This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Celiac is a chronic autoimmune disease caused by a reaction to gluten in food. The disease has a genetic factor and in clinical practice, manifestations are quite diverse from no symptoms to faint symptoms or severe cases can have typical malabsorption symptoms such as chronic diarrhea, anemia, etc. iron deficiency blood, thin weight loss...
This is considered a rare digestive disorder in which it is common in children, however, in recent years, the detection rate of this pathology has increased along with the recording of many extra-gastrointestinal and clinical symptoms. seen in many age groups.
1.The role of endoscopy in Celiac disease
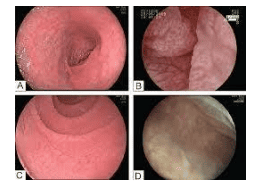
1.1. Gastroduodenal endoscopy Traditionally, Celiac disease was diagnosed using tissue biopsy of the duodenum in combination with serum autoantibodies. Since the improvement of video endoscopes used in everyday practice including the introduction of narrow band imaging (NBI) and near focus modes (Near Focus), Detailed examination of the duodenal mucosa results in an accurate radiological diagnosis.
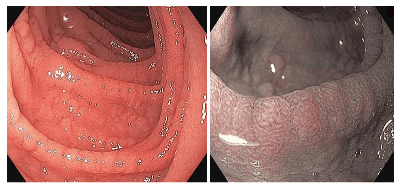
The endoscopic signs of Celiac disease are scalloped, or nodular, folds, fissures, and duodenal fissures. This is in contrast to the normal duodenum, which is covered with finger-like villi that provide a large surface area for nutrient absorption.
In Celiac disease, the villi are usually shorter and less pronounced than in normal mucosa. Under endoscopy, the villi pattern can be further enhanced by filling the gastrointestinal tract with water and this approach has been routinely used in the evaluation of diseases of both the duodenum and the jejunum.
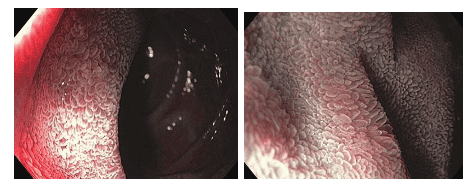
Immersion in water is very simple, consisting of removing air from the duodenal lumen, followed by injection of 90-150 ml of water. Then the signs of Celiac disease such as scalloped, nodular folds, fis detect villous lesions in the duodenum with high accuracy. However, although this approach has the effect of reducing the number of biopsies required, it is still important to confirm the diagnosis by histopathological analysis, especially to exclude diseases that may present with a similar presentation. so.
With the development of endoscopic techniques, more and more endoscopic images suggestive of Celiac disease have been recorded, thereby helping the endoscopic surgeon to conduct biopsies more easily.
Typical endoscopic images of the descending duodenum after inflation include: reduced number of duodenal mucosal folds (Kercking's fold), rough duodenal mucosa, visible network submucosa vascular network (mucosal atrophy), may show deep grooves, fissures, examination, papules, or lithographic images.
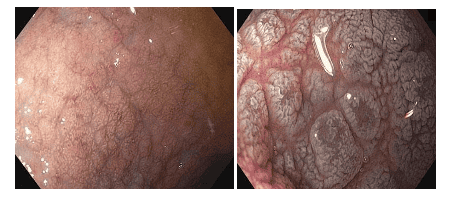
Although the sensitivity of these features is low, not all patients have them, but seeing these findings suggests the endoscopist to perform a biopsy. A staining agent such as methylene blue or indigo carmine can be used to visualize mucosal surface changes more clearly, especially atrophy of intestinal villi and vascular network. Magnified endoscopic technologies also allow increased sensitivity in detecting villi in the duodenal mucosa to over 90%.
However, the research results show that the use of endoscopic imaging to diagnose Celiac disease at different centers has not been unified, so so far it cannot replace the results of duodenal biopsy. .
