This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Liver fibrosis is a condition in which liver cells are damaged continuously for a long time, liver fibrosis is divided into many levels from mild to severe with different symptoms and cure rates.
1. Degrees of liver fibrosis
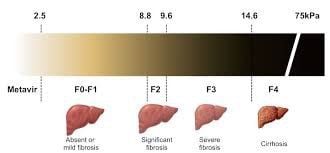
According to the histopathological Metavir classification, liver fibrosis stages include:
F0 (no fibrosis) F1 (portal fibrosis) F2 (portal fibrosis with few bridges) F3 (bridged fibrosis) ) F4 (cirrhosis). There are 4 degrees of liver fibrosis:
No fibrosis or mild fibrosis when the patient is at: F0, F1 Significant fibrosis when: ≥ F2 (F2 to F4) Severe fibrosis when: ≥ F3 (F3 to F4 ) Cirrhosis (F4). The role of determining the degree of liver fibrosis The determination of the degree of liver fibrosis has 3 main roles as follows:
Determine the degree of liver damage to decide to start treatment, especially for inflammation Chronic liver disease caused by hepatitis C virus, avoiding progression to cirrhosis in the presence of significant fibrosis. Establish a special monitoring regime, determine the optimal time to start screening for complications (hepatocellular carcinoma, esophageal varices...) for severe fibrosis. Follow-up treatment: evaluate progression or regression of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Usually:
Stage F1, F2: treatment can be restored Stage F3, F4: usually treatment does not restore, only stopping the progression of liver fibrosis.
2. Recognizing levels of liver fibrosis
Stage F1 This first stage, the patient rarely shows any pathological symptoms because it appears extremely faint. New fibrous scar tissue begins to form, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, nausea, loss of appetite, and common digestive disorders. This stage is easily overlooked or mistaken as a manifestation of another disease.
Stage F2 This time more scar tissue appears, fibrous tissue in the patient's liver can be seen more clearly. The amount of fibrous tissue cells at this stage increases greatly, making the liver function significantly impaired, toxins stagnate, not being excreted, causing other organs to be affected, causing disturbances in the body's metabolism. body. The typical symptom of this stage is jaundice.
Stage F3 Stage 3 liver fibrosis has caused liver dysfunction in part because the amount of liver cells is replaced by fibrous tissues mainly. F3 liver fibrosis is much higher than F2 liver fibrosis, causing the liver to lose most of its function. The remaining normal liver cells will have to work harder, replacing the part of liver cells with cirrhosis leading to overload, more and more stagnant toxins, causing liver cells to gradually be damaged and transition to the stage. fibrosis. The symptoms are quite obvious such as: the patient feels body aches, swelling of the limbs and gradually spreads to the whole body.
Stage F4 Liver cells are completely damaged, liver disease has progressed to the final stage, the liver is no longer functional, the disease is getting worse and worse. Patients must face other pathological symptoms or manifestations of complications caused by cirrhosis. F4 liver fibrosis is the most dangerous stage.
3. Methods of assessing liver fibrosis
The methods of evaluating liver fibrosis include 2 main groups: invasive and non-invasive.
Invasive: percutaneous fine-needle liver biopsy to obtain a sample of liver tissue to observe under the microscope Non-invasive: biomarker, imaging and liver elastography. In particular, liver biopsy is considered the gold standard to assess liver fibrosis. However, liver biopsy is a deeply invasive method, has complications, and presents some limitations: results are affected by sample size, biopsy site and pathologist's analysis. . Therefore, at present, in the world, many non-invasive methods of liver fibrosis assessment have been developed and are being developed, which can replace part of liver biopsy with different accuracy.
Currently, the elastographic ultrasound diagnostic method is the best method to assess the damage in the liver parenchyma and the degree of cirrhosis, helping to diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases, hepatitis C, and liver disease. alcoholic steatosis, chronic kidney failure... . Accordingly, the patient lies on his back, his right hand is placed behind his head, the operator places the transducer on the intercostal skin where the liver biopsy is usually located and presses it with a slight pressure and the test consists of 10 consecutive measurements at the same time. position. The machine will automatically calculate the average value. The results are analyzed by the machine and give specific numbers. The advantage of the technique is that it is non-invasive, easy to perform in patients with obesity and ascites, and can be applied to many different organs.
>> See more: The role of herbs in the treatment and prevention of liver fibrosis - Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.