This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Khuong - Infectious Doctor - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Human history has witnessed many epidemics of diseases transmitted from animals to humans. Currently, a number of diseases have cures as well as vaccines. However, awareness and implementation of measures to prevent diseases from animals to humans still need to be propagated and educated because many new diseases have emerged, typically the Covid-19 pandemic, diseases originating from Bat species appeared in Wuhan - China.
1. Animals can transmit diseases to humans
Some parasites from dogs and cats can be transmitted to humans. Young animals such as dogs and cats are often infected with roundworms and hookworms. Wild animals can also infect parasites and infect humans. For example, people can contract the parasite in raccoons, known as Baylisascaris, if they happen to ingest soil contaminated with the feces of an infected panda.
·For many immunocompromised people, when caring for pets can be exposed to and infected by various types of pathogens.
Coronavirus (CoV) is a large family of viruses that can cause illness ranging from the common cold to severe, life-threatening illnesses such as 2002 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV) and Inflammatory Respiratory Syndrome. Middle East region (MERS-CoV) 2012. However, in December 2019, a new strain of coronavirus (SARS-CoV 2) causing acute pneumonia in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China was identified and have the potential to spread around the world (Figure 2}.
Historically, viral strains causing major epidemics have all been identified of animal origin, (Figure 1, Figure 3) eg:
SARS-CoV (2002-2003): derived from civets MERS-CoV (2012): derived from camels The virus strain SARS-CoV 2 is currently suspected to have originated in bats, or has could be a hybrid of corona viruses that exist in bats and snakes.
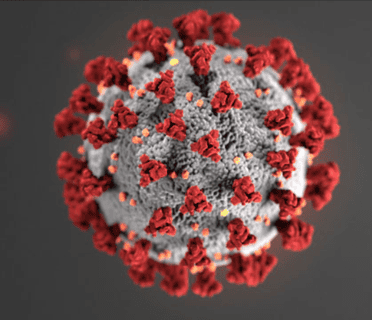
Virus Sars-CoV 2. Nguồn: CDC
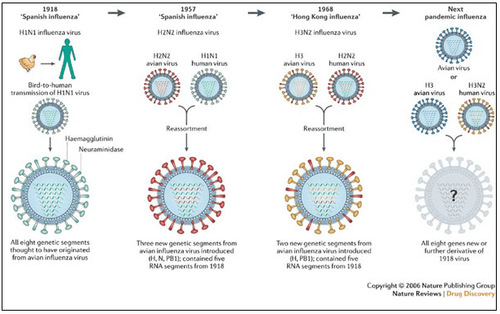
Hình 3. Hình ảnh virus Cúm theo thời gian
2. Diseases transmitted from animals to humans
| Bệnh | Tác nhân | Động vật liên quan | Phương thức lan truyền |
| Kí sinh trùng | |||
| Bệnh ngủ châu Phi | Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense | Nhiều động vật hoang dại và vật nuôi | Truyền qua vết đốt do ruồi tsetse |
| Bệnh sán dải Echinococcosis | Echinococcus spp. | Thường do chó, cáo, chó sói, cừu và gặm nhấm. | Ăn các tạng nhiễm nang sán |
| Bệnh ấu trùng sán dây lợn và sán dây Cysticercosis & Taeniasis | Taenia solium, Taenia saginata | Thường từ heo và gia súc | Do ăn hoặc uống phải thức ăn nguồn nước ô nhiễm trứng sán hay ăn thịt heo sống và chưa chín có nang cysticerci |
| Cryptococcosis | Cryptococcus neoformans | Từ chim, giống như bồ câu | Hít phải nấm |
| Bệnh giun xoắn Trichinosis | Trichinella spiralis, Trichinella britovi | Heo, các gặm nhấm, ngựa, gấu, hải mã | Ăn thịt bị nhiễm |
| Bệnh Histoplasmosis | Histoplasma capsulatum | Chim, dơi | Hít phải nấm |
| Bệnh Toxoplasmosis | Toxoplasma gondii | Mèo, gia súc, gia cầm | Phơi nhiễm với phân mèo và thịt chưa nấu chín. |
| Bệnh Chagas | Trypanosoma cruzi | Thú có vú, Triatominae (kissing bug) | Vết cắn, đốt |