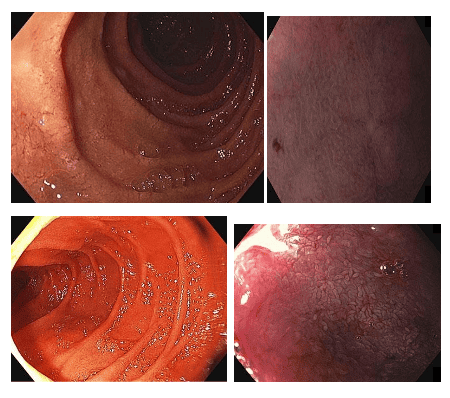
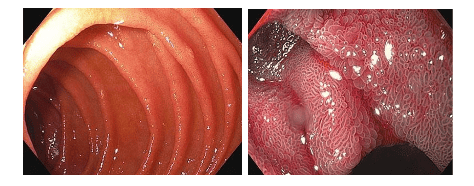
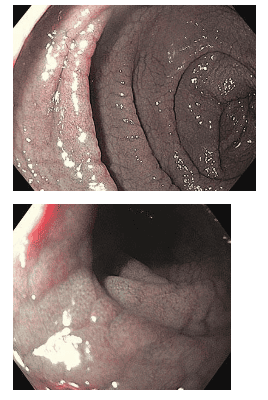
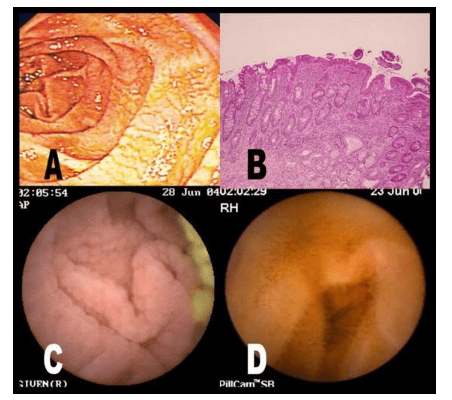
Upper left image presents the initial diagnosis of Celiac disease with fissures in mucosal folds and absence of villi as mucosal images are observed with NBI staining and endoscopic modes. Near Focus in the image on the right.
The images below were obtained from the same patient after five months of a gluten-free diet. The lower left image shows normal folds and the right image uses the NBI view and the image of small finger-like villi in the Near Focus view.
1.2 Colonoscopy Biopsy during colonoscopy in patients with persistent diarrhea, even when many symptoms point to Celiac disease, will help rule out additional lymphocytic colitis or colitis body. The endoscopist may also insert the endoscope into the terminal ileum to look for lesions and biopsies to rule out Crohn's.
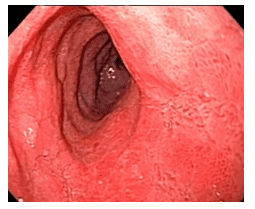
1.3.Capsule endoscopy This is a commonly used technique to detect lesions in the small intestine in many different diseases including Celiac. Features noted on capsule endoscopy in Celiac include mucosal atrophy, flattened mucosal folds, and striated intestinal mucosa, possibly mosaic.
Some authors have suggested that in patients with a positive immunoassay and who cannot undergo endoscopy or do not want endoscopy, capsule endoscopy can be used as an alternative diagnostic tool. for histopathological biopsy results in duodenum. However, the correlation between capsule endoscopy image and histopathology is controversial.
A prospective multicenter study in Europe documented the sensitivity and specificity of capsule endoscopy in detecting characteristic Celiac lesions (vile atrophy, mucosal loss of folds, notching) folds. 95% and 73% respectively, but when compared with histopathological results, the concordance is only moderate.
