This is an automatically translated article.
Estrace pills come in pill form that contain estrogen, a hormone made by a woman's ovaries. Supplementing with Estrace is effective in reducing moderate to severe hot flashes and improving natural physiology for women.
1. What effect does Estrace have?
Estrace is an estrogen-containing tablet, indicated for use in the following cases:
Treatment of moderate to severe hot flashes associated with perimenopause; Treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy associated with menopause; Treatment of hypogonadism due to primary ovarian failure; Treatment of breast cancer in women or men with metastatic disease ; Treatment of advanced androgen-dependent prostate carcinoma in men; Osteoporosis Prevention: When Estrace is prescribed for the purpose of preventing postmenopausal osteoporosis, this therapy should only be considered for women at significant risk of osteoporosis and after other osteoporosis therapies. , it is important to supplement calcium.
2. Contraindications of the drug Estrace
Estrogen should not be used by people with any of the following conditions:
Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding. Known, suspected, or history of breast cancer except in appropriately selected patients undergoing treatment for the metastatic stage. Known or suspected estrogen-dependent cancer. Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or a history of these conditions. Have active or recent heart disease such as thromboembolic disease (eg, stroke, myocardial infarction). Liver dysfunction or physical disease of the liver. Ever had a hypersensitivity reaction to estradiol. Known or suspected pregnancy.
3. How is Estrace used?
Estrace drug is in the form of tablets and is taken orally. Estrace should be prescribed with the lowest dose of estrogen needed to prevent menopausal symptoms and progression of osteoporosis. The time of taking the drug should be cyclically during the first 21 to 25 days of each month. In patients with an intact uterus, progestins should be administered sequentially for 12 to 14 days of estrogen administration to prevent endometrial growth, which predisposes to estrogen-stimulated carcinoma. For the indications for use of Estrace for the prevention of osteoporosis, this prophylactic therapy should be initiated with a 0.5 mg tablet daily as soon as possible, possibly after menopause. Subsequent dosing may be titrated up and down based on the clinical condition of the patient and plasma estradiol levels. Ideally, plasma estradiol concentrations should be maintained around 50 pg/mL. In the event of a missed dose, a missed dose should be taken as soon as possible after remembering. However, if the missed dose is almost time for the next dose, the patient should be advised to take the next dose without doubling the dose. If a woman accidentally takes an overdose of estrogen, she may experience nausea, breast discomfort, fluid retention, bloating, or vaginal bleeding. These symptoms usually resolve spontaneously after the drug's half-life without the need for specific therapeutic intervention.
4. Notes when using Estrace
4.1 Cardiovascular dysfunction: Estrogen and estrogen/progestin therapy in patients is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, including: myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, thromboembolism varicose veins, pulmonary embolism. If there is any suspicion that these conditions may be present, the patient should stop taking estrogen immediately.
In addition, in subjects with pre-existing risk factors for arterial disease (eg, hypertension, diabetes, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia and obesity) and/or Venous thromboembolism should be closely monitored and evaluated before starting treatment with Estrace.
4.2 Malignancy The use of estrogens in women is associated with an increased risk of endometrial cancer, about 2 to 12 times higher than that of non-users. This is proportional to the duration of treatment and the dose of estrogen. In addition, the risk of breast cancer is also noted to be increased if estrogen and progestin are used in postmenopausal women.
Therefore, subjects who are assigned to be treated with Estrace for a long period of time should have regular gynecological examinations as well as instructions to monitor abnormal signs, especially monthly breast self-examination at home. .
4.3 Dementia According to research in healthy postmenopausal women 65 years of age and older, estrogen supplementation may cause dementia.
4.4 Gallbladder disease A 2- to 4-fold increased risk of gallbladder disease requiring surgery in postmenopausal women receiving estrogen has been reported.
4.5 Visual Abnormalities Retinal Vascular Thrombosis has been reported in patients taking estrogen. Therefore, the drug should be discontinued pending examination if sudden partial or total loss of vision, double vision or migraine occurs.
If examination reveals papilledema or retinal vascular damage, exogenous estrogen supplementation should be permanently contraindicated.
