This is an automatically translated article.
Choline is an essential nutrient needed for a wide range of functions from maintaining cells to creating neurotransmitters. Although rare, a choline deficiency often presents as elevated liver enzymes and can lead to liver disease, heart disease, and even neurological disorders.
1. What is Choline?
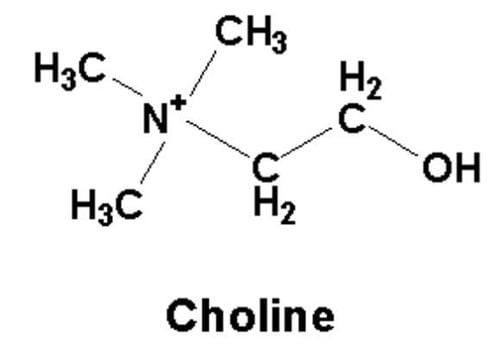
Choline is an essential nutrient that occurs naturally in a number of foods and is available as a supplement. The body can also produce small amounts on its own in the liver, but not enough to meet daily needs. Choline is converted into a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which helps muscles contract, triggers pain responses, and plays a role in the brain's memory and thinking functions. Most choline is metabolized in the liver, where it is converted to phosphatidylcholine, which aids in building fat-transporting proteins and breaking down cholesterol. It is also "food" for the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Choline là một chất dinh dưỡng cần thiết cho cơ thể
2. Some people are at risk of Choline deficiency
Although choline deficiency is rare, some people are at increased risk:
Endurance athletes: levels decrease during long endurance exercise, such as running a marathon. It's not clear if taking the supplement improves performance. Heavy drinking: alcohol can increase your choline requirements and your risk of deficiency, especially when intake is low. Postmenopausal women: Estrogen helps with choline production in your body. Since estrogen levels tend to decrease in postmenopausal women, they may be at greater risk of becoming deficient. Pregnant women: choline requirements increase during pregnancy. This is most likely because the fetus needs choline to develop.
3. The relationship between Choline and diseases to health
3.1. Heart-related diseaes
Choline is thought to both protect and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Choline, along with the B vitamin folate, helps reduce homocysteine levels in the blood by converting it to methionine. High homocysteine levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Choline may also help reduce blood pressure and stroke.
But choline can also have a negative impact on the heart. Choline is metabolized by gut bacteria to a by-product called trimethylamine (TMA), which is then converted in the liver to trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO). Higher blood levels of TMAO have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease in animal studies. However, it is not clear what the relationship of TMAO to CVD is, or whether it is just a marker of an underlying disease process leading to CVD.
Other large previous epidemiological studies have shown, conversely, no association between high choline intake and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, although these studies also did not specifically measure concentrations of choline. TMAO levels in the blood. There seems to be a link between a diet high in choline-rich foods and cardiovascular disease, but the reasons for this link need to be studied further.
3.2. Type 2 diabetes
In three large groups of men and women, higher intakes of phosphatidylcholine were associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Those with the highest choline diet showed a 34% increased risk of type 2 diabetes compared with those who ate the least. The exact mechanism of this association is still unclear and needs to be investigated further.
Bệnh tiểu đường tuýp 2 có thể được giảm thiểu khi tăng cường choline trong chế độ ăn
3.3. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
There is a link between choline deficiency and liver disease. Phosphatidylcholine carries fat away from the liver, so a choline deficiency can cause the liver to store too much fat. This increases the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which can then progress to cirrhosis (inflammation of the liver cells followed by thickening and hardening of liver tissue), liver cancer, or liver failure. . This ultimately interferes with the normal function of the liver. Changes in choline or phosphatidylcholine metabolism can also negatively impact some of the biochemical pathways that lead to this disease.
This disease occurs most often in people who are overweight or obese, and the main treatment is to reduce body fat through calorie restriction and exercise. Although a choline deficiency can lead to liver dysfunction, it remains unclear whether choline or choline supplements can be treated.
3.4. Cognitive abilities
Choline is linked to brain health because it is converted to acetylcholine, which plays a role in memory and thinking. Studies have found that people with Alzheimer's disease have lower levels of an enzyme that converts choline to acetylcholine, and therefore hypothesized that higher dietary choline intake might prevent cognitive decline awake.
Although some observational studies have found that higher choline intake is associated with higher levels of cognitive function such as memory, clinical trials have not found that supplementation Choline supplementation significantly improved these cognitive measures.
4. Food sources rich in Choline
Choline is found in many foods. High choline foods include lean chicken, fish, lean pork, eggs, beef, shrimp, peanut butter, low-fat milk, broccoli, and green beans. Below is a list of common foods high in choline.

