This is an automatically translated article.
Ebola is a serious and fatal disease in humans caused by the Ebola virus. The largest Ebola epidemic in history broke out for the first time in West Africa in 2014. Health organizations around the world are still taking precautions to prevent the spread of Ebola.
1. What is Ebola disease?
1.1. Classify
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a life-threatening disease with frequent outbreaks and occurs mainly in the African continent. The Ebola epidemic most affected humans and primates such as monkeys, apes and chimpanzees. The cause of the disease is infection with one of the viruses belonging to the genus Ebolavirus, including:Ebola virus (Zaire Ebolavirus); Sudan virus (species Sudan Ebolavirus); Taï forest virus (species Taï Forest Ebolavirus, formerly known as Côte d'Ivoire Ebolavirus); Bundibugyo virus (species Bundibugyo Ebolavirus); Reston virus (species Reston Ebolavirus); Bombali virus (species Bombali Ebolavirus). Of these, only four are known to cause disease in humans: Ebola, Sudan, Taï Forest and Bundibugyo. Reston virus causes disease in primates and pigs. It is not clear whether the Bombali virus, discovered in bats, infects animals, humans, or both.
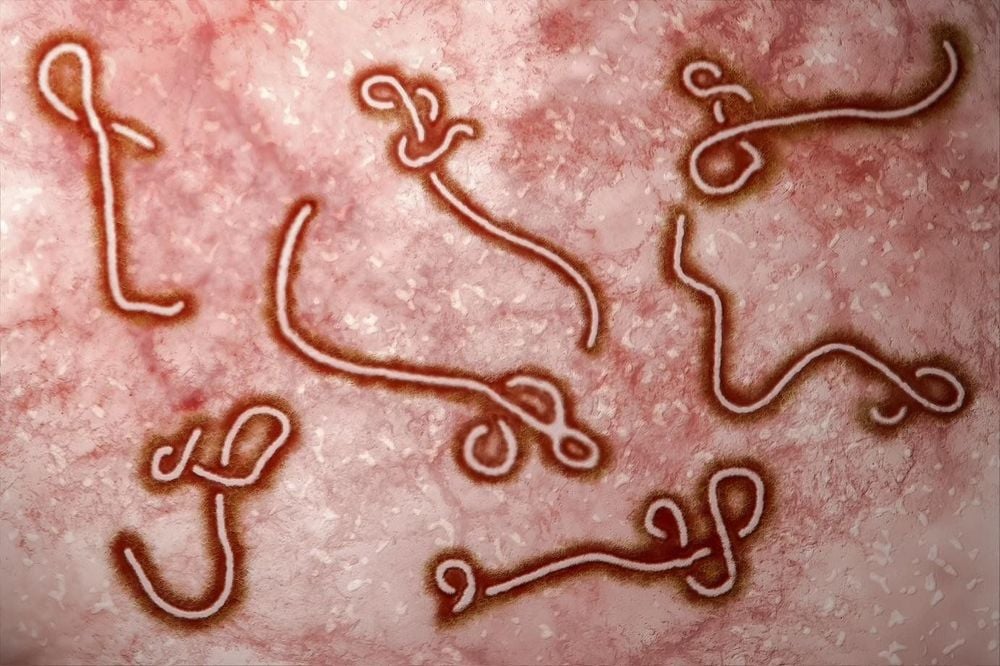
Hình ảnh virus gây bệnh Ebola
1.2. Source
Ebola virus was first detected in 1976 near the river called Ebola - now within the border of the Democratic Republic of Congo. Since then, the virus has infected many people over time, leading to outbreaks in several African countries.
Scientists don't know where the Ebola virus came from. However, based on the nature of similar viruses, they believe the virus came from animals, most likely from bats or primates. Animals infected with the virus will pass it on to others, such as apes, monkeys, antelope and eventually humans.
1.3. Path of spread
Initially, the virus will spread to humans through direct contact with the blood, body fluids, and tissues of animals. The Ebola virus then spreads from person to person through direct contact with the bodily fluids of a patient or person who has died from Ebola. Specifically, when a person touches infected bodily fluids (or objects where the virus is present), and then allows the virus to enter open wounds in the skin or mucous membranes in the eyes, nose, or mouth.People can also contract the virus if they have sex with an infected person, even a recovered Ebola patient. The virus is still able to survive in some body fluids, such as semen, from men, even after they have recovered from the disease.
Patients who have recovered from Ebola virus infection may still face related symptoms such as: Fatigue, muscle aches, eye and vision problems, as well as stomach upset.