| Bệnh giun đũa chó, mèo | Toxocara canisToxocara cati | Chó, mèo | Phơi nhiễm với phân |
| Virus | |||
| Bệnh sốt xuất huyết Ebola virus | Ebolavirus spp | Tinh tinh, khỉ đột, dơi ăn trái cây, khỉ, linh dương và nhím | Thông qua dịch cơ thể và các tạng |
| Các loại sốt xuất huyết khác (Marburg viral haemorrhagic fever, Lassa fever, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever, Rift Valley fever) | Các loại virus thông thường | Thay đổi (đôi khi không biết), thường là lạc đà, thỏ rừng, nhím, gia súc, cừu, dê, ngựa và heo. | Nhiễm trùng thường xảy ra thông qua tiếp xúc trực tiếp các động vật nhiễm. |
| Cúm | Influenza A virus | Ngựa, heo, chim nuôi và chim hoang dại, động vật có vú dưới nước như hải cẩu, chòn vizon, cá voi và động vật nhai lại. | Các giọt bắn thông qua không khi |
| Bệnh dại | Rabies virus | Thường chó, dơi, khỉ, gấu trúc, cáo, chồn hôi, gia súc, chó sói, cầy mangut và mèo | Thông qua nước bọt do cắn, cào của các động vật nhiễm. |
| Bệnh Covid 19 | Chủng Virus Corona SARS-CoV-2 | Thường do Dơi… | |
| Bệnh Leptospirosis | Leptospira interrogans | Chuột, chó | Qua tiếp xúc trực tiếp, gián tiếp với nước tiểu, của động vật nhiễm |
| Bệnh do loài gặm nhấm Tularemia | Francisella tularensis | Loài gặm nhấm có răng của khép (type A) và gặm nhấm (type B) | Ve, chấy rận trên hươu nai, và côn trùng khác. |
| Lao | Mycobacterium bovis | Các gia súc nhiễm, hươu nai, lạc đà không bướu, heo, mèo nuôi, các động vật ăn thịt hoang dại và gặm nhấm | Qua sữa, không khi bắn ra, đờm, phân, nước tiểu và mủ của các động vật nhiễm. |
| Bệnh lây qua thực phẩm (thường dẫn đến tiêu chảy | Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. và Trichinella spp. | Các động vật nuôi để lấy thịt (gia súc, gia cầm) | Các thực phẩm động vật còn sống hay nấu không chín. |
| Bệnh phong | Mycobacterium leprae | Chủ yếu ở các con thú có vú nhưng là khi châu Phi, thỏ và chuột cũng có thể | Bất kỳ một tiếp xúc nào với thú có vú qua nước tiểu, phân và mủ của động vật nhiễm, đất bị nhiễm. |
| Bệnh than | Bacillus anthracis | Thường là các động vật ăn cỏ như gia súc, dê, lạc đà, ngựa và heo | Do ăn hoặc hít phải, da tiếp xúc với bào tử |
| Bệnh vi khuẩn Brucellosis | Brucella spp. | Gia súc, dê | Thịt hay sữa nhiễm |
| Bệnh mèo cào | Bartonella henselae, Bartonella quintana | Mèo | Vết cắn hoặc cào do mèo bị nhiễm bệnh |
| Bệnh liên cầu lợn | (do vi khuẩn liên cầu lợn: Streptococcus suis) | Lợn | Tập quán ăn tiết canh, tiếp xúc trực tiếp với lợn hoặc thịt lợn, đặc biệt là ăn tiết canh và ăn thịt lợn và các phủ tạng của lợn chưa nấu chín. |
| Căn nguyên khác như Prion | |||
| Bệnh bò điên (Variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease) | PrP(vCJD) | Gia súc | Ăn thịt từ động vật nhiễm bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) |
3. How to prevent diseases from animals to humans
Diseases from animals to humans are extremely dangerous, requiring us to take effective preventive measures. From the beginning of the 21st century to the present, about 70% of dangerous pandemics have been transmitted from animals to humans. To date, the world has recorded more than 200 diseases transmitted from animals to humans with many different pathogens. Infectious diseases from animals to humans have caused 2.4 billion illnesses and 2.2 million deaths.
