This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Pharmacist Dinh Thi My Hanh - Faculty of Pharmacy - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.All systems of the body depend on water to function properly. Drinking enough water will help your body regulate its temperature, prevent constipation, remove waste products, and perform all major functions. However, excess water in the body can lead to water intoxication. This happens when the salt and other electrolytes in the body become too dilute. If electrolytes in the body drop too low too quickly, it can be fatal.
1. What is excess water?
Overhydration is a condition in which the body absorbs more water than it loses. A person may develop dehydration if the body has a disorder that reduces its ability to excrete water or increases its tendency to retain water in the body.
There are 2 cases of excess water in the body, that is:
1.1. Increased water intake This happens when you drink more water than your kidneys can remove in your urine. People, especially athletes, who drink too much water to avoid dehydration during exercise can develop overhydration.
People can also drink too much water because of a mental disorder called polyneuropathy. The result is drinking too much water but not adding enough sodium to it. As a result, excess water often leads to low blood sodium levels (hyponatremia), which is dangerous.
1.2. Excess water retention is more common in people whose kidneys do not excrete normally, for example in people with heart, kidney, or liver disorders, or in premature babies, with immature kidneys. Certain medical conditions can cause the body to retain water such as:
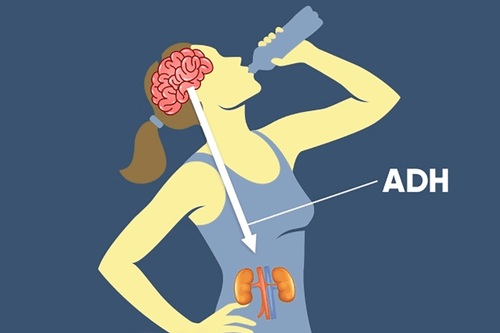
Congestive heart failure (CHF). Liver failure. Kidney disease. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone: In this syndrome, the pituitary gland secretes too much vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone), which stimulates the kidneys to retain water when it is not needed. Uncontrolled diabetes. Schizophrenia state. Some medications also cause excess water in susceptible individuals. Includes:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). MDMA (commonly known as ecstasy). Antidepressants. Diuretic . Both of these types of excess water are dangerous because they throw off the balance between water and sodium in the blood.

Vận động viên chạy marathon là những người có nguy cơ cao cơ thể thừa nước
2. Subjects at risk of overhydration
Overhydration is more common in endurance athletes who drink a lot of water before and during exercise such as:
Marathoners and ultramarathons (races longer than 42,195 km). Triathlon athlete. Athletes cyclists, rowers, hikers. Soldiers participate in training exercises. It is also more common in people with heart failure, diabetes, kidney or liver disease.
3. Symptoms of excess water in the body
Brain cells are especially sensitive to excess water and low blood sodium levels. When the body is in a mild or moderate degree of excess water, the brain cells have time to adapt, so only mild symptoms (if any) occur later such as nausea, headache, mood changes. mental state (confusion or disorientation).
When overhydration occurs rapidly, vomiting and loss of balance occur. If more severe, signs of excess water may appear as confusion, convulsions or coma.
When excess water occurs and blood volume remains normal, excess water usually moves into the cells, tissue swelling (edema) does not occur. When excess blood flow occurs, fluid can build up in the lungs and lower legs.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of excess body water
Your doctor will ask about your medical history to distinguish between excess water (too much water) or excess fluid in the blood (too much salt and hypervolemia) and do blood and water tests. urine to check electrolyte levels.
Treatment of excessive body water depends on the severity of the symptoms and the cause of the condition. Treatment may include:
Reducing fluid intake: Regardless of the cause of the excess water, fluid intake should usually be limited (but only on the advice of a doctor). Treating the Cause of Excess Water: If dehydration occurs with excess blood due to heart, liver, or kidney disease, limiting sodium intake is also helpful because sodium causes the body to retain water. Stop any medications that cause water retention problems. Use diuretics to increase urine output. Replace sodium in severe cases.

Đau đầu là một trong những dấu hiệu cơ thể thừa nước
5. How can you prevent overhydration?
Endurance athletes can reduce their risk of becoming excessively dehydrated by weighing themselves before and after a race. This helps determine how much water has been lost and needs to be replenished.
During exercise, try to drink 2 to 4 cups of fluids every hour. If you exercise for longer than an hour, you can opt for a sports drink. These drinks contain sugar along with electrolytes like sodium and potassium that the body loses through sweat. Drink as your body needs
If you have a medical condition such as diabetes, heart failure or kidney disease, talk to your doctor about the best treatment options and contact your doctor if you feel thirsty abnormal. This could be a sign of a medical problem that needs to be treated.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: healthline.com, msdmanuals.com