Người bệnh sau nhiễm Ebola có thể xuất hiện tình trạng mệt mỏi
2. Characteristics of the virus causing the Ebola epidemic
Ebola is not a respiratory disease, so it is not transmitted through the air like flu viruses; Ebola is spread by direct contact from an open wound or mucous membrane of a healthy person, with the blood and other body fluids (such as urine, feces, saliva, vomit, sweat, and semen) of another person. get sick or have died from Ebola; Ebola can also be spread by direct contact with objects contaminated with the virus (such as needles or syringes), infected animals, or semen from a man who has had Ebola before (although currently they have made a full recovery); Children can also contract Ebola through breast milk, so a mother who has Ebola or has suspected symptoms should not breastfeed Signs and symptoms of Ebola include: Fever, severe headache , muscle pain, weakness, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain and unexplained bleeding; The incubation period for Ebola (from exposure to the source of infection until signs or symptoms appear) can be from 2 to 21 days. Average is 8-10 days; Ebola virus has great resistance to the environment, in the temperature of about 56°C, it can live for 30 minutes;
All current sterilization chemicals can kill the Ebola virus; There is currently no FDA-approved antiviral treatment or vaccine for Ebola. Several experimental vaccines and treatments are being studied and used in certain places (like during an outbreak).

Đau đầu là một trong các triệu chứng nhiễm Ebola
3. Ebola epidemic situation in Vietnam
According to the Department of Preventive Medicine, as of August 2014, nearly 2,000 cases of Ebola virus have been recorded, of which the mortality rate accounts for 90%. The number of cases and deaths from the Ebola virus in African countries continues to increase, and the virus continues to spread from the epicenter of the epidemic to neighboring countries.
While other West African countries have worked to contain the outbreak of the most terrible Ebola virus disease in the past 4 decades, Asian countries are also very active in preparing for disease prevention . Particularly in our country, an expert from the World Health Organization (WHO) said that the risk of Ebola infection in Vietnam is very low. This virus is not transmitted through the respiratory tract, but only through close contact with the source of the disease, while the preparation stage of our country is very good and timely. Therefore, the communication work needs to be updated accurately, avoiding confusion for the community.
However, according to WHO, Vietnam is one of the countries in the distribution range of the fruit bat family Pteropodidae. This could be the natural host of this dangerous virus. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid being subjective, and at the same time deploying extensive propaganda to all classes of people important information, thereby joining hands to prevent the disease.
4. Prevention of Ebola disease
Avoid contact with other people's blood and body fluids; Do not share objects that may come into contact with another person's blood or body fluids, such as clothing, bedding, or needles; Avoid burial or burial rituals that involve the body of someone who has died of Ebola; Avoid contact with bats, monkeys and apes, or the raw meat of these animals; Avoid going to medical facilities that are treating patients with Ebola; Careful personal hygiene. Wash your hands with soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer;

Rửa tay bằng xà phòng giúp phòng ngừa dịch bệnh Ebola
Find out about the epidemic situation from official sources before traveling to other countries and regions; If you have been to an Ebola-affected area, seek medical attention immediately if you develop fever, headache, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, or unexplained bleeding. In summary, Ebola is a rare and dangerous disease, which has been detected and caused epidemics in several African countries. Ebola virus outbreaks most likely begin when people come into contact with infected animals (bats or primates). The disease is then spread from person to person through blood or bodily fluids. Healthcare workers, as well as family and friends who have been in close contact with Ebola patients, are most at risk.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: cdc.gov