Regular veterinary care will protect owners from diseases from pets. A few simple ways can help protect you and your family from ZDs caused by parasites. Specifically:
Ensure that your pets receive veterinary care to avoid spreading disease to you and your family due to parasitic infections. Practice with the 4Ps (Pick up Pet Poop Promptly, and dispose of properly). pets; Wash hands frequently with soap and water, especially after touching pets and avoid contact with animal feces; Follow proper food handling procedures to reduce the risk of food transmission However, in Vietnam, our country also instructs provinces and cities to strengthen surveillance of avian influenza to humans. conduct vaccination for poultry.When detecting infected poultry, it is necessary to immediately notify the veterinary agency for handling measures
With the H5N6 epidemic: The Food and Agriculture Organization of the International (FAO) is supporting monitoring. monitoring avian flu at the market, monitoring slaughterhouses, besides, the World Organization for Animal Health is monitoring wild birds, isolates are sent to international laboratories for genetic sequencing. If the poultry is in an area at risk of influenza, it is necessary to vaccinate the birds. When detecting infected poultry, it is necessary to immediately notify the veterinary agency for handling measures. Swine spirochetes: vaccination, serum antibody testing, establishment of disease-free facilities. Rabies : The number of people who died from rabies in 2014 was greatly reduced compared to the previous year. Currently, Vietnam has about 10 million dogs. In which, many animals are adopted freely in rural and mountainous areas, so it is very difficult to prevent epidemics and vaccinate against rabies. Rabies does not appear in cities, but only in rural and remote areas. Therefore, it is necessary to propagate to the people to understand and the veterinary sector should have extensive vaccination campaigns to rural and mountainous areas. Anthracnose disease: Recently there was an outbreak in Meo Vac, Ha Giang, because people killed sick cattle and distributed them to relatives in the village. Due to the custom of eating dead cattle, diseases in upland people make them susceptible to diseases transmitted from cattle. Therefore, it is necessary to have propaganda measures so that people understand and do not eat dead and sick cattle. Swine streptococcus disease: clinical supervision, not eating sick pigs, blood soup, washing hands with clean water after slaughter are the preventive measures that health experts recommend to people. Blue ear disease in pigs also contributes to an increase in swine streptococcus. Therefore, when pigs have blue ear disease, do not eat, but need to take preventive measures and immediately report to the veterinary facility. Viral encephalitis: Although the number of cases is small, it causes death and serious complications. The disease is transmitted from animals such as birds, horses, .. through mosquito bites to humans. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to kill mosquitoes and vaccinate children against encephalitis

Suy trì thói quen rửa tay để giúp găn ngùa vi khuẩn
To effectively prevent diseases transmitted from animals to humans mentioned above, it is necessary to propagate and vaccinate animals to prevent epidemics. Localities and veterinary agencies are also proactive in breeding and disinfecting to prevent the risk of disease thoroughly. Organize safe breeding, periodically vaccinate breeders. Department of Animal Health cooperates with FAO to prevent rabies and manage dogs, aiming to vaccinate 70% of dogs. Vaccinate animals in anthracnose epidemic areas. When detecting anthracnose disease, they must not be slaughtered or eaten, but should immediately report to the veterinary agency for thorough settlement. The National Steering Committee for Prevention and Control of Cattle and Poultry Diseases and Human Influenza Pandemic will meet regularly, improve laboratory capacity, and closely coordinate with the Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development and localities. effective measures in the near future. In addition, it is also worth mentioning the parallel of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the World Health Organization (WHO), and the World Organization for Animal Health to eliminate diseases transmitted from animals to humans. limit their spread on the world map.
Diseases transmitted from animals to humans can leave dangerous complications if they are not examined and treated in time, fortunately some diseases and epidemics can be prevented with vaccines. . In addition to vaccines for animals, we should also actively prevent humans, especially those with low resistance such as children.
Vinmec International General Hospital has been deploying immunization services with a variety of vaccines for different audiences, from infants, young children, adults, and women before and during pregnancy pregnant. Including vaccines against diseases.... The advantages of vaccination at Vinmec include:
Patients will be examined and screened by specialist doctors for all physical problems and health problems. health, advice on preventive vaccines and injection regimens, monitoring and post-vaccination care before ordering vaccination according to the latest recommendations of the Ministry of Health & World Health Organization to ensure the best performance and safety. A team of experienced and professional pediatric doctors and nurses, understand children's psychology and apply effective pain relief during the vaccination process. 100% of vaccinated patients were monitored 30 minutes after injection and reassessed before leaving. Undertake medical supervision before, during and after vaccination at Vinmec Health System and always have an emergency team ready to coordinate with the vaccination department to handle cases of anaphylaxis, respiratory failure - circulatory arrest, ensuring Ensure timely and correct handling when incidents occur. Vaccines are imported and stored in a modern cold storage system, with a cold chain that meets GSP standards, keeping vaccines in the best conditions to ensure quality.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References
Huynh Hong Quang.Common medicine on the prevention of diseases transmitted from animals to humans, Quy Nhon Institute of Malaria - Parasites - Insects website (July 17, 2018) Sayer SJ, Silver R, Simone K, Barton Behravesh C. Prioritizing zoonoses for global health capacity building—themes from One Health zoonotic disease workshops in 7 countries, 2014–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017 Super. Mark E.J. Woolhouse* and Sonya Gowtage-Sequeria. Host Range and Emerging and Reemerging Pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Dec; 11(12): 1842–1847.