This article has been reviewed and approved by Duong Xuan Loc, MD, MSc – Gastrointestinal Surgeon, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital.
Esophageal polyps are a rare condition, often asymptomatic. Whether surgery is necessary depends on the specific type of polyp.
1. What Are Esophageal Polyps?
The esophagus is the initial part of the digestive tract, running from the throat to the stomach's cardiac orifice. It traverses the thoracic cavity in front of the spine, starting at the upper sphincter (C6) and ending at the lower sphincter (T11). Esophageal polyps are lesions caused by the proliferation of the mucosa and submucosal tissue of the esophagus. They are less common than polyps in the stomach or intestines.
There are two main types of esophageal polyps:
- Polyps within the esophageal wall: These primarily arise from stromal tissues, originating from smooth muscle and fibrous tissues.
- Polyps in the esophageal lumen: These are submucosal lesions covered by normal squamous cells.
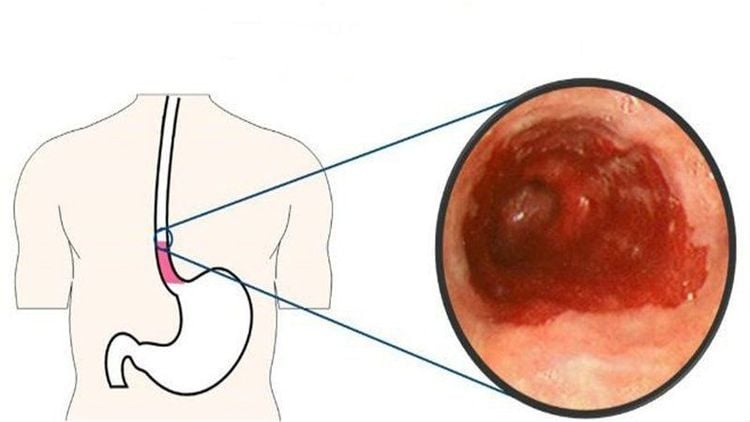
- Common Types of Esophageal Polyps
Glycogen-Rich Polyp:
Histological examination reveals thickened epithelial layers with hypertrophic squamous cells containing glycogen, often associated with inflammation.
Ectopic Sebaceous Gland Polyps:
Mature sebaceous glands located deep within the mucosa. Endoscopic imaging shows yellow or gray circular or oval patches, measuring 1-5mm, sometimes extending to several centimeters.
Squamous Cell Polyp:
Extremely rare, it can appear anywhere in the esophagus but is typically found in the lower esophagus. These are round, smooth, pink-colored, pedunculated lesions and are non-malignant.
HPV-Related Polyps:
Rarely occurring, these are associated with papillomas in the larynx, trachea, or bronchi.
Dysplastic Polyps:
These are cauliflower-like tumors, ranging in size from a few millimeters to over 1 cm.
Other types
Other types of esophageal polyps include polyps caused by reflux esophagitis, fibrous polyps, smooth muscle tumors, neurogenic tumors, granular cell tumors, malignant melanomas, squamous cell carcinomas, or adenocarcinomas presenting as polyps.
Esophageal polyps are often asymptomatic and are usually detected incidentally during routine health checks. Larger polyps, however, may cause difficulty swallowing or a sensation of chest discomfort during meals.

2. Treatment for Esophageal Polyps
Once an esophageal polyp is detected, even if biopsies indicate that it is benign, it is essential to address it promptly. Regular monitoring with annual esophageal endoscopy and biopsies is recommended to track changes.
Treatment options depend on the location, size, and nature of the polyp:
Non-invasive management: For polyps like glycogen-rich or ectopic sebaceous polyps, treatment may not be necessary.
Surgical options: For other types, treatment may involve:
- Endoscopic polypectomy via gastrointestinal endoscopy.
- Open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic polypectomy.
Treating esophageal polyps is not difficult. It is recommended to begin treatment when the polyp is still small, as recovery will be faster and complications are less likely. Vinmec International Hospital is currently one of the best medical facilities in the country, equipped with state-of-the-art technology and staffed by highly experienced and skilled doctors. The hospital offers a professional, clean, and comfortable treatment environment.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.