment becomes difficult when the seizure is severe and spreads to the cheek and sphincter muscles. Side effects such as transient mild facial paralysis may occur, but severe, long-term complications have not been reported.
Patients with hemifacial seizures treated with botulinum toxin must receive injections 3-4 times per year for life. This method only temporarily treats symptoms because it does not solve the nerve vascular compression that causes nerve VII irritation.
2. Jannetta Microvascular Decompression Surgery Microvascular decompression surgery was first applied in 1970 and has brought about positive results in the treatment of the disease. Up to now, this method has been carried out in many medical centers around the world and there are many research works that have been conducted for high treatment efficiency.
Patient is operated by suboccipital incision behind the sigmoid sinus, after pulling the cerebellum to one side under the microscope, it will dissect and identify nerve VII. Nerve VII emerges from the nucleus of the VII nerve located at the sulcus sulcus. The bundles of nerve VII run about 5 mm above the pontine surface. The white color of this bundle is easily distinguished from the yellowish surface of the capillary cerebellar villi. The Root exit zone of the facial nerve has a free portion located near the VIII nerve. The point of compression is almost always in the range from the bulbar groove to this free part.
After dissection of the compressive artery loops from the VII nerve, insert a Teflon pad in the middle so that the blood vessel does not directly compress the VII nerve. With this mechanism, only to end the pathophysiological cycle, can the root cause of hemifacial seizures be treated.
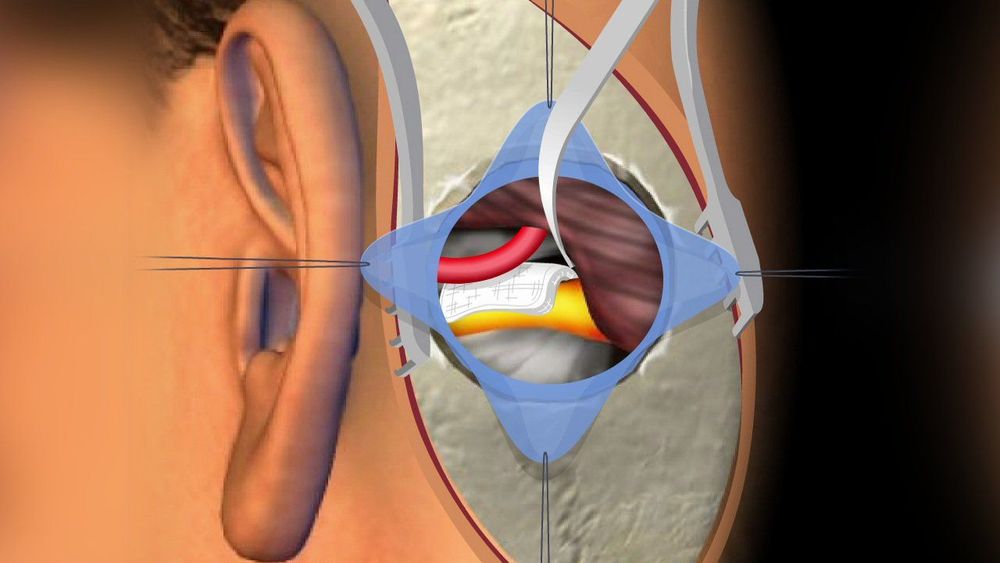
Surgical results: 85-93% of the disease is cured, about 70% of cases are gone right after surgery, nearly 30% of the remaining cases only decrease and disappear after 3 months to 1 year. Common complications include tinnitus, hearing loss (6-13%), temporary and permanent facial weakness or paralysis (6-10%), hoarseness, dizziness (1-6%).
With the advancement of modern equipment, neurosurgery has made new strides, not only curing the disease but also ensuring the patient's function, ensuring quality of life as well as minimizing complications related to surgery.
Therefore, in addition to modern microsurgery glasses, the combination of endoscopic support and electrophysiological monitoring of the facial nerve and auditory nerve in surgery has helped the neurosurgeon to minimize Unfolding the brain, preserving the function of the nervous structure brings the highest surgical efficiency while minimizing complications, bringing a sense of security to the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.