This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thi Khuong - Infectious Doctor - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Human history has witnessed many epidemics of diseases transmitted from animals to humans. Currently, a number of diseases have cures as well as vaccines. However, awareness and implementation of measures to prevent diseases from animals to humans still need to be propagated and educated because many new diseases have emerged, typically the Covid-19 pandemic, diseases originating from Bat species appeared in Wuhan - China.
1. Diseases from animals to humans are very dangerous
Diseases from animals to humans are extremely dangerous, requiring us to take effective preventive measures. Currently, emerging and common zoonotic diseases pose threats not only to animal and human health but also to global health security. An estimated 60% of known infectious diseases and up to 75% of new or emerging infectious diseases are of animal origin. Globally, infectious diseases account for 15.8% of all deaths and 43.7% of deaths in low-resource countries. It is estimated that zoonotic diseases cause 2.5 billion human illnesses and 2.7 million human deaths worldwide each year. Emerging zoonoses are responsible for some of the deadliest and most destructive epidemics. However, avian influenza can actually pose a more insidious and long-term threat to human and animal health.
Recently, due to environmental changes, global climate change, the increasing exchange between countries and regions, some infectious diseases have re-emerged and tended to increase; Microbial mutations make emerging infectious diseases such as Ebola, SARS, influenza A (H1N1, H5N1), in December 2019, a coronavirus that causes Covid-19 and a number of diseases caused by parasitic agents that are transmitted from animals to humans.

Động vật có thể truyền nhiễm nhiều bệnh nguy hiểm cho trẻ nhỏ
2. Modes of disease transmission from animals to humans
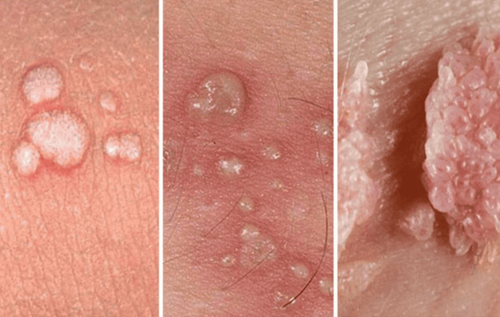
Animals: Pets can carry parasites and transmit parasites to humans. Proper and clean hand washing can significantly reduce the risk. Zoonotic disease (ZDs) is a disease that can be passed between animals and humans. ZDs can be caused by viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi. Some common diseases. For ZDs caused by parasites, symptoms and signs can be differentiated based on the type of parasite and the person. Sometimes people infected with ZDs can get the disease, but others have no symptoms and show no symptoms. Others may have symptoms such as diarrhea, muscle aches, and fever.
Food can be a source of infection with ZDs when animals such as cows and pigs are infected with Cryptosporidium spp. or Trichinella spp. People can contract cryptosporidiosis if they accidentally swallow food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected animal. This can happen, for example, when orchards or water sources near cow pastures and people consume fruit that are not washed in clean or untreated water sources for drinking and hand washing. reasonable. Humans can contract helminthiasis by ingesting raw or undercooked meat of bears and pigs infected with Trichinella spp.
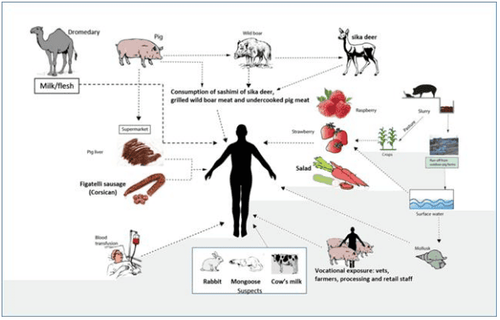
Hình 1: Các thú cưng có thể mang và đào thải ký sinh trùng sang người
References
Huynh Hong Quang.Common medicine on the prevention of diseases transmitted from animals to humans, Quy Nhon Institute of Malaria - Parasites - Insects website (July 17, 2018) Sayer SJ, Silver R, Simone K, Barton Behravesh C. Prioritizing zoonoses for global health capacity building—themes from One Health zoonotic disease workshops in 7 countries, 2014–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017 Super. Mark E.J. Woolhouse* and Sonya Gowtage-Sequeria. Host Range and Emerging and Reemerging Pathogens. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005 Dec; 11(12): 1842–1847.