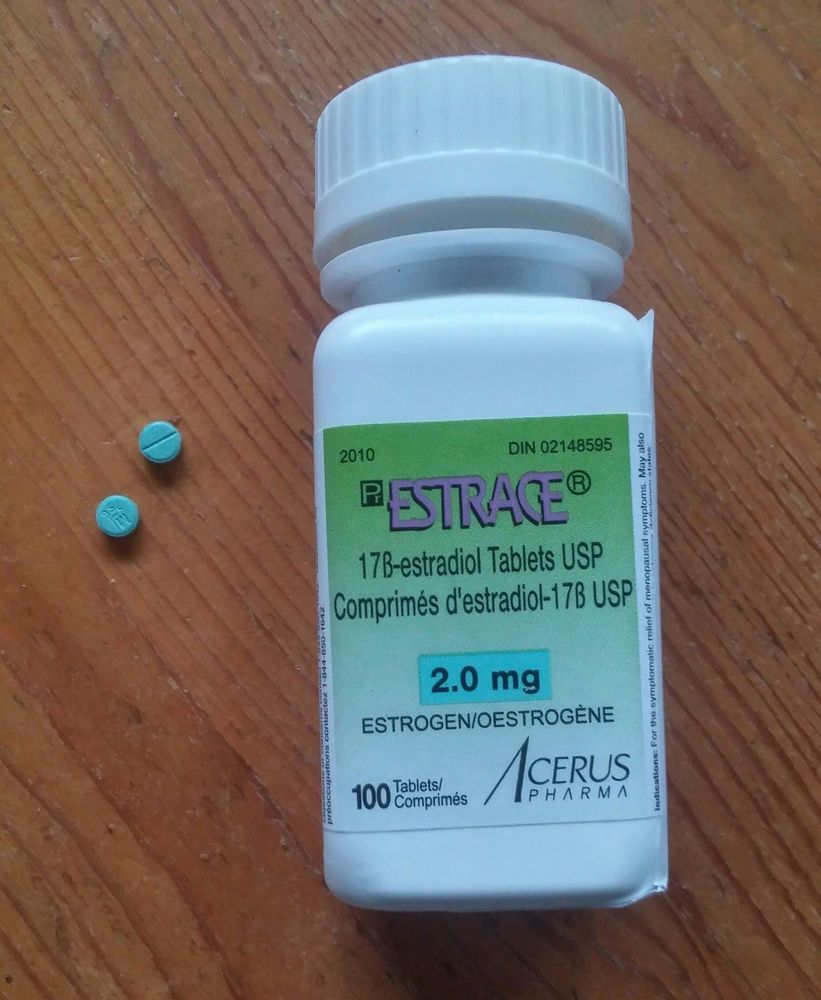
Thuốc Estrace được bào chế dưới dạng viên nén và được dùng qua đường uống
5. Possible side effects when taking Estrace
The following adverse reactions have been reported with Estrace or estrogen and/or progestin-containing therapies:
5.1 Genitourinary system Abnormal vaginal bleeding; Dysmenorrhea ; Increase the size of the uterus, cervix; Vaginitis, vaginal yeast infection; Changes in the amount of cervical secretions; Ovarian cancer, endometrial hyperplasia or endometrial cancer. 5.2 Breast Increase in size; Nipple discharge; Swollen lymph nodes; Breast cancer. 5.5 Cardiovascular system Venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thrombophlebitis; Myocardial infarction, stroke, hypertension; Gastrointestinal system; Nausea, vomiting; Abdominal pain, bloating; Cholestatic jaundice; Increased incidence of gallbladder disease; Pancreatitis. 5.6 Skin Hyperpigmentation or melasma, which may persist even after drug discontinuation; Erythema multiforme; Redness of the skin; Scalp hair loss; Hairy hair; Itching, rash. 5.7 Eyes Retinal Vascular Thrombosis; Change in the curvature of the cornea; Intolerance to contact lenses. 5.8 Central nervous system Headache, migraine, dizziness; Anxiety, mood disorders, irritability; Seizures, convulsions; Dementia. 5.9 Other organ systems Weight gain; Decreased tolerance to carbohydrates; Edema; Leg cramps; Changes in sexual desire; Urticaria; Angioedema; Anaphylactic reactions; Hypocalcemia; Asthma exacerbations . In summary, the use of Estrace drug as a way of supplementing hormones derived from women's ovaries, thereby helping to improve the discomforts of perimenopause and menopause. Because the drug Estrace has a non-specific effect on the body systems, patients during treatment need to be periodically monitored, early detection of undesirable effects for timely adjustment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: accessdata.fda.gov, webmd.com