Choline được tìm thấy trong nhiều loại thực phẩm
4.1. Peanut butter
Peanut butter contains more Choline than 38% of foods. 100 grams of peanut butter contains 11% of the Choline that you need to consume daily.
Peanut butter is also rich in calories, fat and monounsaturated fat
4.2. Egg
Eggs contain more Choline than 54% of foods. 100 grams of Eggs contain 53% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Eggs are also rich in Cholesterol, Vitamin B2 and Vitamin A
4.3. Soy bean
Soybeans contain more Choline than 52% of foods. 100 grams of Soybeans contain 21% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Soybeans are also rich in Protein, Iron and Potassium.

Chất choline có thể tìm thấy trong đậu nành
4.4. Mackerel
Mackerel contains more Choline than 50% of foods. 100 grams of Mackerel contains 18% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Mackerel is also rich in Sodium, Ash and Fat
4.5. Green bean
Green beans contain more Choline than 49% of foods. 100 grams of green beans contain 18% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Chickpeas are also rich in Potassium, Fiber and Iron
4.6. Pork
Pork contains more Choline than 48% of foods. 100 grams of Pork contains 17% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Pork is also rich in Protein, Vitamin B1 and Potassium
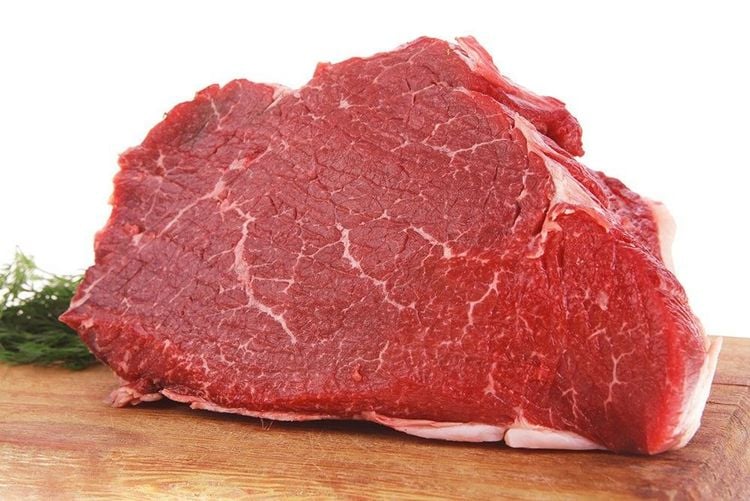

Hàm lượng choline trong thịt lợn khá cao
4.7. Lamb
Lamb contains more Choline than 48% of foods. 100 grams of Lamb and Lamb contains 17% Choline that you need to consume daily.
Lamb is also rich in Cholesterol, Protein and Saturated Fat
4.8. Chicken meat
Chicken contains more Choline than 46% of foods. 100 grams of turkey meat contains 16% of the amount of Choline that you need to consume daily.
Chicken is also rich in Protein, Cholesterol and Vitamin B3
4.9. Beef
Beef contains more Choline than 45% of foods. 100 grams of beef contains 15% of the amount of Choline that you need to consume daily.
Beef is also rich in Protein, Zinc and Cholesterol

Bạn có thể bổ sung thịt bò để tăng cường choline
4.10. Frog legs
Frog legs contain more Choline than 39% of foods. 100 grams of frog legs contains 12% of the amount of Choline that you need to consume daily.
Frog legs are also rich in water, copper and protein.
5. Signs of Deficiency and Toxicity
5.1. Signs of deficiency
Most deficiency is rare in healthy people, as the body can make some choline on its own. Additionally, the amount of dietary choline an individual needs can vary widely and depend on different factors. For example, premenopausal women may have a lower need for choline in their diet because higher amounts of estrogen stimulate the production of choline in the body. A higher choline requirement may be necessary in people with a genetic variant that interferes with the normal metabolism of choline. Choline deficiency can actually lead to muscle or liver damage and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Pregnant women: aside from the low average dietary intake in the general public, prenatal supplements usually do not contain choline.
Patients dependent on parenteral nutrition: total parenteral nutrition is given intravenously for those whose digestive system cannot tolerate solid foods due to illness, surgery or other conditions. other digestive conditions.

Phụ nữ tiền mãn kinh có nhu cầu về choline thấp hơn
5.2. Toxicity
Very high levels of choline can lead to low blood pressure (hypotension) and liver toxicity. It can also lead to excess production of trimethylamine-N-oxide, which is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Other symptoms include excessive sweating, increased body odor, or nausea. The tolerable upper intake level for choline for adults 19 years of age and older is 3,500 mg per day and is based on amounts that have been shown to produce these side effects. Reaching this high is most likely due to taking very high doses of the supplement, not just dieting.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.