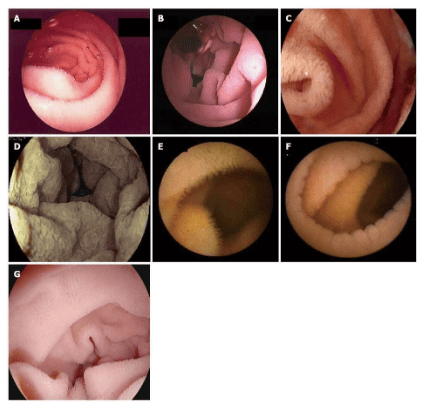
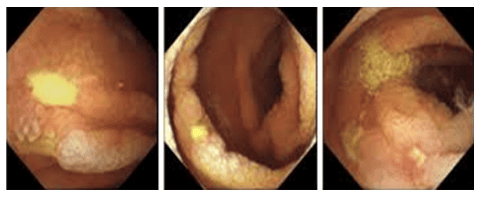
Image of intestinal mucosal atrophy and notched intestinal mucosa in Celiac disease on capsule endoscopy. A: Presence of villi with water injection filling the survey area; B, C, D: Atrophy of the entire villi; E: Presence of normal villi on capsule endoscopy view; F: Total villi atrophy with capsule endoscopy; G: Duodenal villi model with I-scan
technology
1.4. Double-balloon small-bowel endoscopy In difficult-to-treat, persistently recurrent cases of Celiac, a number of European studies have recognized the need to perform double-balloon small-bowel endoscopy to detect complications and lesions. inflammation in rosacea and ileum as well as excluding the presence of lymphoma.
The use of dyes such as indigo carmine also improves detection rates of suspected malignancies such as T-cell lymphomas; The feasibility of this technique has also been demonstrated by several studies.
2. Other imaging methods
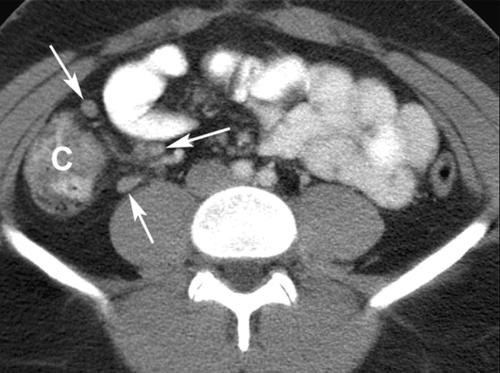
Non-invasive imaging methods can be used for monitoring in the management of Celiac patients such as barium scan, abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography... including segmental atrophy of intestinal villi, loss of jejunal folds, edema of the jejunal wall, dilation of the pink or ileal segments, and reversal of mid-jejuno-ileal folds.
On ultrasound, you can see mesenteric vascular hyperperfusion, dilated small bowel loops, diffuse thickening of the intestinal wall, mesenteric lymphadenitis. On computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, these images will be clearer.
3. Histopathology
Histopathology in Celiac was first described in 1954 with biopsies from the ileal mucosa. Until now, in the guidelines of the American Gastroenterology Association, it is recommended to take multiple biopsies of the duodenal mucosa for diagnosis. When biopsies of 4 or more pieces were taken, the rate of new diagnoses increased statistically significantly.
Targeted biopsies of 1-2 pieces at 9 o'clock or 12 o'clock in the duodenal mucosa in addition to four biopsies in the damaged part of the duodenum increase diagnostic sensitivity to 96%. The histopathological findings in Celiac include lymphocytic infiltration in the epithelial layer, thickening of the basement membrane, decreased goblet cell count, cleft hyperplasia, and varying degrees of intestinal villi atrophy.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious address trusted by many patients in performing diagnostic techniques and treating chronic inflammatory bowel diseases... Along with that, at Vinmec Hospital, the practice Currently diagnosed through gastrointestinal endoscopy with Olympus CV 190 endoscope, with NBI function (Narrow Banding Imaging - endoscope with narrow light frequency band) results in clearer mucosal pathological analysis images than with conventional endoscopy, detecting ulcerative lesions in the gastrointestinal tract.
Vinmec Hospital with modern facilities and equipment and a team of experienced experts who are always dedicated in medical examination and treatment, customers can rest assured with the gastrointestinal endoscopy service at the hospital. Vinmec International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.