This article is professionally consulted by Pham Thi Yen Specialist Level I - Obstetrician - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Fever after a cesarean section is defined as a fever of 38°C or higher occurring more than 24 hours after surgery. This symptom can be caused by various factors with varying severity
1. Causes of fever after cesarean section
There are many causes of fever after a cesarean section, with varying degrees of severity.
- Breast diseases such as postpartum breast engorgement but can also be mastitis, breast abscess, milk stasis.
- Cesarean section wound infection (cystitis, acute pyelonephritis, pneumonia...) or postpartum cesarean section infection (vulvar, vaginal, perineal infection.
- Endometritis, generalized metritis, adnexitis, pelvic peritonitis, generalized peritonitis, sepsis).
2. Symptoms of fever after cesarean section
2.1. Postpartum fever due to breast diseases
Usually, after childbirth, mothers often experience engorgement due to plugged milk ducts. In this case, mothers need to increase the frequency of breastfeeding by expressing milk manually or using a pump. To reduce pain after breastfeeding, mothers should apply cold compresses and wear a bra or bandage to support the breasts that is not too tight. In this case, there is no need to visit a medical facility.
Mothers should seek medical attention if they have mastitis with the main symptoms: fever, breast engorgement, pain, redness, cracked nipples, usually on one side, or else it may progress to breast abscess. The main signs of breast abscess are swelling, redness, tenderness, and pus when punctured
2.2. Fever due to cesarean incisional infection:
This is a condition in which the cesarean incision is swollen with bloody or purulent discharge, and redness around the suture line, and in which an immediate medical attention is necessary.
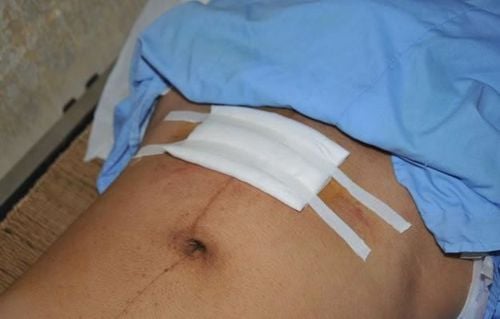
2.3. Fever due to infection in the perineum, vulva, vagina, or cervix
The main symptoms are swelling, redness, pain, and sometimes pus at the incision site or tear. The uterus contracts well, and lochia may be moderately or extremely odorous. The mother may have a mild fever of 38-38.5°C, in which case they need to seek examination and treatment.
2.4. Fever due to endometritis:
This is a postpartum complication caused by uterine manipulation, amniotic fluid infection, prolonged labor, or sometimes retained placenta. Endometritis, if left untreated, can lead to more serious complications such as total uterine infection, peritonitis, sepsis... Clinical symptoms include fatigue, fever of 38-39°C from the 2nd postpartum day. The uterus contracts slowly, is soft, and tender to touch. Lochia has a foul odor and sometimes contains pus... The mother needs to go to a medical facility for examination and treatment.
2.5. Fever due to uterine and adnexal infections:
From the uterus, postpartum infection after cesarean section can spread to nearby organs such as broad ligaments, fallopian tubes, and ovaries... The main symptom is usually late, on the 8th - 10th day after birth. The mother may have a prolonged high fever and lower abdominal pain. The uterus is enlarged, contracts slowly, and is tender… complications include peritonitis or rupture of putural sac into the bladder, vagina, or rectum, which is very dangerous.
2.6. Fever due to pelvic peritonitis:
Symptoms can appear early, about 3 days after birth, or later, about 7-10 days after a period of postpartum infection after cesarean section in the uterus or vulva, vagina. The mother has a high fever of 39°C - 40°C, accompanied by chills. Severe pain in the lower abdomen, and this area may be rigid on palpation
2.7. Fever due to generalized peritonitis:
The main symptoms are general fatigue, high fever, weight loss, rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, vomiting. Abdominal distension, pain, if left untreated, can lead to generalized peritonitis requiring hysterectomy.
2.8. Fever due to sepsis:
This condition is caused by obstetric interventions or non-sterile instruments. Due to improper treatment of infections, inadequate antibiotic dosage or duration... It can also be due to surgery performed too early when the localized infection in the genital area has not been contained with antibiotics, allowing bacteria to spread into the bloodstream. The main symptoms are high fever and chills multiple times a day. In some cases, the fever is prolonged, the general condition is weakened, and it may lead to shock, hypotension, and coma if not treated promptly; in mild cases, a hysterectomy is required, and in severe cases, the mother will die.
2.9. Fever due to thrombophlebitis
This is a rare disease in our country. It usually appears on the 18th day after cesarean section with the following clinical manifestations: high fever, pain at the site of thrombophlebitis, the patient cannot walk if the deep veins are thrombosed. If the abdominal veins are thrombosed, the patient has abdominal pain, especially mesenteric vein thrombosis, the disease can manifest in the veins of the lungs, brain... with symptoms of pain in these organs, sometimes paralysis if the clot can be surgically removed.
3. Prevention of postpartum fever after cesarean section

To avoid fever after a cesarean section, mothers need to pay attention to protecting the incision site to prevent infection and avoid engorgement, plugged milk ducts…
Early detection of incisional infection is crucial. If the incision is red, swollen, painful, or has yellow discharge, these are abnormal signs, and the mother needs to go to a specialized hospital for examination.
Increase physical activity: After giving birth, mothers should not lie still in bed but should turn to their right or left side on the first day after surgery. From the second day onwards, mothers should sit up and walk around.
Abdominal massage (avoiding the incision site) every day helps the uterus contract well and expel lochia faster. Early breastfeeding should be encouraged, as the act of breastfeeding also increases uterine contractions and prevents postpartum bleeding.
Personal hygiene: Wipe the body with warm water or take a quick shower, avoiding soaking the body in a bathtub, which can wet the incision. After showering, use a clean cotton ball to dry the incision, leave the incision open without a bandage, and keep the incision dry. The incision can be cleaned with a betadine or povidine-iodine 10% solution to help the incision heal faster and prevent infection.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
Reference source: National guide to reproductive health services, Ministry of Health.